Coroutine
创建协程
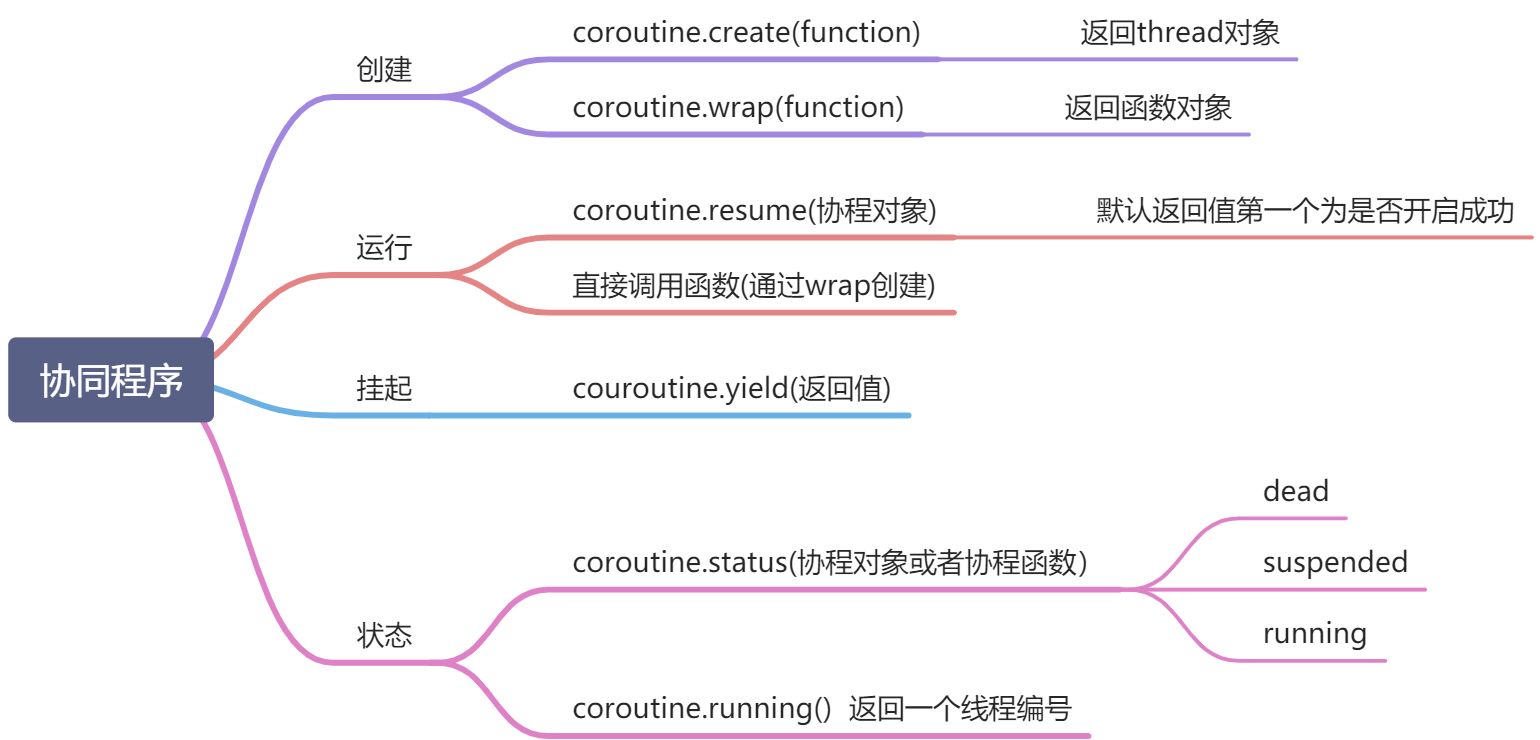
-- *** 协程的创建 *** --fun = function() print(123)end-- 常用方式co = coroutine.create(fun)-- 协程的本质是一个线程对象print(co) --> thread: 00000000007ce248print(type(co)) --> threadco2 = coroutine.wrap(fun)print(co2) --> function: 0000000000a39720print(type(co2)) --> function-- *** 协程的运行 *** ---- 第一种方式 对应 通过create创建的协程coroutine.resume(co) --> 123-- 第二种方式 对应 通过wrap创建的协程co2() --> 123-- *** 协程的挂起 *** --fun2 = function() local i = 1 while true do print(i) i = i + 1 -- 协程的挂起函数 coroutine.yield(i) endendco3 = coroutine.create(fun2)-- 默认第一个返回值:协程是否启动成功-- 第二个返回值为yield中的返回值isOk, tempI = coroutine.resume(co3) --> 1print(isOk, tempI) --> true 2isOk, tempI = coroutine.resume(co3) --> 2print(isOk, tempI) --> true 3isOk, tempI = coroutine.resume(co3) --> 3print(isOk, tempI) --> true 4-- 这种方式的协程也有返回值,没有 协程是否启动成功 的返回值co4 = coroutine.wrap(fun2)print("返回值:" .. co4())print("返回值:" .. co4())print("返回值:" .. co4())--[[output:1返回值:22返回值:33返回值:4--]]-- ** 协程的状态 ** ---- coroutine.status(协程对象)--[[dead 结束suspended 暂停running 进行中--]]print(coroutine.status(co3)) --> suspendedprint(coroutine.status(co)) --> dead-- 该函数能够得到当前正在运行的协程的线程号coroutine.running()


