序言
rocketmq 中有 producer、consumer、nameserver、broker 4 种角色,必须通过网络进行通信,而 remoting 模块便是实现远程通信的基础模块,本文介绍 remoting 模块的实现原理、协议、架构和接口。
一、实现原理
说起远程通信便不得不说 netty,但是 netty 过于底层,只是一个框架,而非一个产品,remoting 模块便是基于 netty 实现的。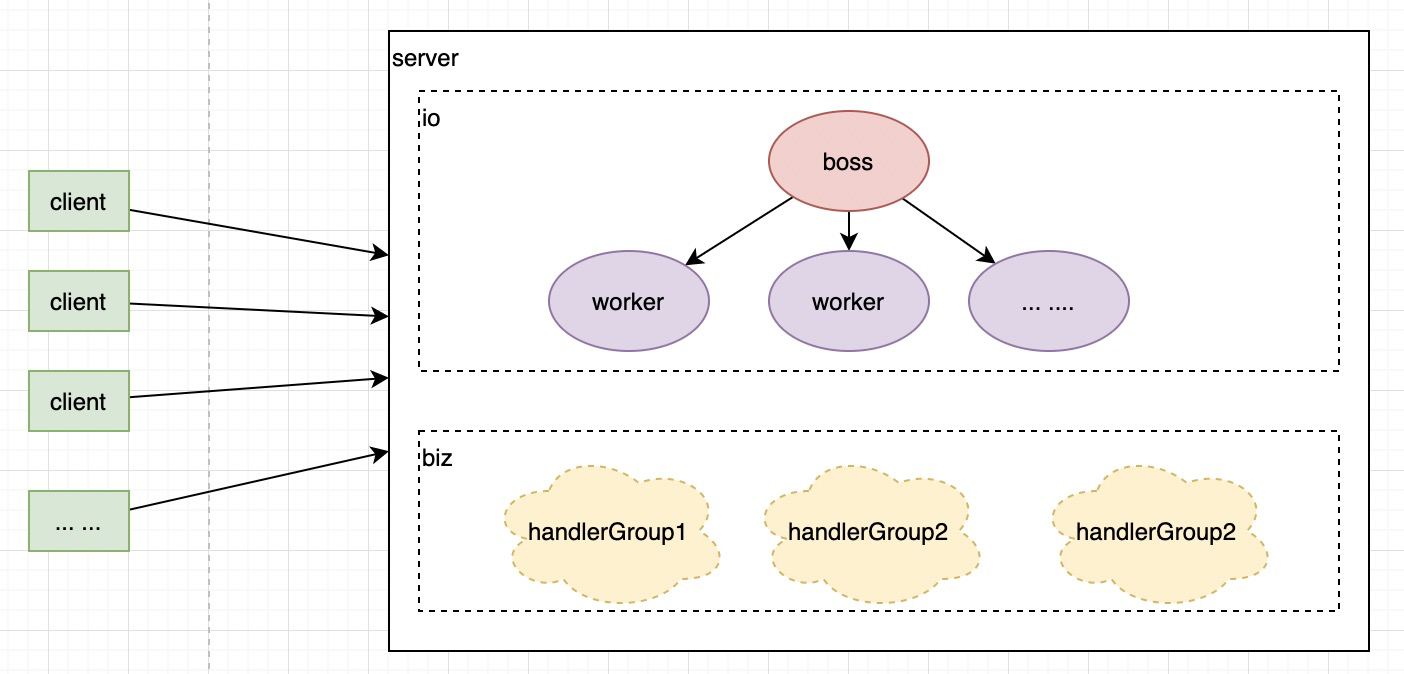
netty 的 nio server总共有三类线程。第一类是boss 线程,其用于处理 accept 事件,并将其分配给 worker 线程;第二类是 worker 线程,其用于处理 read 和 write 事件;第三类是 handler 线程,其用于处理特定的 handler (handler 线程是可选的,不设置时使用 worker 线程处理 handler)。
二、架构
url 类图如下,我们分别介绍下各个类的相关方法:
RemotingService
| 方法名 | 概述 |
|---|---|
| start | 启动 |
| shutdown | 关闭 |
| registerRPCHook | 注册hook,会在被执行 |
RemotingServer
| 方法名 | 概述 |
|---|---|
| registerProcessor | 注册处理器 |
| registerDefaultProcessor | 注册默认处理器 |
| localListenPort | 返回本地监听的端口号 |
| getProcessorPair | 获取一个请求类型的处理器和线程池。 |
| invokeSync | 同步发送请求。通过参数中 channel 确定给哪个 client 发消息 |
| invokeAsync | 异步发送请求 |
| invokeOneway | 发送请求不关心返回值 |
RemotingClient
| 方法名 | 概述 |
|---|---|
| updateNameServerAddressList | 太有业务语义的方法 |
| getNameServerAddressList | 注册默认处理器 |
| registerProcessor | client 端注册的处理器处理什么? |
| setCallbackExecutor | 设置执行 callback 的线程池 |
| getCallbackExecutor | |
| isChannelWritable | 还有不可写的 channel 吗? |
| invokeSync | 同步调用 |
| invokeAsync | 异步调用 |
| invokeOneway | oneway |
三、消息的协议设计与编码解码
请求 DTO-RemotingCommand
在Client和Server之间完成一次消息发送时,需要对发送的消息进行一个协议约定,因此就有必要自定义RocketMQ的消息协议。同时,为了高效地在网络中传输消息和对收到的消息读取,就需要对消息进行编解码。在RocketMQ中,RemotingCommand这个类在消息传输过程中对所有数据内容的封装,不但包含了所有的数据结构,还包含了编码解码操作。 RemotingCommand类的部分成员变量如下:
| Header字段 | 类型 | Request说明 | Response说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| code | int | 请求操作码,应答方根据不同的请求码进行不同的业务处理 | 应答响应码。0表示成功,非0则表示各种错误 |
| type | RemotingCommandType | 枚举值 Request | 枚举值 Response |
| language | LanguageCode | 请求方实现的语言 | 应答方实现的语言 |
| version | int | 请求方程序的版本 | 应答方程序的版本 |
| opaque | int | 相当于reqeustId,在同一个连接上的不同请求标识码,与响应消息中的相对应 | 应答不做修改直接返回 |
| flag | int | 区分是普通RPC还是onewayRPC得标志 | 区分是普通RPC还是onewayRPC得标志 |
| remark | String | 传输自定义文本信息 | 传输自定义文本信息 |
| extFields | HashMap |
请求自定义扩展信息 | 响应自定义扩展信息 |
| body | byte[] | ||
| serializeTypeCurrentRPC | SerializeType | 序列化方式 | 序列化方式 |
| customHeader | CommandCustomHeader | 自定义 header | header |
消息协议
下面来看下RocketMQ通信协议的格式:
可见传输内容主要可以分为以下4部分:
(1)消息长度
:总长度,四个字节存储,占用一个int类型;
(2)序列化类型&消息头长度
:同样占用一个int类型,第一个字节表示序列化类型,后面三个字节表示消息头长度;
(3)消息头数据
:经过序列化后的消息头数据;
(4)消息主体数据
编码
public ByteBuffer encodeHeader(final int bodyLength) {// 1> header length sizeint length = 4;// 2> header data lengthbyte[] headerData;headerData = this.headerEncode();length += headerData.length;// 3> body data lengthlength += bodyLength;ByteBuffer result = ByteBuffer.allocate(4 + length - bodyLength);// lengthresult.putInt(length);// header lengthresult.put(markProtocolType(headerData.length, serializeTypeCurrentRPC));// header dataresult.put(headerData);result.flip();return result;}
解码
/*** @param byteBuffer 不包括"消息长度"在内的数据* @return 解码结果*/public static RemotingCommand decode(final ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {int length = byteBuffer.limit();int oriHeaderLen = byteBuffer.getInt();int headerLength = getHeaderLength(oriHeaderLen);byte[] headerData = new byte[headerLength];byteBuffer.get(headerData);RemotingCommand cmd = headerDecode(headerData, getProtocolType(oriHeaderLen));int bodyLength = length - 4 - headerLength;byte[] bodyData = null;if (bodyLength > 0) {bodyData = new byte[bodyLength];byteBuffer.get(bodyData);}cmd.body = bodyData;return cmd;}
四、三种通信方式
从 RemotingServer 和 RemotingClient 的接口中可以看出,一共有三种发送消息的类型:
- async-异步
- sync-同步
- oneway-只发送,不关心接收
异步
异步执行流程图如下:
异步执行分为 3 个步骤:
- 创建连接(异步操作,分为链接和等待链接完成)
- 发送请求(异步操作,分为发送请求和发送请求成功)
- 接受 response(异步接受response)
这三个步骤在 netty 框架中都是异步执行的,但是对于使用者而言只感受到了一次异步,其原因是把创建连接同步化,并且把等待请求完成和等待 response 两次异步合二为一,不等待请求完成即返回。
创建连接
private Channel createChannel(final String addr) throws InterruptedException {ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {return cw.getChannel();}//同步开始建立连接if (this.lockChannelTables.tryLock(LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {try {boolean createNewConnection;cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);if (cw != null) {if (cw.isOK()) {return cw.getChannel();} else if (!cw.getChannelFuture().isDone()) {createNewConnection = false;} else {this.channelTables.remove(addr);createNewConnection = true;}} else {createNewConnection = true;}if (createNewConnection) {ChannelFuture channelFuture = this.bootstrap.connect(RemotingHelper.string2SocketAddress(addr));log.info("createChannel: begin to connect remote host[{}] asynchronously", addr);cw = new ChannelWrapper(channelFuture);this.channelTables.put(addr, cw);}} catch (Exception e) {log.error("createChannel: create channel exception", e);} finally {this.lockChannelTables.unlock();}} else {log.warn("createChannel: try to lock channel table, but timeout, {}ms", LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);}//同步等待连接建立完毕if (cw != null) {ChannelFuture channelFuture = cw.getChannelFuture();if (channelFuture.awaitUninterruptibly(this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())) {if (cw.isOK()) {log.info("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] success, {}", addr, channelFuture.toString());return cw.getChannel();} else {log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[" + addr + "] failed, " + channelFuture.toString(), channelFuture.cause());}} else {log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] timeout {}ms, {}", addr, this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis(),channelFuture.toString());}}return null;}
可以看出其创建连接之后,同步等待连接建立完毕。
发送消息
由于remoting 模块支持异步,而 netty 中发送消息成功并等待 response 两个操作都是异步的,所以需要一个 bean 保存请求相关信息,将两个异步操作以一个异步操作的方式展示给调用方,在 netty 中使用 ResponseFuture 完成该功能,其属性如下:
| 类型 | 名称 | 概述 |
|---|---|---|
| int | opaque | 请求的唯一标识,用于关联请求和响应 |
| Channel | processChannel | 关联的 channel |
| long | timeoutMillis | 该次请求剩余等待响应返回的超时时间,若 timeout ms 后,仍然未返回响应,认为该次请求超时 |
| InvokeCallback | invokeCallback | 回调函数 |
| long | beginTimestamp | ResponseFuture 创建的时间,和 timeout 比较,用于判断请求是否超时 |
| CountDownLatch | countDownLatch | 和工作线程进行同步 |
| AtomicBoolean | executeCallbackOnlyOnce | |
| RemotingCommand | responseCommand | response 的封装类 |
| 请求发送是否成功 | sendRequestOK | |
| 异常 | cause |
本质就是自己实现了一个 future ,通过 countDownLatch 实现主线程和 worker 线程直接的同步。
同步
同步执行流程图如下:
和异步的区别有两点:
- 发送请求后不是直接返回,而是对 ResponseFuture wait 直到服务端返回 response
- response 返回后不是执行 callback ,而是设置 response 以唤醒等待的请求
oneway
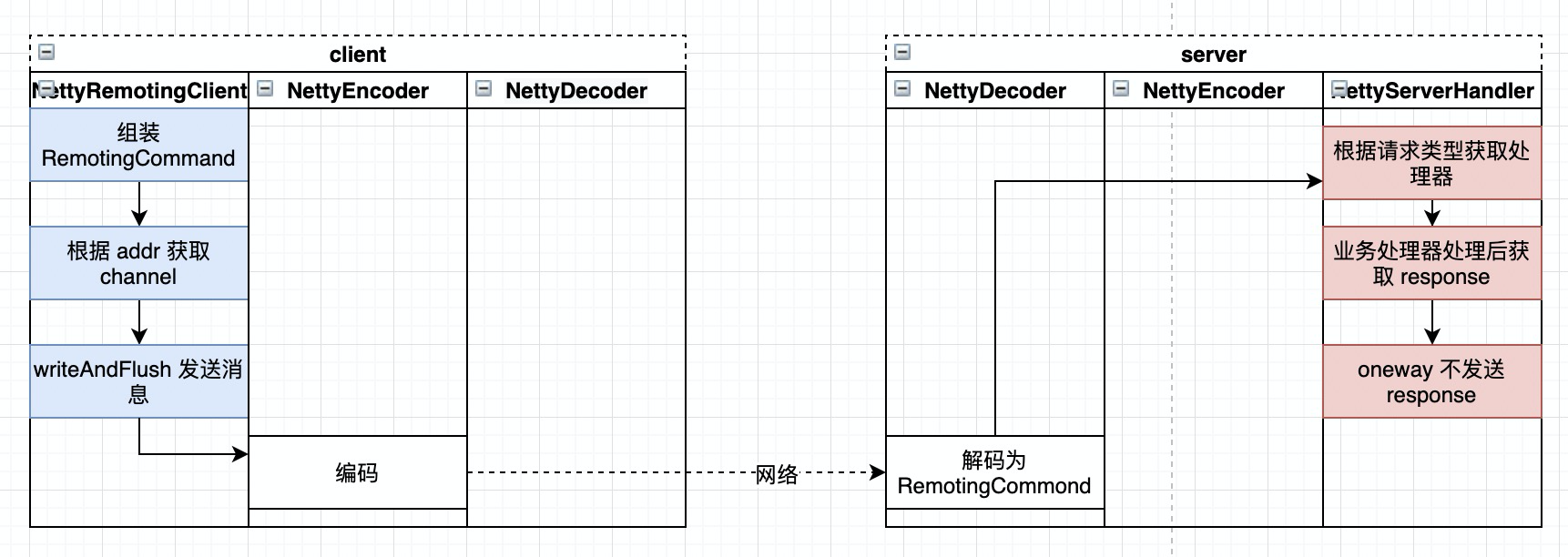
oneway 是最简单的形式,只有请求,不关心 response。
五、一些细节
异常处理机制&接口定义
我理解异常处理机制和接口定义是同一件事,也即如何对调用方屏蔽实现的复杂性,比如一次请求包括连接创建、发送请求、等待响应三个步骤,但是从调用方的角度考虑,就是调用一个方法,获取返回值。其他如建立连接超时、发送请求超时调用方根本不想理解这么多概念,实现方要保证
- 异常场景下的稳定性,也即充分考虑所有异常,能处理就处理,不能处理视情况决定是否抛出(对于业务代码,就是一个大 try - catch 变成系统异常,拒绝考虑实现的复杂性,统一暴露为系统异常)
- 暴露调用方想知晓的细节给调用方(哪些是调用方想知晓的呢?)
remoting 模块的异常体系如下:
| 类名 | 含义 | 何处抛出? | 何处处理? |
|---|---|---|---|
| RemotingCommandException | 1. Processor 处理时解码失败 2. RemotingCommond 校验 field 异常 3. 自定义 header 解码失败 |
||
| RemotingConnectException | client 建立与server 连接异常 | 1. 无法连接到 nameserver 时抛出(nameserver 地址无效、连接失败等) 2. 根据addr 建立连接失败 |
1. sendKernelImpl 时交由 SendMessageHook 处理 2. 交由 SendCallback 处理 |
| RemotingSendRequestException | 请求发送失败异常 | 1. channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(listener); 抛出的异常会被当转换为 RemotingSendRequestException 2. listener 失败并不会抛出 RemotingSendRequestException |
|
| RemotingTimeoutException | 超时 | 调用超时即抛出该异常 | |
| RemotingTooMuchRequestException | 超时 | 调用超时即抛出该异常 |
超时机制
如何实现异步?
由于异步需要
问题
- remoting 是 producer 、consumer 和 broker 通信的框架吗?
- 如果是,对于消息体的大小有无优化?
- remotign 对于异常是如何处理的?
- 同步的超时处理?
- 同步的加锁处理?

