ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor解析
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor适用于延时执行,或者周期性执行的任务调度,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor在实现上继承了ThreadPoolExecutor,所以依然可以将ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor当成ThreadPoolExecutor来使用,但是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的功能要强大得多,因为ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor可以根据设定的参数来周期性调度运行,下面是四个和周期性相关的方法:
1.scheduled()
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor implements ScheduledExecutorService {public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {if (command == null || unit == null)throw new NullPointerException();RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t = decorateTask(command, new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null, triggerTime(delay, unit)));delayedExecute(t);return t;}public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {if (callable == null || unit == null)throw new NullPointerException();RunnableScheduledFuture<V> t = decorateTask(callable,new ScheduledFutureTask<V>(callable, triggerTime(delay, unit)));delayedExecute(t);return t;}}
说明 : 这两个方法只是第一个参数不同,如果你想延时一段时间之后运行一个Runnable,那么使用第一个方法,如果你想延时一段时间然后运行一个Callable,那么使用的第二个方法。
2.scheduleAtFixedRate()
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)if (command == null || unit == null)throw new NullPointerException();if (period <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft = new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null, triggerTime(initialDelay, unit), unit.toNanos(period));RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);sft.outerTask = t;delayedExecute(t);return t;}
说明: 该方法会延时一段时间,然后根据设定的参数周期执行Runnable,在执行时将严格按照规划的时间路径来执行,比如周期为2,延时为0,那么执行的序列为0,2,4,6,8….,
3.scheduleWithFixedDelay()
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit){if (command == null || unit == null)throw new NullPointerException();if (delay <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();//保证了任务的延时执行 或周期执行ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft = new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null, triggerTime(initialDelay, unit), unit.toNanos(-delay));RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);sft.outerTask = t;delayedExecute(t);return t;}
说明:该方法会延时一段时间,然后根据设定的参数周期执行Runnable,在执行时将基于上次执行时间来规划下次的执行,也就是在上次执行完成之后再次执行。比如上面的执行序列0,2,4,6,8…,如果第2秒没有被调度执行,而在第三秒的时候才被调度,那么下次执行的时间不是4,而是5,以此类推。
通过上面的代码我们可以发现,前两个方法是类似的,后两个方法也是类似的。前两个方法属于一次性调度,所以period都为0,区别在于参数不同,一个是Runnable,而一个是Callable,它们最后都变为了Callable了,以上四个方法最后都会调用一个方法: delayedExecute(t),下面看一下这个方法:
4.delayedExecute()
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {if (isShutdown())reject(task);else {super.getQueue().add(task);if (isShutdown() &&!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&remove(task))task.cancel(false);elseensurePrestart();}}
说明:该方法先判断线程池是否被关闭了,如果被关闭了,则拒绝任务的提交,否则将任务加入到任务队列中去等待被调度执行。最后的ensurePrestart的意思是需要确保线程池已经被启动起来了。下面是这个方法:
5.ensurePrestart()
void ensurePrestart() {int wc = workerCountOf(ctl.get());if (wc < corePoolSize)addWorker(null, true);else if (wc == 0)addWorker(null, false);}
说明:该方法主要是增加了一个没有任务的worker,有什么用呢?我们还记得Worker的逻辑吗?addWorker方法的执行,会触发Worker的run方法的执行,然后runWorker方法就会被执行,而runWorker方法是循环从workQueue中取任务执行的,所以确保线程池被启动起来是重要的,而只需要简单的执行addWorker便会触发线程池的启动流程。对于调度线程池来说,只要执行了addWorker方法,那么线程池就会一直在后台周期性的调度执行任务。
6. ScheduledFutureTask.java
ScheduledFutureTask类图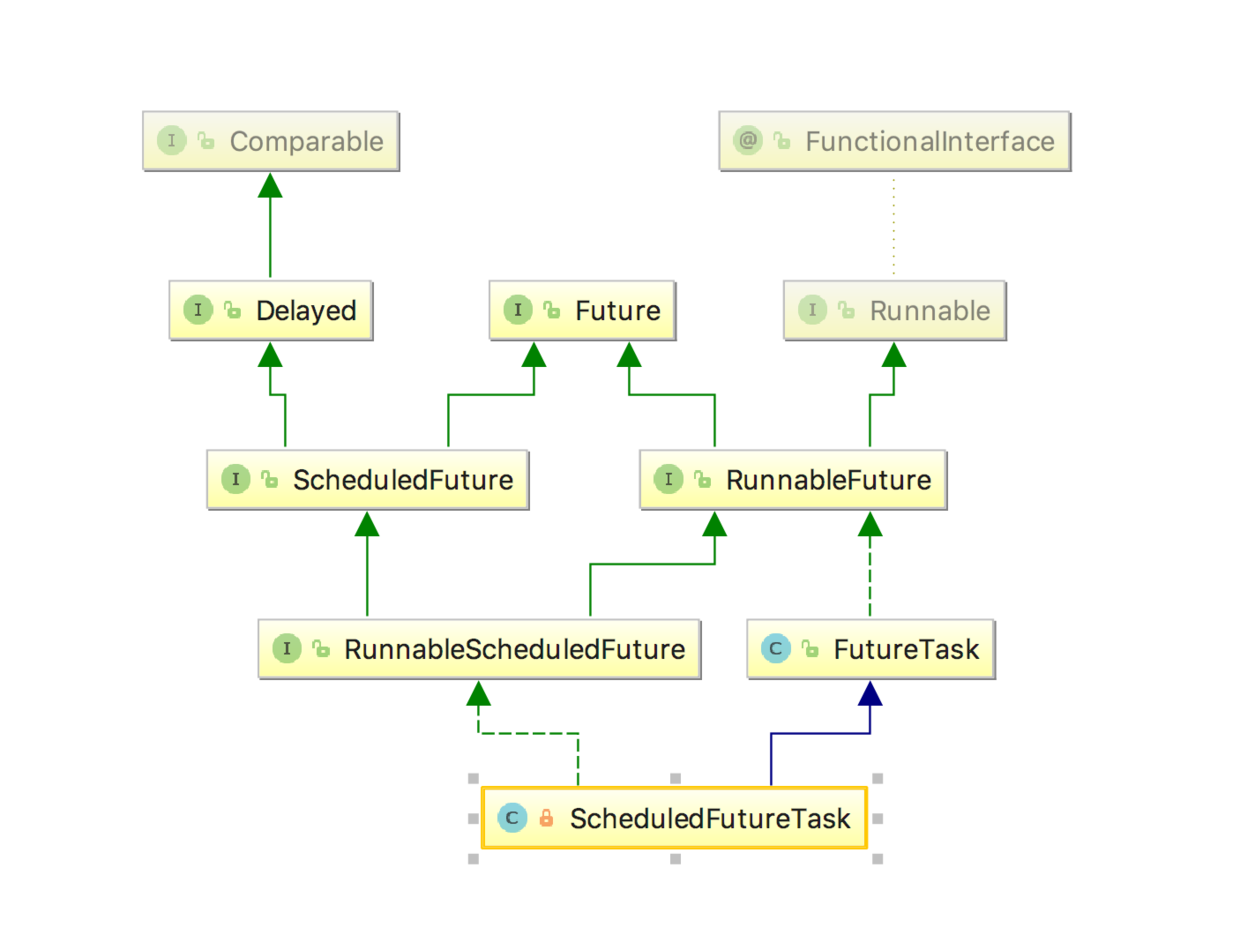
ScheduledFutureTask是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的内部类,它实现了Runnable接口,并重写run方法,而这个run方法是整个类的核心,下面来看一下这个run方法的内容:
public void run() {
boolean periodic = isPeriodic();
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic))
cancel(false);
else if (!periodic)
ScheduledFutureTask.super.run();
else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
setNextRunTime();
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}
}
private void setNextRunTime() {
long p = period;
if (p > 0)
time += p;
else
time = triggerTime(-p);
}
说明:该方法首先判断是否是周期性的任务,如果不是,则直接执行(一次性),否则执行,然后设置下次执行的时间,然后重新调度,等待下次执行。这里有一个方法需要注意,也就是setNextRunTime,上面我们提到scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay在传递参数时不一样,后者将delay值变为了负数,所以此处的处理正好印证了前文所述。
7.reExecutePeriodic方法
reExecutePeriodic方法会将任务再次被调度执行,下面的代码展示了这个功能的实现:
RunnableScheduledFuture
void reExecutePeriodic(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {
if (canRunInCurrentRunState(true)) {
super.getQueue().add(task);
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(true) && remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
ensurePrestart();
}
}
说明:可以看到,这个方法就是将我们的任务再次放到了workQueue里面,那这个参数是什么?在上面的run方法中我们调用了reExecutePeriodic方法,参数为outerTask,而这个变量是什么?这个变量指向了自己,而this的类型是什么?是ScheduledFutureTask,也就是可以被调度的task,这样就实现了循环执行任务了。
8.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
上面的分析已经到了循环执行,但是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的功能是周期性执行,所以我们接着分析ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是如何根据我们的参数走走停停的。这个时候,是应该看一下ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的构造函数了,我们来看一个最简单的构造函数:
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
我们知道ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的父类是ThreadPoolExecutor,所以这里的super其实是ThreadPoolExecutor的构造函数,在ThreadPoolExecutor的构造函数中有this.workQueue = workQueue,则在ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor中,workQueue是一个DelayedWorkQueue类型的队列,上面的分析我们明白了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是如何循环执行任务的,而这里我们明白了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor使用DelayedWorkQueue来达到延迟的目标,所以组合起来,就可以实现ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor周期性执行的目标。下面我们来看一下DelayedWorkQueue是如何做到延迟的吧,上文中提到一个方法:getTask,这个方法的作用是从workQueue中取出任务来执行,而在ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor里面,getTask方法是从DelayedWorkQueue中取任务的,而取任务无非两个方法:poll或者take,下面我们对DelayedWorkQueue的take方法来分析一下:
9.DelayedWorkQueue
DelayedWorkQueue是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的内部类,
1. take()方法代码如下
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
if (first == null)
available.await();
else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
first = null; // don’t retain ref while waiting
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
在for循环里面,首先从queue中获取第一个任务,然后从任务中取出延迟时间,而后使用available变量来实现延迟效果。
private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
queue队列它是一个RunnableScheduledFuture类型的数组
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue = new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
2.add()方法
public boolean add(Runnable e) {
return offer(e);
}
public boolean offer(Runnable x) {
if (x == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = (RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)x;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow();
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0) {
queue[0] = e;
setIndex(e, 0);
} else {
siftUp(i, e);
}
if (queue[0] == e) {
leader = null;
available.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
说明:add方法直接转到了offer方法,该方法中,首先判断数组的容量是否足够,如果不够则grow,增长的策略如下:
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // grow 50%
每次增长50%,入戏下去。增长完成后,如果这是第一个元素,则放在坐标为0的位置,否则,使用siftUp操作,下面是该方法的内容:
3.siftUp()
private void siftUp(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo(e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
setIndex(e, k);
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
这个数组实现了堆这种数据结构,使用对象比较将最需要被调度执行的RunnableScheduledFuture放到数组的前面,而这得力于compareTo方法,下面是RunnableScheduledFuture类的compareTo方法的实现,主要是通过延迟时间来做比较。
RunnableScheduledFuture.compareTo()
public int compareTo(Delayed other) {
if (other == this) // compare zero if same object
return 0;
if (other instanceof ScheduledFutureTask) {
ScheduledFutureTask<?> x = (ScheduledFutureTask<?>)other;
long diff = time - x.time;
if (diff < 0)
return -1;
else if (diff > 0)
return 1;
else if (sequenceNumber < x.sequenceNumber)
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
long diff = getDelay(NANOSECONDS) - other.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
return (diff < 0) ? -1 : (diff > 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
上面是生产元素,下面来看一下消费数据。在上面我们提到的take方法中,使用了一个方法如下:
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?> finishPoll(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> f) {
int s = —size;
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> x = queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
setIndex(f, -1);
return f;
}
这个方法中调用了一个方法siftDown,这个方法如下:
private void siftDown(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) {
int half = size >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size && c.compareTo(queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo(c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
setIndex(c, k);
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
说明:Replaces first element with last and sifts it down. Call only when holding lock.
总结一下,当我们向queue插入任务的时候,会发生siftUp方法的执行,这个时候会把任务尽量往根部移动,而当我们完成任务调度之后,会发生siftDown方法的执行,与siftUp相反,siftDown方法会将任务尽量移动到queue的末尾。总之,大概的意思就是queue通过compareTo实现了类似于优先级队列的功能。
在上面的take方法里面,首先获取了delay,然后再使用available来做延迟效果,其中delay是通过RunnableScheduledFuture类的getDelay方法获取,RunnableScheduledFuture类实现了Delayed接口,而Delayed接口里面的唯一方法是getDelay,我们到RunnableScheduledFuture里面看一下这个方法的具体实现:
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(time - now(), NANOSECONDS);
}
time是我们设定的下次执行的时间,所以延迟就是(time - now()),
到此为止,我们梳理了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是如何实现周期性调度的,首先分析了它的循环性,然后分析了它的延迟效果。

