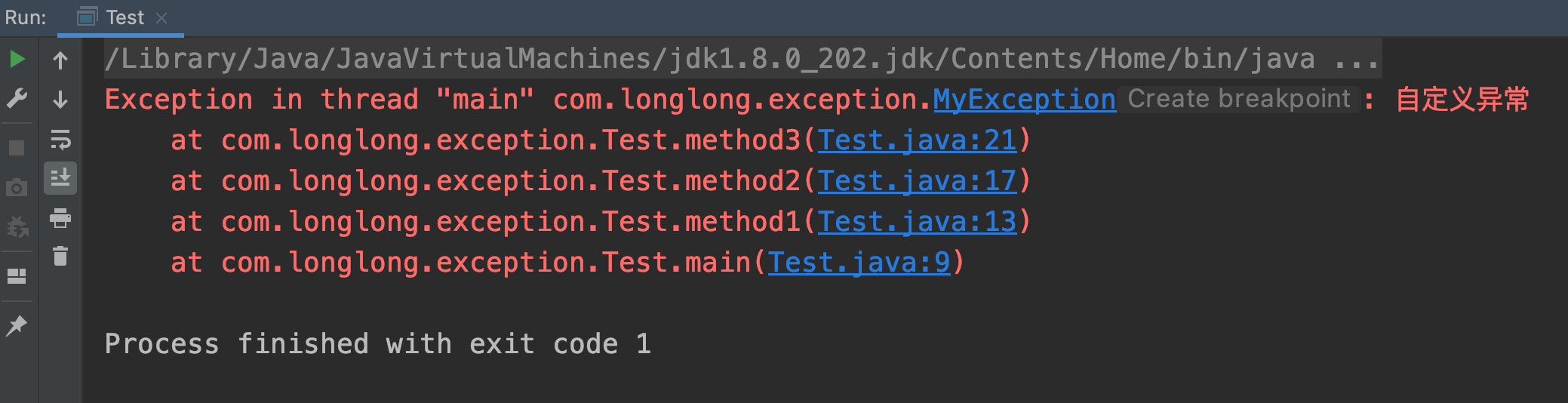
一.如何自定义异常
public class MyException extends RuntimeException {public MyException() {super();}public MyException(String message) {super(message);}public MyException(Throwable cause) {super(cause);}public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) {super(message, cause);}}
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {method1();}private static void method1() {method2();}private static void method2() {method3();}private static void method3() {throw new MyException("自定义异常");}}
二.为什么要优化
抛异常耗时5061ms:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {try {method1();} catch (MyException e) {}}System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);}private static void method1() {method2();}private static void method2() {method3();}private static void method3() {throw new MyException("自定义异常");}}
不抛异常耗时4ms:
private static void method3() {new Object();}
三.抛异常耗时的原因
MyException的构造方法调用了父类的构造方法,最终会调到Throwable的构造方法。
public Throwable(String message) {fillInStackTrace();detailMessage = message;}
public synchronized Throwable fillInStackTrace() {if (stackTrace != null ||backtrace != null) {// 爬异常堆栈信息,耗时fillInStackTrace(0);stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK;}return this;}private native Throwable fillInStackTrace(int dummy);
四.优化
当我们的自定义异常不需要异常堆栈信息时,可以重写fillInStackTrace方法来提升性能。
@Overridepublic Throwable fillInStackTrace() {return this;}
五.JVM对内置异常的优化
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = null;long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 116000; i++) {try {s.length();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);}}
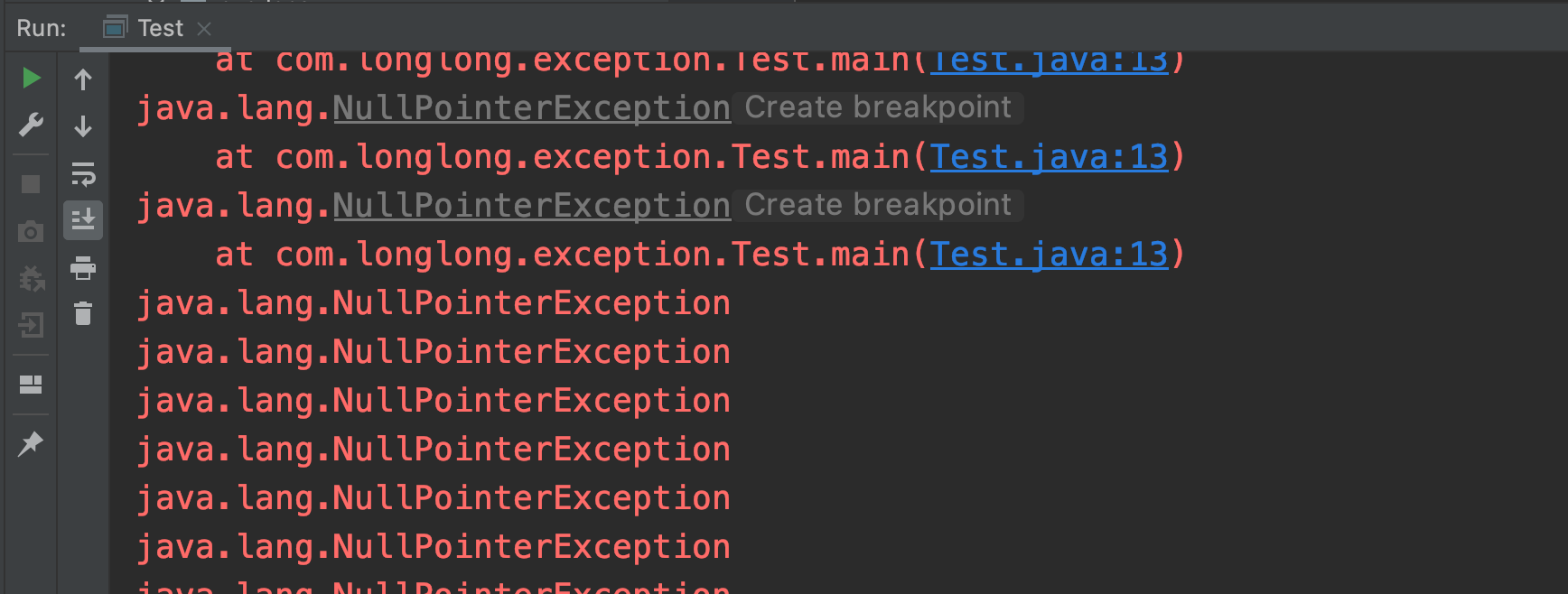
在抛出一定次数的空指针异常后,异常堆栈没了。
出于性能的考虑,当一个异常被抛出若干次后,该方法可能会被重新编译。在重新编译之后,编译器可能会选择一种更快的策略,即抛出一个事先分配好的异常对象,这个对象的堆栈信息为空。
可以调用异常对象的hashcode方法,发现后面的值是一样的。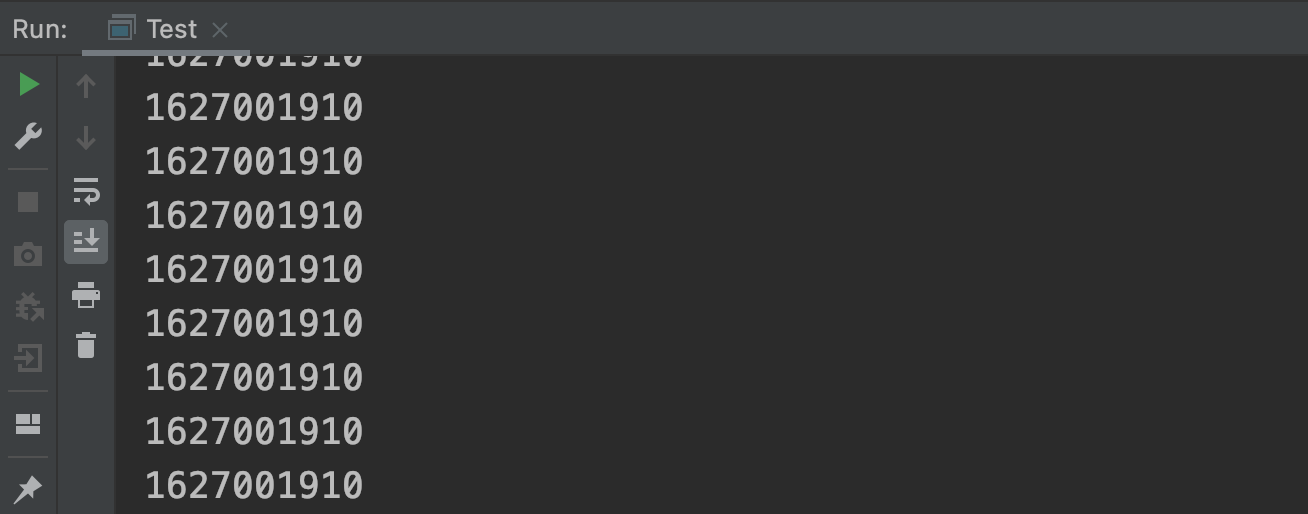
循环100万次耗时3968ms。如果想禁用优化,打印出堆栈信息,可以设置一个jvm参数:-XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow,设置后耗时12270ms。