快速排序
快排的本质是是通过一轮遍历,将小于基准数的数排在指针左边,大于基准数的数排在指针右边,并将基准数插在指针指向的位置。而后将基准数左侧和基准数右侧的无序序列分别递归进行快排。
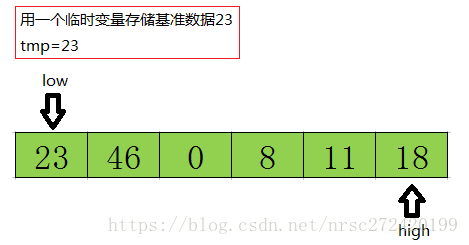
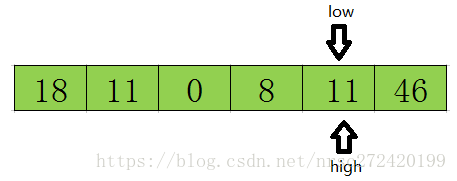
首先从后半部分开始(因为tmp额外存了,low指向的位置被覆盖不要紧,因此从后半部分开始),如果扫描到的值大于基准数据就让high减1,如果发现有元素比该基准数据的值小(上图中18≤tmp),就将high位置的值赋值给low位置。
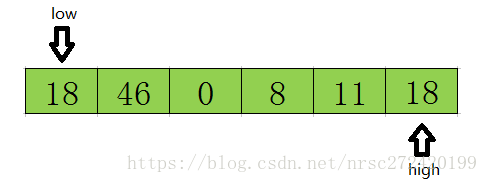
接着开始从前往后扫描,如果扫描到的值小于基准数据就让low加1,如果发现有元素大于基准数据的值(上图46≥tmp),就再将low位置的值赋值给high位置的值,并移动low指针。
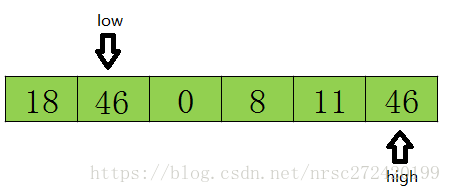
然后再开始从前往后遍历,直到low=high结束循环,此时low或high的下标就是基准数据23在该数组中的正确索引位置(在low或high指针指向的位置插入tmp=23)。
源代码
template<typename T>
void QuickSort(T *const left, const T *const right)
{
T std = *left;
T *lo = const_cast<T*>(left), *hi = const_cast<T*>(right) - 1;
while (lo < hi)
{
while (lo < hi && (*hi) >= std)
--hi;
while (lo < hi && (*lo) <= std)
++lo;
swap(*lo, *hi);
}
*left = *lo;
*lo = std;
if (left <= lo - 2)
QuickSort(left, lo);
if (right >= lo + 3)
QuickSort(lo + 1, right);
}
堆排序
堆是具有一定性质的完全二叉树,对于大顶堆,父节点一定大于等于左右子节点的值;对于小顶堆,父节点一定小于等于左右子节点的值。我们可以将数组映射为堆,利用堆的性质来进行排序。
堆排序的基本思想是:将待排序序列构造成一个大顶堆,此时,整个序列的最大值就是堆顶的根节点。将其与末尾元素进行交换,此时末尾就为最大值。然后将剩余n-1个元素重新构造成一个堆,这样会得到n个元素的次小值。如此反复执行,便能得到一个有序序列了
构建初始堆
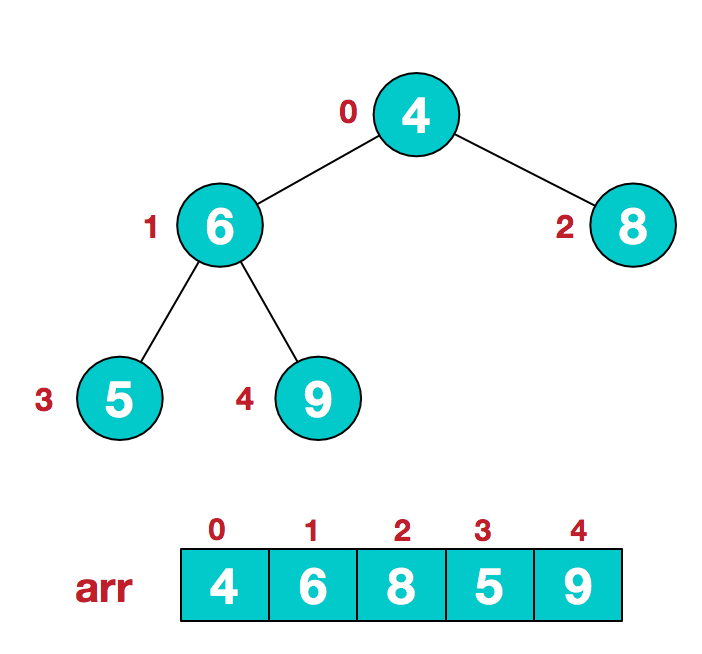<br />此时我们从**最后一个非叶子结点**开始(叶结点自然不用调整,第一个非叶子结点 arr.size()/2-1=5/2-1=1,也就是下面的6结点),从右至左,从下至上进行调整。<br /> 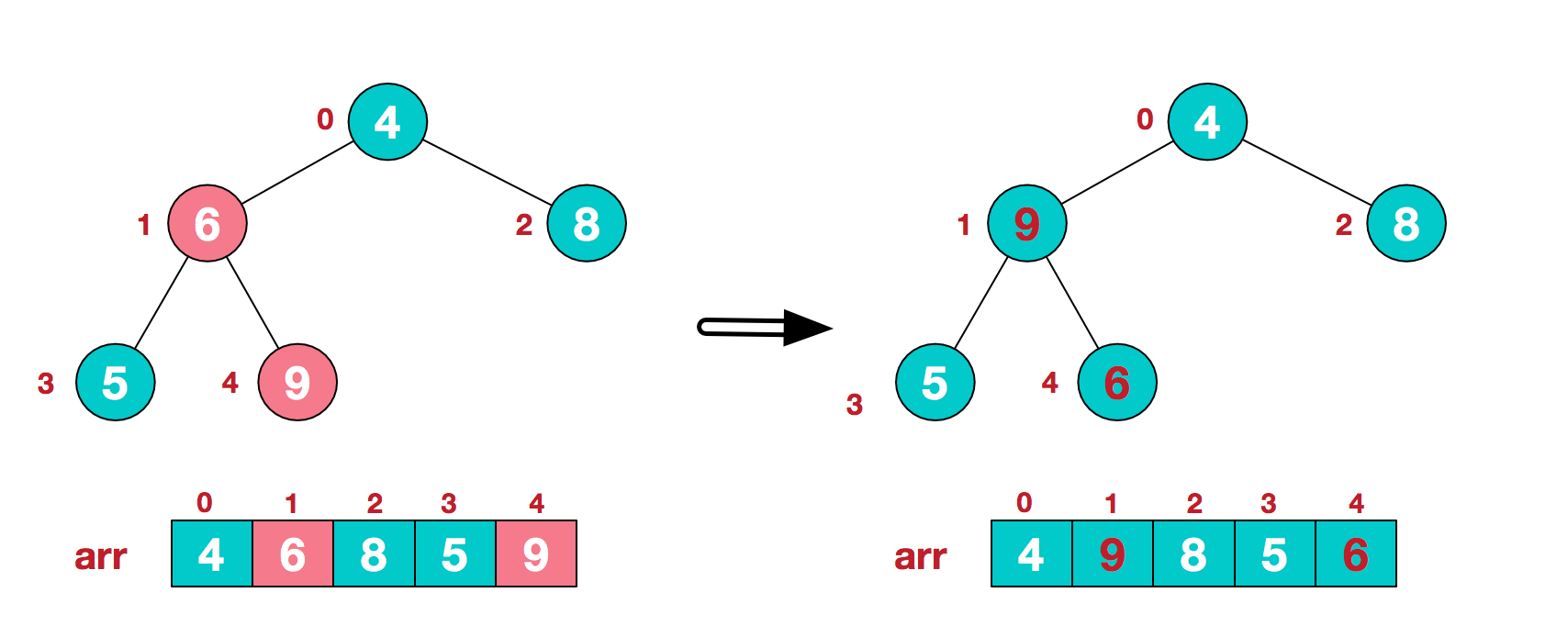<br />找到第二个非叶节点4,由于[4,9,8]中9元素最大,4和9交换。<br /> 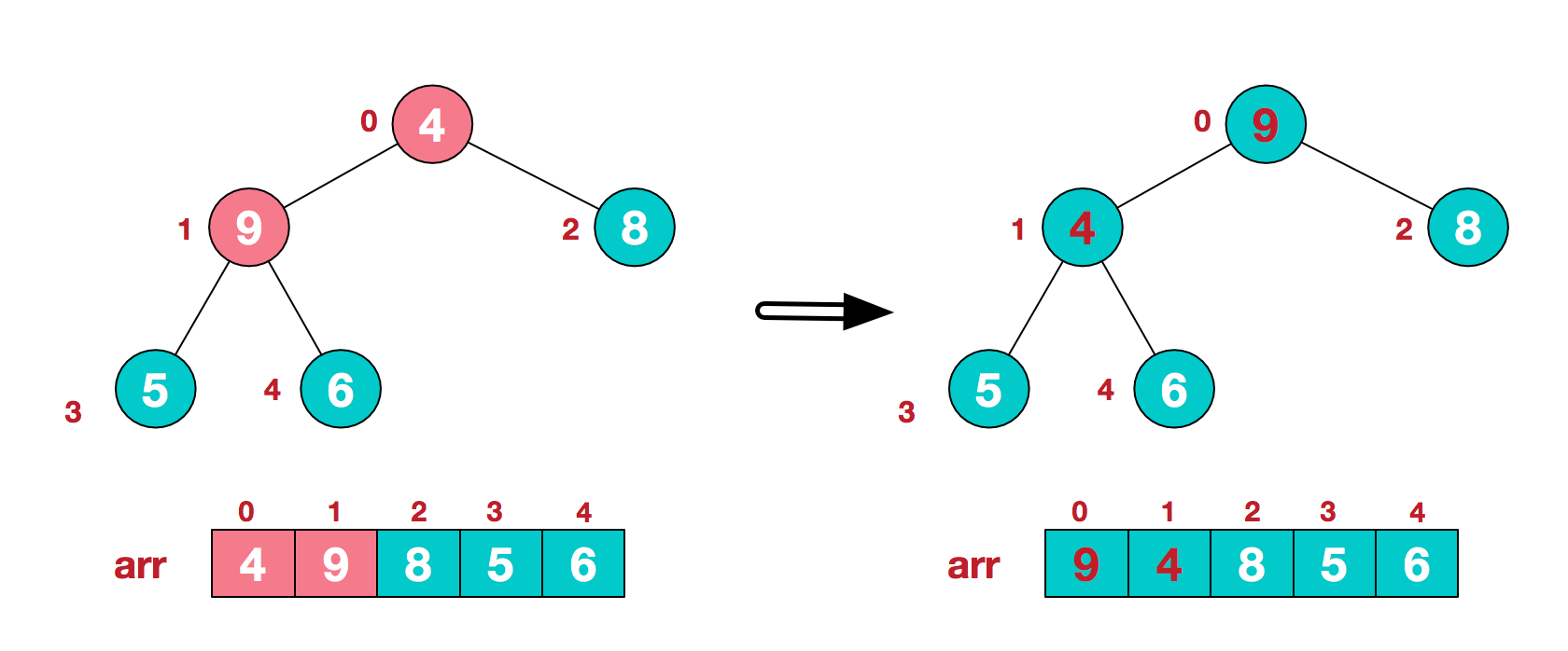<br />这时,交换导致了子根arr[1,3,4]结构混乱,继续调整,arr[1,3,4]中arr[4]=6最大,交换4和6。<br /> 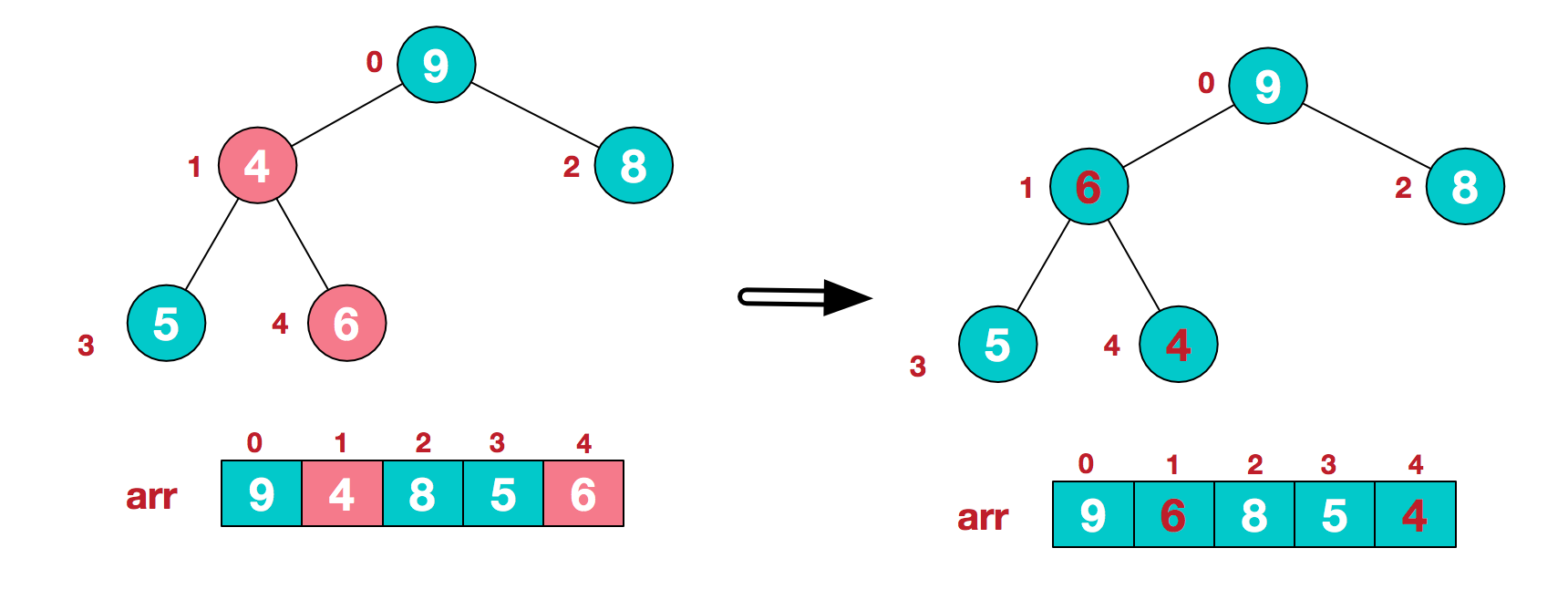<br />此时,我们就将一个无需序列构造成了一个大顶堆。
持续交换堆顶元素与末尾元素
将堆顶的最大元素与数组末尾的元素交换,并将堆的范围从arr[0 : cur.size-1]缩小为[0 : cur.size-2],重新将堆维护至符合性质,重复这一过程直到完成排序。
将堆顶元素9和末尾元素4进行交换。
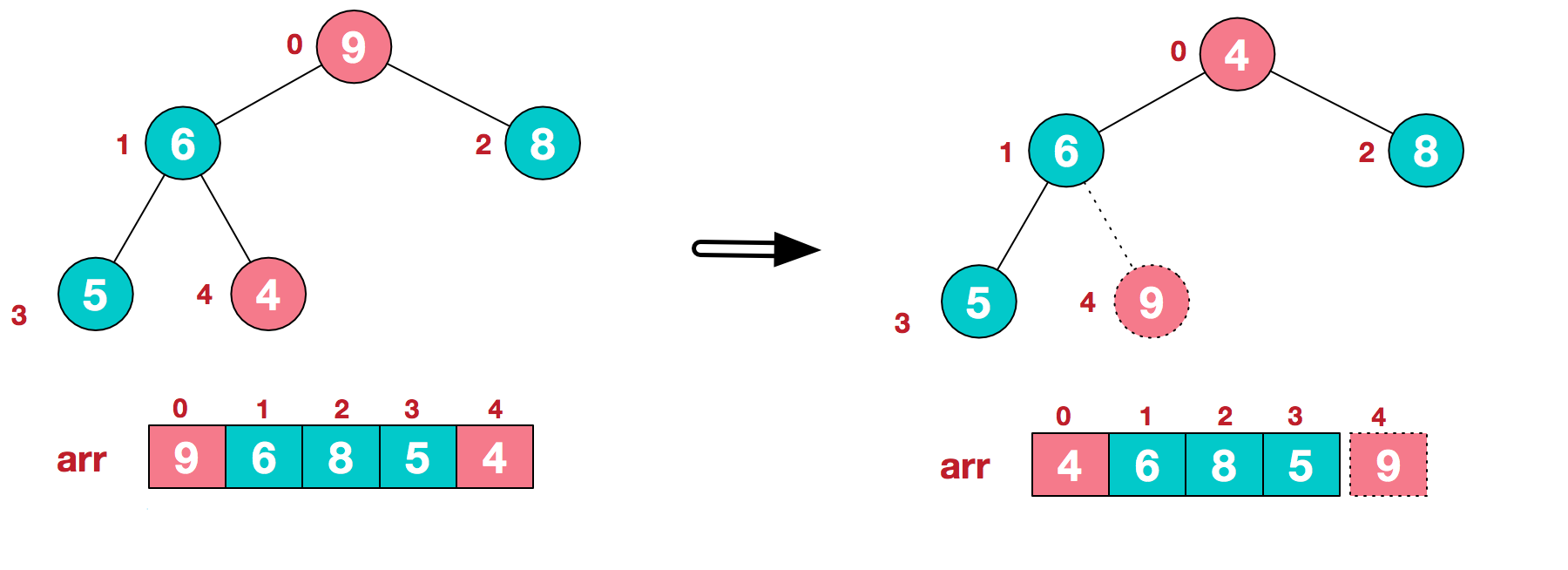
重新调整结构,使其继续满足堆定义。
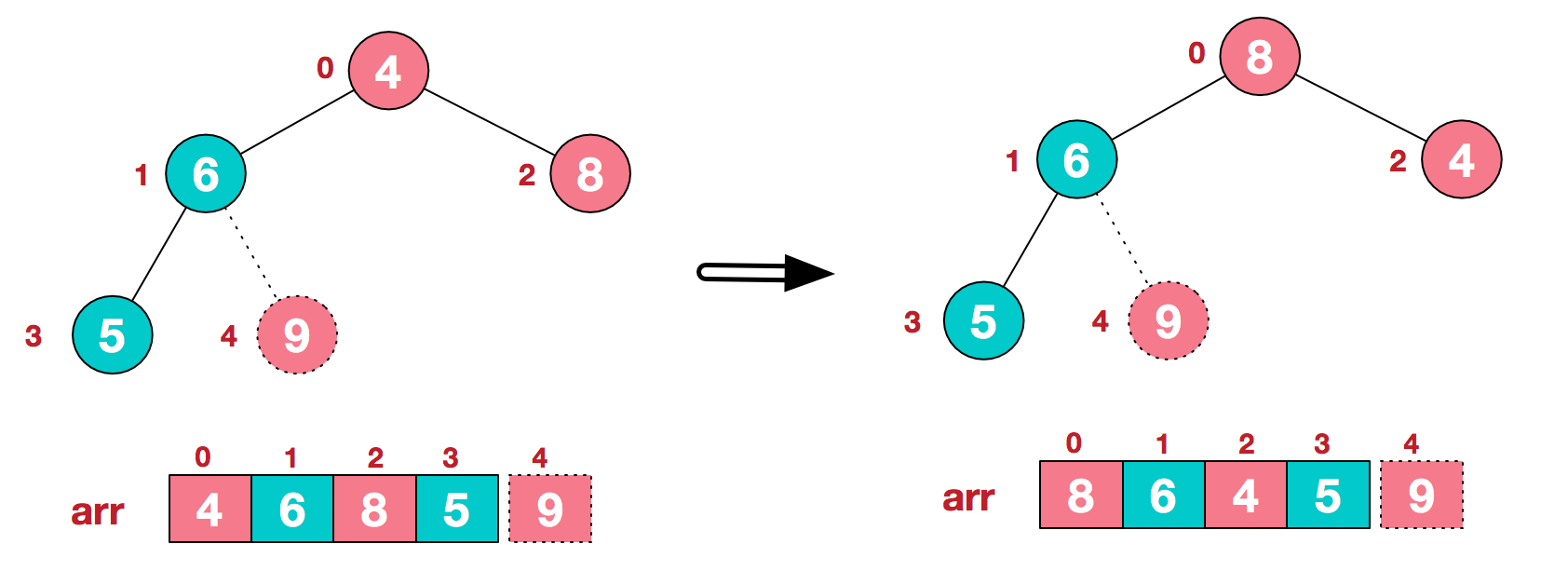
再将堆顶元素8与末尾元素5进行交换,得到第二大元素8。
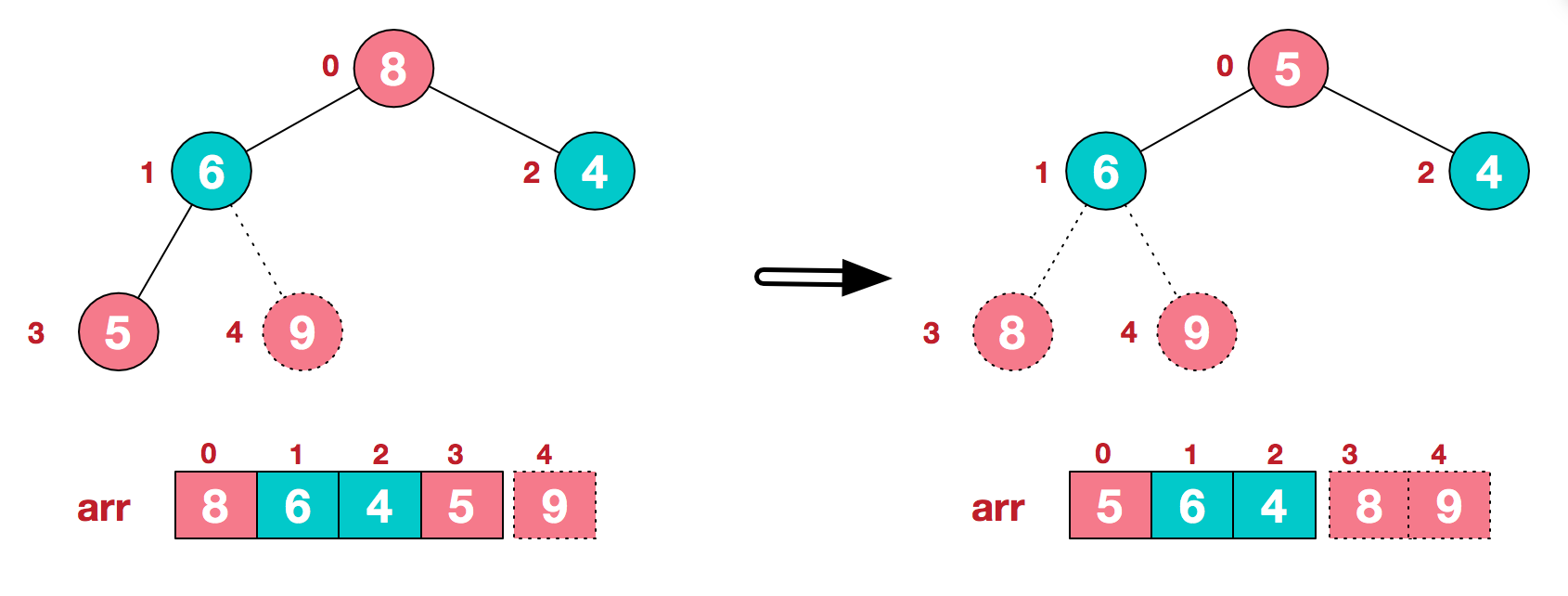
重复以上过程直到整个序列有序。
源代码
template<typename T>
void _adjustHeap(T *const arr, int cur, const int len)
{
int tmp = arr[cur];
for (int child = cur * 2 + 1; child < len; child = child * 2 + 1)
{
if (child + 1 < len && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])
++child;
if (arr[child] > tmp)
{
arr[cur] = arr[child];
cur = child;
}
else
break;
}
arr[cur] = tmp;
}
template<typename T>
void HeapSort(T *const arr, const T *const pt_right)
{
int len = pt_right - arr;
for (int i = len / 2 - 1; i; --i)
_adjustHeap(arr, i, len);
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 1; --i)
{
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
_adjustHeap(arr, 0, i);
}
}
STL库中的sort
面试官:库中的sort函数采用的是什么排序方法?
你:快速排序。
面试官:数据量大和数据量小都适合用快速排序吗?
快速排序的时间复杂度不是稳定的nlogn,最坏情况会变成n^2,怎么解决复杂度恶化问题?
快速排序递归实现时,怎么解决递归层次过深的问题?
递归过深会引发什么问题?
怎么控制递归深度?如果达到递归深度了还没排完序怎么办?
你:嘤嘤嘤?
面试官:恭喜你被刷掉了回家种田去吧。

回答快速排序只答对了1/3,离正确答案还差一大截。
关系型容器如set、map底层采用红黑树,不需要用到sort算法;序列式容器中stack、queue、priority_queue都有特定的出入口,不允许用户操纵元素并排序;剩下的vector、deque和普通的数组适用sort算法。
实现逻辑
STL的sort算法,数据量大时采用QuickSort快排,分段归并排序。一旦分段后的数据量小于某个门槛,为避免QuickSort快排的递归调用带来过大的额外负荷,就改用Insertion Sort插入排序。如果递归层次过深,还会改用HeapSort堆排序。
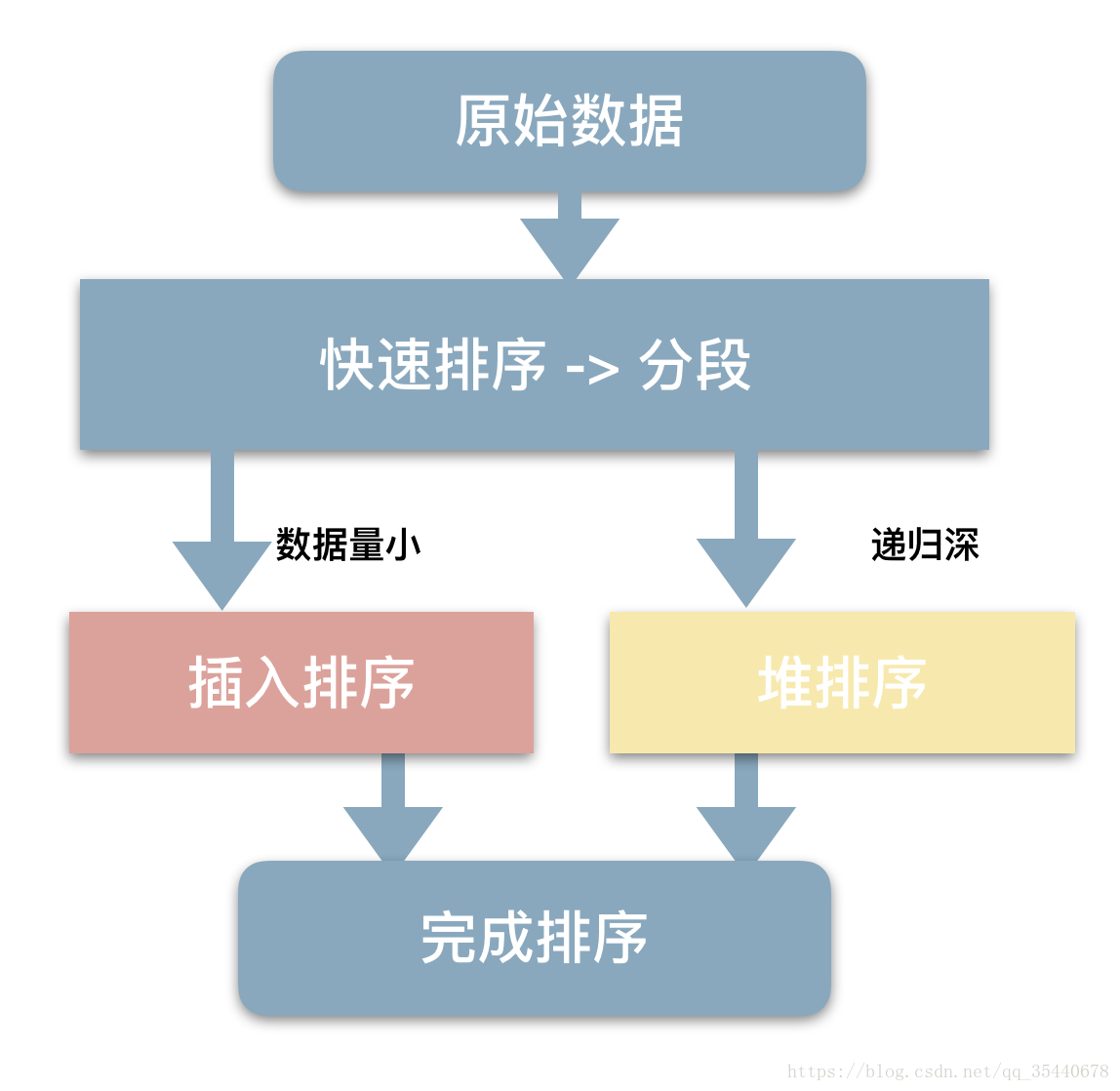
void sort(_Ty First, _Ty Last, int Ideal)
{
int Count = Last - First;
while (32 < Count && Ideal)
{
_Ty Mid = _Partition_by_median_guess(First, Last); //一轮快排
Ideal = (Ideal >> 1) + (Ideal >> 2); //allow 1.5 log2(N) divs ??? 不是log1.33(N)么?
if (Mid - First < Last - Mid) //对短的那部分进行递归
{
sort(First, Mid);
First = Mid;
}
else
{
sort(Mid, Last);
Last = Mid;
}
Count = Last - First;
}
if (32 < Count)
HeapSort(First, Last);
else if (2 < Count)
InsertSort(First, Last);
}
重新回答面试官的问题
面试官:数据量大和数据量小都适合用快速排序吗?
你:数据量小于32的时候用的是插入排序
面试官:快速排序的时间复杂度不是稳定的nlogn,最坏情况会变成n^2,怎么解决复杂度恶化问题?
你:最坏的情况中初始状态呈倒序,解决复杂度恶化问题的方法是选取基准数的时候,当N<40的时候取 First、Mid、Last的中位数;当N≥40的时候取8等分的9个等分点的中位数。
面试官:快速排序递归实现时,怎么解决递归层次过深的问题?
你:递归过深时跳出,数据量大时(Count>32)采用堆排序,反之采用插入排序
面试官:递归过深会引发什么问题?
你:复杂度恶化、爆栈
各种排序效率实测
实验平台:CPU i5 8400@3.8GHz,单线程,VisualStudio2017下,Release(x86)编译。
测试数据通过mt19937随机数生成器生成,每个算法在每个数据量下测试100次,排除耗时远离平均耗时的异常数据点后计算平均值。
使用CPU时钟作为高精度计时工作:
#include <Windows.h>
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&fre);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&start);
f();
QueryPerformanceCounter(&end);
time_ms = (double)(end.QuadPart - start.QuadPart) * 1000 / (double)fre.QuadPart;
| μs / round | STL sort | 快速排序 | 堆排序 | 插入排序 | 选择排序 | 冒泡排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.49 |
| 32 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.77 | 1.87 |
| 64 | 1.51 | 1.80 | 1.24 | 1.12 | 1.93 | 6.36 |
| 128 | 3.60 | 3.97 | 2.57 | 3.26 | 5.02 | 21.97 |
| 256 | 8.33 | 8.90 | 5.23 | 10.72 | 14.34 | 75.37 |
| 1K | 19.29 | 20.26 | 10.85 | 38.90 | 45.49 | 292.08 |
| 8K | 439 | 430 | 239 | |||
| 64K | 4303 | 3964 | 2752 | |||
| 1M | 86ms | 77ms | 111ms |
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <numeric>
#include <algorithm>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
void QuickSort(T *const left, const T *const right)
{
T std = *left;
T *lo = const_cast<T*>(left), *hi = const_cast<T*>(right) - 1;
while (lo < hi)
{
while (lo < hi && (*hi) >= std)
--hi;
while (lo < hi && (*lo) <= std)
++lo;
swap(*lo, *hi);
}
*left = *lo;
*lo = std;
if (left <= lo - 2)
QuickSort(left, lo);
if (right >= lo + 3)
QuickSort(lo + 1, right);
}
template<typename T>
void _adjustHeap(T *const arr, int cur, const int len)
{
int tmp = arr[cur];
for (int child = cur * 2 + 1; child < len; child = child * 2 + 1)
{
if (child + 1 < len && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])
++child;
if (arr[child] > tmp)
{
arr[cur] = arr[child];
cur = child;
}
else
break;
}
arr[cur] = tmp;
}
template<typename T>
void HeapSort(T *const arr, const T *const pt_right)
{
int len = pt_right - arr;
for (int i = len / 2 - 1; i; --i)
_adjustHeap(arr, i, len);
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 1; --i)
{
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
_adjustHeap(arr, 0, i);
}
}
template<typename T>
void BulbSort(T *const left, const T *const right)
{
bool finish;
do
{
finish = true;
for (T *cur = const_cast<T*>(left) + 1; cur < right; ++cur)
{
if (*(cur - 1) > *cur)
{
swap(*(cur - 1), *cur);
finish = false;
}
}
} while (!finish);
}
template<typename T>
void SelectSort(T *const arr, const T *const pt_right)
{
int len = pt_right - arr;
for (int right = len; right; )
{
T _max = arr[0];
int _maxid = 0;
for (int cur = 1; cur < right; ++cur)
{
if (arr[cur] > _max)
{
_max = arr[cur];
_maxid = cur;
}
}
swap(arr[_maxid], arr[--right]);
}
}
template<typename T>
void InsertSort(T *const arr, const T *const pt_right)
{
int len = pt_right - arr;
for (int right = 1; right < len; ++right)
{
T tmp = arr[right];
int i;
for (i = right - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
if (arr[i] > tmp)
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
else
break;
}
arr[i] = tmp;
}
}
vector<double> mean_stdev(const vector<double> &v)
{
vector<double> res(2);
vector<bool> discard(v.size(), false);
res[0] = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0.0) / v.size();
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
{
if (v[i] / res[0] > 10.0)
discard[i] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
{
if (!discard[i])
res[0] += v[i];
}
res[0] /= v.size();
res[1] = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
{
if (!discard[i])
res[1] += (v[i] - res[0]) * (v[i] - res[0]);
}
res[1] = sqrt(res[1] / (v.size() - 1));
return res;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> _sz({ 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 1024 * 8, 1024 * 64, 1024 * 1024 });
mt19937 rd(time(0));
uniform_int_distribution<> dist(0, 1000000);
LARGE_INTEGER Tstart, Tend, fre;
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&fre);
for (int szi = 0; szi < _sz.size(); ++szi)
{
int SIZE = _sz[szi];
vector<double> tSTL, tQuick, tHeap, tInsert, tBulb, tSelect;
int *a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * SIZE), *b = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * SIZE);
for (int ri = 0; ri < 100; ++ri)
{
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i)
a[i] = dist(rd);
memcpy(b, a, SIZE * sizeof(int));
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tstart);
sort(a, a + SIZE);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tend);
tSTL.push_back((double)(Tend.QuadPart - Tstart.QuadPart) * 1000000 / (double)fre.QuadPart);
memcpy(a, b, SIZE * sizeof(int));
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tstart);
QuickSort(a, a + SIZE);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tend);
tQuick.push_back((double)(Tend.QuadPart - Tstart.QuadPart) * 1000000 / (double)fre.QuadPart);
memcpy(a, b, SIZE * sizeof(int));
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tstart);
HeapSort(a, a + SIZE);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tend);
tHeap.push_back((double)(Tend.QuadPart - Tstart.QuadPart) * 1000000 / (double)fre.QuadPart);
if (SIZE >= 1025)
continue;
memcpy(a, b, SIZE * sizeof(int));
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tstart);
InsertSort(a, a + SIZE);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tend);
tInsert.push_back((double)(Tend.QuadPart - Tstart.QuadPart) * 1000000 / (double)fre.QuadPart);
memcpy(a, b, SIZE * sizeof(int));
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tstart);
BulbSort(a, a + SIZE);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tend);
tBulb.push_back((double)(Tend.QuadPart - Tstart.QuadPart) * 1000000 / (double)fre.QuadPart);
memcpy(a, b, SIZE * sizeof(int));
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tstart);
SelectSort(a, a + SIZE);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&Tend);
tSelect.push_back((double)(Tend.QuadPart - Tstart.QuadPart) * 1000000 / (double)fre.QuadPart);
}
if (SIZE < 1025)
{
vector<double> state[6];
state[0] = mean_stdev(tSTL);
state[1] = mean_stdev(tQuick);
state[2] = mean_stdev(tHeap);
state[3] = mean_stdev(tInsert);
state[4] = mean_stdev(tBulb);
state[5] = mean_stdev(tSelect);
cout << "size = " << SIZE << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
printf("%.6lf(%.6lf)\t", state[i][0], state[i][1]);
cout << endl;
}
else
{
vector<double> state[3];
state[0] = mean_stdev(tSTL);
state[1] = mean_stdev(tQuick);
state[2] = mean_stdev(tHeap);
cout << "size = " << SIZE << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
if (SIZE <= 100000)
printf("%.6lf(%.6lf)\t", state[i][0], state[i][1]);
else
printf("%.2lf(%.2lf)\t", state[i][0], state[i][1]);
}
cout << endl << endl;
}
//free(a);
//free(b);
}
//for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i)
// cout << b[i] << " ";
system("pause");
return 0;
}

