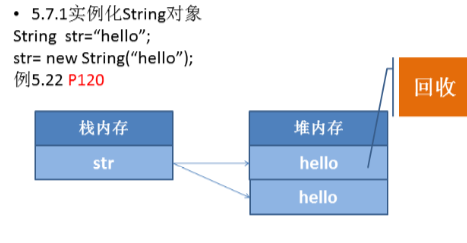
实例化String对象的两种方法
直接赋值
public class text2 {public static void main(String[] args){//实例化String对象String name = "lihua";System.out.println("name:"+name);}}
使用标准new调用
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String name = new String ("lihua"); //实例化String对象
System.out.println("name:"+name);
}
}
String的内容比较
== 比较 ——地址比较/数值比较
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
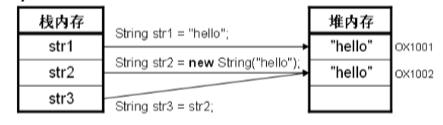
String str1 = "hello"; //直接赋值
String str2 = new String("hello"); //通过new赋值
String str3 = str2; //传递引用
System.out.println("str1==str2-->"+(str1==str2)); //-->false 地址不同
System.out.println("str1==str3-->"+(str1==str3)); //-->false
System.out.println("str2==str3-->"+(str2==str3)); //-->true
}
}
equals() 方法 ——内容比较
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String str1 = "hello"; //直接赋值
String str2 = new String("hello"); //通过new赋值
String str3 = str2; //传递引用
System.out.println("str1 equals str2-->"+(str1.equals(str2))); //-->true
System.out.println("str1 equals str3-->"+(str1.equals(str3))); //-->true
System.out.println("str2 equals str3-->"+(str2.equals(str3))); //-->true
}
}
两种实例化的区别
首先明白一个概念:一个字符串就是一个String类的匿名对象,匿名对象就是已经开辟了堆内存空间的并可以直接使用的对象
当String使用直接赋值(==)的方法之后,只要是以后声明的字符串内容相同,则都不会再开辟新的内存空间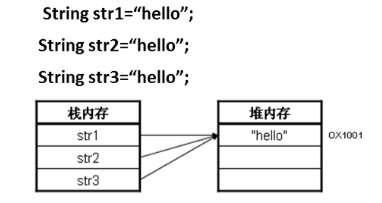
补充:使用new String()实例化String对象×
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String str = new String("Hello"); //通过new关键字实例化
}
}
一个字符串就是一个String类的匿名对象,但如果使用new关键字,无论如何都会开辟一个新的空间。
这时就会开辟两个内存空间,但实际使用的时候只是使用new开辟的空间,另外一个就是垃圾空间了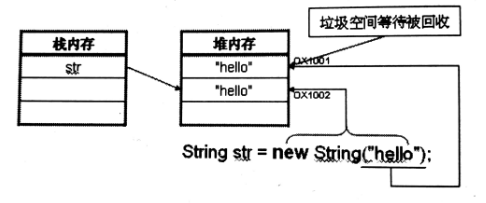
所以对于字符串的操作,直接赋值即可,不要采用构造方法,避免产生垃圾空间。
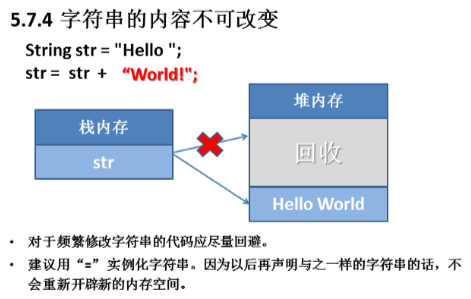
字符串内容不可改变
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String str ="Hello"; //声明字符串
str = str+"World"; //修改字符串
System.out.println("str="+str);
}
}
通用的理论
默认值
int —> 0
double —>0.0
布尔值—>false
对象类型—> null
对于非基本类型/对象类型/引用类型
只定义,不new(实例化):
默认值都是Null
Person per;
String s3; 用的默认值null
new实例化:Xxx xx = new Xxx();
xx值:不是null
xx内部的属性值 目前 全部是数据类型的默认值
String s3 = new String() ; //s3 : “” (空)
Person per = new Person() ; //per: name是null age是0
String类中的常用方法
length和length()的区别
length取得数组长度
length() 取得字符串长度 这是个方法
StringBuffer() 方法
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public StringBuffer append(String s) 将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。 |
| 2 | public StringBuffer reverse() 将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。 |
| 3 | public delete(int start, int end) 移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
| 4 | public insert(int offset, int i) 将 int 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。 |
| 5 | replace(int start, int end, String str) 使用给定 String 中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
下面的列表里的方法和 String 类的方法类似:
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | int capacity() 返回当前容量。 |
| 2 | char charAt(int index) 返回此序列中指定索引处的 char 值。 |
| 3 | void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) 确保容量至少等于指定的最小值。 |
| 4 | void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 将字符从此序列复制到目标字符数组 dst。 |
| 5 | int indexOf(String str) 返回第一次出现的指定子字符串在该字符串中的索引。 |
| 6 | int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 从指定的索引处开始,返回第一次出现的指定子字符串在该字符串中的索引。 |
| 7 | int lastIndexOf(String str) 返回最右边出现的指定子字符串在此字符串中的索引。 |
| 8 | int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 返回 String 对象中子字符串最后出现的位置。 |
| 9 | int length() 返回长度(字符数)。 |
| 10 | void setCharAt(int index, char ch) 将给定索引处的字符设置为 ch。 |
| 11 | void setLength(int newLength) 设置字符序列的长度。 |
| 12 | CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end) 返回一个新的字符序列,该字符序列是此序列的子序列。 |
| 13 | String substring(int start) 返回一个新的 String,它包含此字符序列当前所包含的字符子序列。 |
| 14 | String substring(int start, int end) 返回一个新的 String,它包含此序列当前所包含的字符子序列。 |
| 15 | String toString() 返回此序列中数据的字符串表示形式。 |