类中类.
为什么使用内部类:
- 对同一包的其他类隐藏
- 内部类可以访问外部类的私有数据
6.3.1 使用内部类访问对象状态
package chapter06;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;public class TalkingClock {private int interval;private boolean beep;public TalkingClock(int interval, boolean beep) {this.interval = interval;this.beep = beep;}// 内部类public class TimePrinter implements ActionListener {@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {}}}
可以直接使用外部类的字段:
package chapter06;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;public class TalkingClock {private int interval;private boolean beep;public TalkingClock(int interval, boolean beep) {this.interval = interval;this.beep = beep;}// 内部类public class TimePrinter implements ActionListener {@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {System.out.println(beep);}}}
- 有指向外部对象的隐式引用

- 编译器自动添加引用,
outer.beep
6.3.2 内部类的特殊语法规则
显式引用外部类:
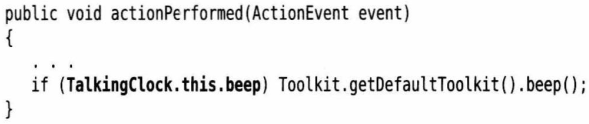
显式引用内部类进行构造:
ActionListener listener = this.new TimePrinter();
创建 public 的内部类的对象:


