简介

准备数据
flow.txt
1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 2001363157995052 13826544101 5C-0E-8B-C7-F1-E0:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 264 0 2001363157991076 13926435656 20-10-7A-28-CC-0A:CMCC 120.196.100.99 2 4 132 1512 2001363154400022 13926251106 5C-0E-8B-8B-B1-50:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 240 0 200
是手机号码跟后面的上下行流量
我们要统计每个手机号码后面的流量
代码
FlowBean
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;import java.io.DataInput;import java.io.DataOutput;import java.io.IOException;public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean> {private long upFlow;private long downFlow;private long sumFlow;//序列化框架在反序列化的时候创建对象的实例会去调用我们的无参构造函数public FlowBean() {}public FlowBean(long upFlow, long downFlow, long sumFlow) {super();this.upFlow = upFlow;this.downFlow = downFlow;this.sumFlow = sumFlow;}public FlowBean(long upFlow, long downFlow) {super();this.upFlow = upFlow;this.downFlow = downFlow;this.sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow;}public void set(long upFlow, long downFlow) {this.upFlow = upFlow;this.downFlow = downFlow;this.sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow;}//序列化的方法@Overridepublic void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {out.writeLong(upFlow);out.writeLong(downFlow);out.writeLong(sumFlow);}//反序列化的方法//注意:字段的反序列化的顺序跟序列化的顺序必须保持一致@Overridepublic void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {this.upFlow = in.readLong();this.downFlow = in.readLong();this.sumFlow = in.readLong();}@Overridepublic String toString() {return upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow;}/*** 这里进行我们自定义比较大小的规则* 在reduce中会进行自动排序*/@Overridepublic int compareTo(FlowBean o) {return (int) (o.getSumFlow() - this.getSumFlow());}//getter和setter方法
流量求和类
里面包含map,reduce,还有
package com.folwsum;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FlowSum {
//在kv中传输我们自定义的对象是可以的,不过必须要实现hadoop的序列化机制,也就是implement writable
//输入的LongWritable,Text
//输出 Text,FlowBean
public static class FlowSumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, FlowBean> {
Text k = new Text();
FlowBean v = new FlowBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//将抽取到的每一行数据进行字段的切分
String line = value.toString();
String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, ' ');
//抽取我们业务所需要的字段,
String phoneNum = fields[1];
//取上下行流量
long upFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length -3]);
long downFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length -2]);
k.set(phoneNum);
v.set(upFlow, downFlow);
//赋值一次就序列化出去了,不会数据都是一致的
context.write(k, v);
}
}
public static class FlowSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, FlowBean, Text, FlowBean> {
FlowBean v = new FlowBean();
//这里reduce方法接收到的key就是某一组<手机号,bean><手机号,bean><手机号,bean>当中一个的手机号
//这里的reduce方法接收到的value就是这一组kv对中的所有bean的一个迭代器
//reduce会把手机号码归类
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long upFlowCount = 0;
long downFlowCount = 0;
for (FlowBean bean : values) {
upFlowCount += bean.getUpFlow();
downFlowCount += bean.getDownFlow();
}
v.set(upFlowCount, downFlowCount);
context.write(key, v);
}
}
//job驱动
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
//上面这样写,不好,换了路径又要重新写,我们改为用他的类加载器加载他自己
job.setJarByClass(FlowSum.class);
//告诉框架,我们程序所用的mapper类和reduce类是什么
job.setMapperClass(FlowSumMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowSumReducer.class);
//告诉框架我们程序输出的类型,
// 如果map阶段和最终输出结果是一样的,这2行可以不写
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
//告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件,结果输出所用的组件是什么
//TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件,准备的叫做读取文本的输入组件
//程序默认的输出组件就是TextOutputFormat,下面那个可以注释
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
//告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路径下
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/Users/jdxia/Desktop/website/hdfs/flowsum/input/"));
//告诉框架我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/Users/jdxia/Desktop/website/hdfs/flowsum/output/"));
//这边不用submit,因为一提交就和我这个没关系了,我这就断开了就看不见了
// job.submit();
//提交后,然后等待服务器端返回值,看是不是true
boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true);
//设置成功就退出码为0
System.exit(res ? 0 : 1);
}
}
按总量排序需求
MR程序在处理数据的过程中会对数据排序(map输出的kv对传输到reduce之前,会排序),排序的依据是map输出的key
所以,我们如果要实现自己需要的排序规则,则可以考虑将排序因素放到key中,让key实现接口:WritableComparable
然后重写key的compareTo方法
排序默认是按照字典排序
自定义排序,他自己他自定义的每个类里面都有compareTo方法
比如LongWritable
或者一些类实现或继承了一些比较接口
如果是我们自己定义的类呢?
如下
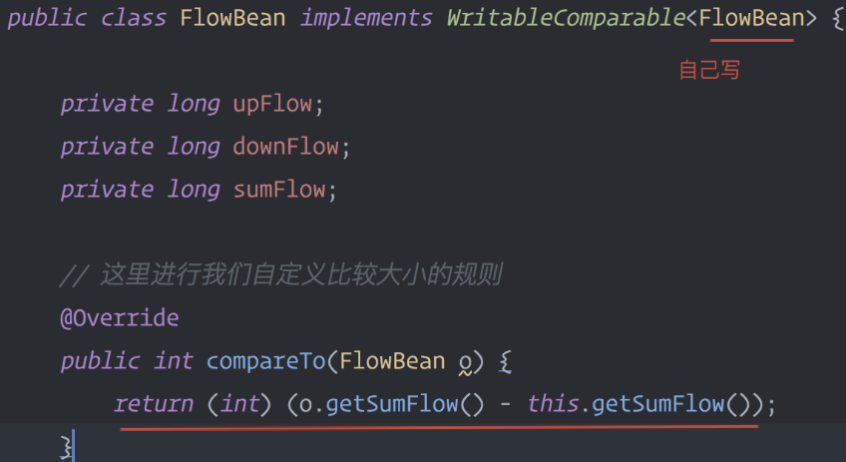
然后代码
这边主要是把Bean当做key,就可以用到bean中自定义的compareTo
package com.folwsum;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FlowSum {
public static class FlowSumSortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, Text> {
FlowBean k = new FlowBean();
Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//将抽取到每一行数据按照字段划分
String line = value.toString();
String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, ' ');
//抽取我们需要的业务字段
String phoneNum = fields[1];
//取上下行流量
long upFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 3]);
long downFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 2]);
k.set(upFlow, downFlow);
v.set(phoneNum);
//赋值一次就序列化出去了,不会数据都是一致的
context.write(k, v);
}
}
public static class FlowSumSortReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean> {
@Override
protected void reduce(FlowBean bean, Iterable<Text> PhoneNum, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//这边写的时候会自动排序的
context.write(PhoneNum.iterator().next(), bean);
//for (Text text : PhoneNum) {
// context.write(text, bean);
//}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
//用类加载器加载自己
job.setJarByClass(FlowSum.class);
//告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么
job.setMapperClass(FlowSumSortMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowSumSortReducer.class);
//告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
//告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么
//TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
//告诉框架,我们要处理的数据在哪个路径下
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/Users/jdxia/Desktop/website/data/input"));
//告诉框架我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/Users/jdxia/Desktop/website/data/output/"));
//这边不用submit,因为一提交就和我这个没关系了,我这就断开了就看不见了
// job.submit();
//提交后,然后等待服务器端返回值,看是不是true
boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true);
//设置成功就退出码为0
System.exit(res ? 0 : 1);
}
}
注意
reducer中
Iterable<FlowBean> values
这个循环遍历的话,他是对遍历出来的对象不断的重新赋值
如果把遍历出来的对象存到链表中,永远是最后一个遍历出来的值是一 个
这时如果你需要把遍历出来的对象保存起来,那需要自己每次new出个对象,然后把值赋值给自己的对象,然后保存起来

