1. 数组
数组(Array)是一种线性表数据结构。它用一组连续的内存空间,来存储一组具有相同类型的数据。
1.1 两数之和(1)
解法一:暴力穷举
public static void main(String[][] args) {new Main().twoSum(new int[]{2, 7, 11, 15}, 9)}public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {int n = nums.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {return new int[]{i, j};}}}return new int[0];}
解法二:a + b = target那么b = target - a; 可以用O(n)的空间Set来存储原始数组,然后计算target-a是否在Set中。
public static void main(String[][] args) {new Main().twoSum(new int[]{2, 7, 11, 15}, 9)}public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {Map<Integer, Integer> numIndexMap = new HashMap<>(nums.length + (nums.length >> 1));for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (numIndexMap.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {return new int[]{numIndexMap.get(target - nums[i]), i};}numIndexMap.put(nums[i], i);}return new int[0];}
1.2 三数之和(15)
解法一:固定target用左右指针法 ```java public static void main (String[][] args) {
}
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {Arrays.sort(nums);List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>(nums.length >> 1);// 枚举 afor (int first = 0; first < nums.length; ++first) {// 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {continue;}// c 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端int third = nums.length - 1;// 枚举 bfor (int second = first + 1; second < nums.length; ++second) {// 跳过第一个 并且 需要和上一次枚举的数不相同if (second != first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {continue;}// 需要保证 b 的指针在 c 的指针的左侧while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > -nums[first]) {--third;}// 如果指针重合,随着 b 后续的增加// 就不会有满足 first+b+c=0 并且 b<c 的 c 了,可以退出循环if (second == third) {break;}if (nums[second] + nums[third] == -nums[first]) {resultList.add(Arrays.asList(nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]));}}}return resultList;}
- 解法二:```javapublic static void main (String[][] args) {}
1.3 盛最多水的容器(11)
- 解法一: ```java public static void main (String[][] args) {
}public int maxArea(int[] height) {int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;int result = 0;while (l < r) {result = Math.max(result, Math.min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l));if (height[l] <= height[r]) {++l;} else {--r;}}return result;}
- 解法二:```javapublic static void main (String[][] args) {}
1.4 删除有序数组中的重复项(26)
解法一:
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {int slow = 1, fast = 1;while (fast < nums.length) {if (nums[fast] != nums[fast - 1]) {nums[slow] = nums[fast];++slow;}++fast;}return nums.length == 0 ? 0 : slow;}
1.5 移动零(283)
解法一:
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {int slow = 0;int fast = 0;while (fast < nums.length) {if (nums[fast] != 0) {nums[slow] = nums[fast];slow++;}++fast;}for (int i = slow; i < nums.length; i++) {nums[i] = 0;}}
1.6 加一(66)
解法一:
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {for (int i = digits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (digits[i] == 9) {digits[i] = 0;} else {digits[i] += 1;return digits;}}int[] ans = new int[digits.length + 1];ans[0] = 1;return ans;}
1.7 合并两个有序数组(88)
解法一:把数组2幅值到数组1排序即可 ```java public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {nums1[m + i] = nums2[i];}Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
- 解法二:双指针```javapublic void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {int ptrOne = 0, ptrTwo = 0;int[] sorted = new int[m + n];int cur;while (ptrOne < m || ptrTwo < n) {if (ptrOne == m) {cur = nums2[ptrTwo++];} else if (ptrTwo == n) {cur = nums1[ptrOne++];} else if (nums1[ptrOne] < nums2[ptrTwo]) {cur = nums1[ptrOne++];} else {cur = nums2[ptrTwo++];}sorted[ptrOne + ptrTwo - 1] = cur;}if (m + n >= 0) {System.arraycopy(sorted, 0, nums1, 0, m + n);}}
1.8 轮转数组(189)
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3 输出: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
解法一:copy数组
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {int n = nums.length;int[] newArr = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {newArr[(i + k) % n] = nums[i];}System.arraycopy(newArr, 0, nums, 0, n);}
解法二:翻转
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {k %= nums.length;reverse(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);reverse(nums, 0, k - 1);reverse(nums, k, nums.length - 1);}public void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {while (start < end) {int temp = nums[start];nums[start] = nums[end];nums[end] = temp;start ++;end--;}}
2. 链表
2.1 单链表反转(206)
解法一:双指针
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if (null == head || null == head.next) {return head;}ListNode curr = head;ListNode prev = null;while (null != curr) {ListNode next = curr.next;curr.next = prev;prev = curr;curr = next;}return prev;}
解法二:栈 ```java public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (null == head || null == head.next) {return head;}Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();ListNode temp = head;while(temp != null) {stack.push(temp);temp = temp.next;}temp = stack.pop();ListNode dummyHead = temp;while (!stack.isEmpty()) {temp.next = stack.pop();temp = temp.next;}temp.next = null;return dummyHead;
}
<a name="d0hI6"></a>### 2.2 链表中有环(141, 142)- 解法一:快慢指针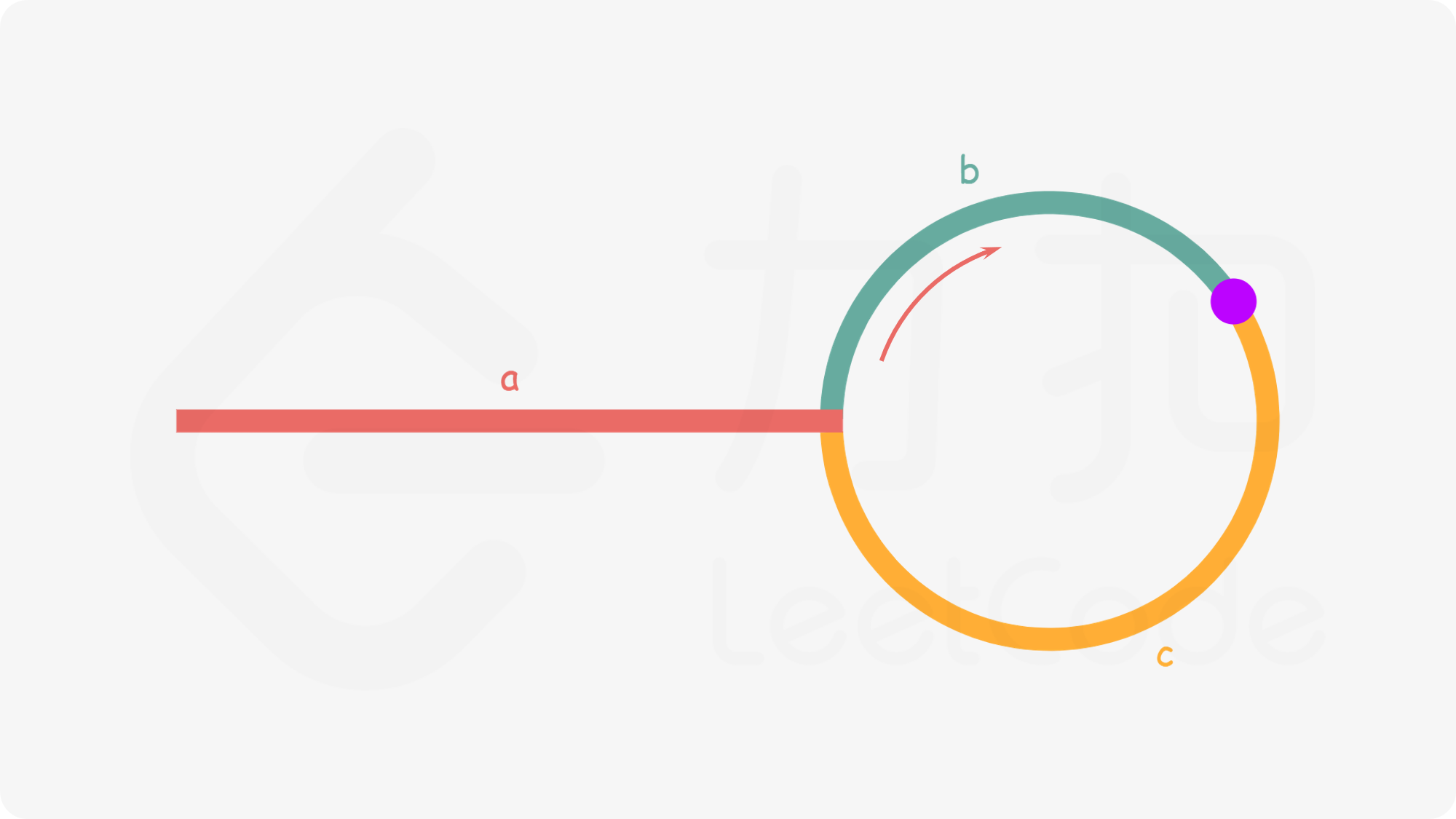```java// 是否存在public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if ( null == head|| null == head.next) {return false;}ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head.next;while(slow != fast) {if (null == fast || null == fast.next ) {return false;}slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}return true;}// 返回找到的节点public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if ( null == head|| null == head.next) {return null;}ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while(null != fast) {if (null == fast.next) {return null;}slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if (slow == fast) {ListNode temp = head;while(temp != slow) {temp = temp.next;slow = slow.next;}return temp;}}return null;}
解法二:hash表
// 是否找到public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if (null == head || null == head.next) {return false;}Set<ListNode> nodeSet = new HashSet<>();ListNode temp = head;while (null != temp) {if (nodeSet.contains(temp)) {return true;}nodeSet.add(temp);temp = temp.next;}return false;}// 返回入环节点public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if (null == head || null == head.next) {return null;}Set<ListNode> nodeSet = new HashSet<>();ListNode temp = head;while (null != temp) {if (nodeSet.contains(temp)) {return temp;}nodeSet.add(temp);temp = temp.next;}return null;}
2.3 合并两个有序链表(21)
解法一:递归 ```java public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {return list2;} else if (list2 == null) {return list1;} else if (list1.val < list2.val) {list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);return list1;} else {list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);return list2;}
}
- 解法二:循环```javapublic ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();ListNode prev = dummyHead;while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {if (list1.val <= list2.val) {prev.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;} else {prev.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;}prev = prev.next;}// 合并后 list1 和 list2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表prev.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;return dummyHead.next;}
2.4 删除链表倒数第 n 个结点(19)
解法一:双路指针,间隔n
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);ListNode front = head;// 抽象头节点ListNode temp = dummy;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {front = front.next;}while (front != null) {front = front.next;temp = temp.next;}temp.next = temp.next.next;return dummy.next;}
解法二:入栈后 pop出 prev指针
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);ListNode temp = dummyHead;Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();while (null != temp) {stack.push(temp);temp = temp.next;}ListNode prev = stack.pop();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {prev = stack.pop();}if (prev.next != null) {prev.next = prev.next.next;}return dummyHead.next;}
解法三:计算长度
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {int count = 0;ListNode temp = head;while(null != temp) {++count;temp = temp.next;}if ( count < n ){return head;}ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();dummyHead.next = head;temp = dummyHead;for (int i = 0; i < count - n; i++) {temp = temp.next;}if (temp.next != null) {temp.next = temp.next.next;}return dummyHead.next;}
2.5 求链表的中间结点(876)
解法一:空间换时间 用数组记录
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {ListNode[] nodeArr = new ListNode[100];int count = 0;while (head != null) {nodeArr[count] = head;++count;head = head.next;}return nodeArr[count / 2];}
解法二:快慢指针
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {ListNode first = head;ListNode second = head;while(second != null && second.next != null) {first = first.next;second = second.next.next;}return first;}
2.6 两两交换链表中的节点(24)
解法一:
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {// 持有headListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();dummyHead.next = head;ListNode first = dummyHead;while (null != first.next && null != first.next.next) {ListNode second = first.next;ListNode third = second.next;// 交换first.next = third;second.next = third.next;third.next = second;// 移动到下一轮first = second;}return dummyHead.next;}
解法二:递归
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode newHead = head.next;// 把他看成自后节点的引用head.next = swapPairs(newHead.next);newHead.next = head;return newHead;}
2.7 K个一组翻转链表(25)
解法一:遍历
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {if (null == head || null == head.next) {return head;}ListNode curr = head;// 计算长度 O(n)int count = 0;while (null != curr) {curr = curr.next;++count;}curr = head;ListNode start = null, end = curr, res = null;ListNode pre;for (int i = 0; i < count / k; i++) {start = curr;//局部反转pre = null;int index = k;while (index != 0) {ListNode temp = curr.next;curr.next = pre;pre = curr;curr = temp;index--;}//记录要返回的nodeif (i == 0) {res = pre;}//拼接反转的部分if (i != 0) {end.next = pre;end = start;}}if (curr != null)end.next = curr;return res;}
2.8 LRU 缓存(146)
解法一: ```java public static void main (String[][] args) {
}
- 解法二:```javapublic static void main (String[][] args) {}

