Difficulty: Medium
Related Topics: Linked List, Depth-first Search
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
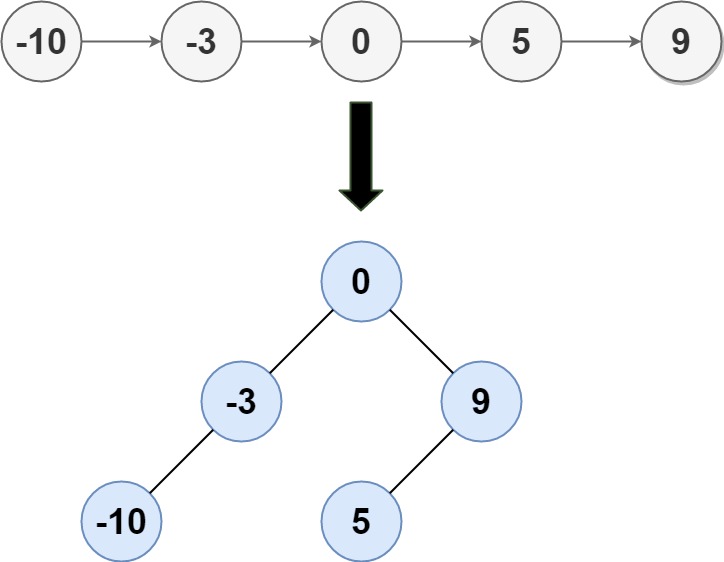
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = []Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [0]Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3]Output: [3,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 10<sup>4</sup>]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution
Language: Java
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*//*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/class Solution {public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {return dfs(head, null);}/*二分查找的步骤就是一颗 BST,所以可以使用二分查找来生成 BSTNOTE: 通过二分查找生成的 BST 必定平衡的二分查找有两种实现方法1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_search_algorithm#Procedure2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_search_algorithm#Alternative_procedure这里使用第二种方法方便一些*/private TreeNode dfs(ListNode lo, ListNode hi) {if (lo == hi) return null;ListNode mid = mid(lo, hi);TreeNode root = new TreeNode(mid.val);root.left = dfs(lo, mid);root.right = dfs(mid.next, hi);return root;}// 通过双指针技巧获得 mid 节点// slow 指针一次走一步// fast 指针一次走两步// 如果链表没有环的话,那么在 fast 走到终点时,slow 一定在中间private ListNode mid(ListNode node, ListNode last) {ListNode slow = node;ListNode fast = node;while(fast != last && fast.next != last) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}return slow;}}

