组合模式是什么?
组合模式(Composite Pattern)是一种结构型的设计模式,它允许我们将对象组成树状结构来表现“整体-部分”的层级结构。组合能让客户端以一致的方式处理个体对象与对象组合。
树状结构是一种常见的数据结构,例如:文件系统、系统菜单等。文件系统由目录和文件组成,目录的内容可以是文件,也可以是目录。组合模式让我们在处理这类层级的数据结构时,模糊了简单元素与复杂元素的差异,客户端可以像处理简单元素那样来处理复杂元素。
UML 类图
用 UML 类图来描述组合模式的结构,在模式中各个角色之间的关系: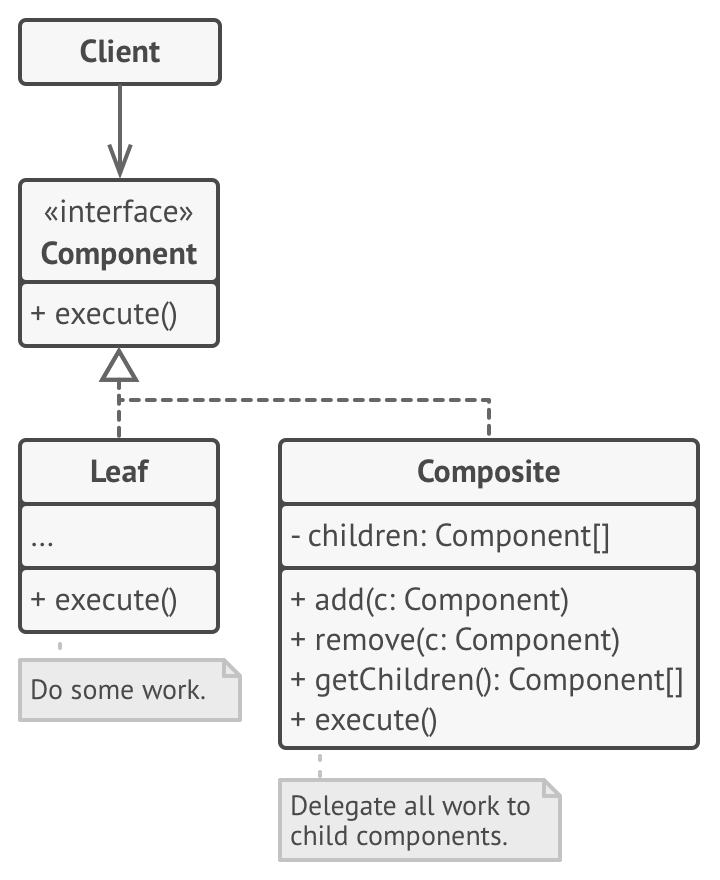
根据上图,总结了模式中各个角色的职责以及它们之间的关系:
- 部件抽象了树状结构中的简单元素(叶节点)和复杂元素(组合),描述了它们的共同操作。
- 叶节点是树状结构中的基本元素,它不包含任何子节点。
- 组合也称为容器,它包含了一组叶节点或其他组合,但它不知道这些子元素的具体类型,它只通过抽象的部件与子元素交互。组合接收到操作请求时,会将工作分配给所有的子元素,聚合它们的计算结果,再将最终的结果返回给客户端。
- 客户端通过部件与任意的元素交互,因此它能够以相同的方式操作树状结构中的简单元素和复杂元素。
案例
让我们通过一个案例来帮助我们进一步理解组合模式。我们来模拟实现 tree 命令,tree 命令的功能是以树状的形式显示指定目录的内容,例如:
$ tree BOOK/BOOK/├── COMPUTER│ ├── Effecitve\ Java.pdf│ └── Introduction\ to\ Algorithms.pdf└── FICTION├── Magic\ Novel│ ├── A\ Song\ of\ Ice\ and\ Fire.epub│ └── Harry\ Potter.epub└── One\ Hundred\ Years\ of\ Solitude.txt
首先,我们需要定义一个抽象的文件部件,以描述所有部件的共同操作:tree。
public abstract class AbstractFile {protected String name;// constructor, getter and setter/*** list contents of directories in a tree-like format.*/public final void tree() {tree(0);}protected void tree(int deep) {StringBuilder lineBuilder = new StringBuilder();if (deep > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < deep - 1; i++) {lineBuilder.append(" ");}lineBuilder.append("└── ");}lineBuilder.append(this.name);System.out.println(lineBuilder.toString());};}
普通文件(即叶节点)扩展了抽象文件,同时可定义自己独有的操作,如打开、保存等。
public class File extends AbstractFile {// constructorpublic byte[] open() throws IOException {// Our code for opening the file}public void save(byte[] data) throws IOException {// Our code for saving the file}// other file operations}
目录(组合节点)也是扩展抽象文件,在 tree 方法会遍历所有的子元素,将任务分发给它们。
public class Directory extends AbstractFile {private List<AbstractFile> files = new ArrayList<>();// constructorpublic void add(AbstractFile file) {files.add(file);}public void remove(AbstractFile file) {files.remove(file);}@Overrideprotected void tree(int deep) {super.tree(deep);files.forEach(files -> files.tree(deep + 1));}}
最后我们通过一个用例来模拟 tree 命令的功能:
public class CompositeMain {public static void main(String[] args) {Directory book = new Directory("BOOK");Directory computer = new Directory("COMPUTER");Directory fiction = new Directory("FICTION");Directory magicNovel = new Directory("Magic Novel");File effectiveJava = new File("Effective Java.pdf");File introductionToAlgorithms = new File("Introduction to Algorithms.pdf");File oneHundredYearsOfSolitude = new File("One Hundred Years of Solitude.txt");File aSongOfIceAndFire = new File("A Song of Ice and Fire.epub");File harryPotter = new File("Harry Potter.epub");book.add(computer);book.add(fiction);computer.add(introductionToAlgorithms);computer.add(effectiveJava);fiction.add(magicNovel);fiction.add(oneHundredYearsOfSolitude);magicNovel.add(aSongOfIceAndFire);magicNovel.add(harryPotter);book.tree();}}
案例源码
可在 GitHub 上查看上述案例的完整代码。
参考资料
本文参考的资料如下:
- Head First Design Patterns - Elisabeth Freeman, Chapter 9.
- 《软件秘笈:设计模式那点事》- 郑阿奇,第 9 章。
- https://www.baeldung.com/java-composite-pattern
- https://refactoring.guru/design-patterns/composite
- https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/composite
- https://sourcemaking.com/design_patterns/composite

