1.基础语法
Java8中引入了一个新的操作符 “->” 该操作符称为箭头操作符或 Lambda 操作符。
箭头操作符将 Lambda 表达式拆分成两部分:
左侧:Lambda 表达式的参数列表
右侧:Lambda 表达式中所需执行的功能,既 Lambda 体
(1)语法格式一:无参数,无返回值
() -> System.out.println("Hello Lambda!")
(2)语法格式二:有一个参数,无返回值
(x) -> System.out.println(x)
(3)语法格式三:仅有一个参数,小括号可以省略
x -> System.out.println(x)
(4)语法格式四:两个及以上参数,有返回值,且 Lambda 体中有多条语句
Comparator<Integer> com = (x,y)-> {System.out.println("Hello Lambda!");return Integer.compare(x, y);};
(5)语法格式五:Lambda 体中仅有一条语句,return 和大括号都可省略
Comparator<Integer> com = (x,y)-> Integer.compare(x, y);
(6)语法格式六:Lambda 表达式的参数列表的数据类型可省略不写,因为JVM编译器通过上下文进行”类型推断”
(Integer x,Integer y)-> Integer.compare(x, y);
Lambda心法:
上联:左右遇一括号省
下联:左侧推断类型省
横批:能省则省
2.函数式接口
2.1 定义
函数式接口中只有一个抽象方法。可以使用注解@FunctionalInterface 修饰
2.2 Java内置四大核心函数式接口
| 函数式接口 | 参数类型 | 返回类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer 消费型接口 |
T | void | 对类型为T的对象应用操作:void accept(T t) |
| Supplier 提供型接口 |
无 | T | 返回类型为T的对象:T get() |
| Function 函数型接口 |
T | R | 对类型为T的对象应用操作,并返回结果为R类型的对象:R apply(T t) |
| Predicate 断言型接口 |
T | boolean | 确定类型为T的对象是否满足某约束,并返回boolean值:boolean test(T t) |
2.3 四大核心接口衍生接口
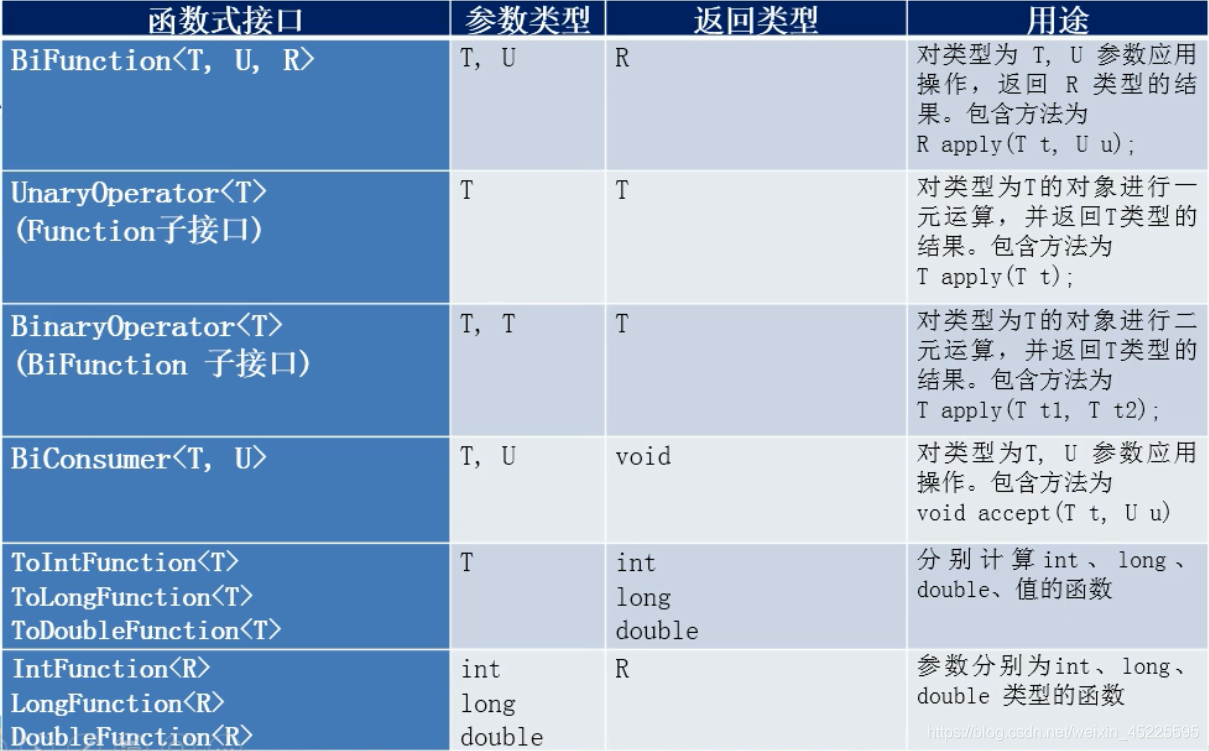
示例代码:
package cn.mineye.feature.java8;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;import java.util.function.Consumer;import java.util.function.Function;import java.util.function.Predicate;import java.util.function.Supplier;/*** <p>* Lambda内置核心接口测试* </p>** @author 571* @since 2021/7/24*/@SpringBootTestpublic class LambdaTest {//Consumer<T> 消费型接口,只进不出@Testpublic void test1() {donate(100.00, (m) -> System.out.println("捐赠:" + m + "元"));}public void donate(double money, Consumer<Double> con) {con.accept(money);}//Supplier<T> 供给型接口,不进有出@Testpublic void test2() {List<Double> list = shitLuck(2, () -> Math.random() * 100);for (Double num : list) {System.out.println("不劳而获:" + num + "元");}}public List<Double> shitLuck(int num, Supplier<Double> sup) {List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {Double n = sup.get();list.add(n);}return list;}//Function<T, R> 函数型接口:有进有出@Testpublic void test3() {String str = work(8D, (h) -> h * 100 + " 元");System.out.println("今天工作8小时,老板给我工钱:" + str);}public String work(Double hour, Function<Double, String> fun) {return fun.apply(hour);}//Predicate<T> 断言型接口:有进有判断@Testpublic void test4() {List<String> list = Arrays.asList("bird", "house", "monkey", "tiger", "dog");List<String> strList = filterStr(list, (s) -> s.length() > 4);for (String str : strList) {System.out.println("长度大于4的单词:" + str);}}public List<String> filterStr(List<String> list, Predicate<String> pre) {List<String> strList = new ArrayList<>();for (String str : list) {if (pre.test(str)) {strList.add(str);}}return strList;}}
3.引用
定义:若 Lambda 表达式体中的内容已有方法实现,则可以使用“方法引用”
3.1 方法引用
语法格式:
- 对象 :: 实例方法
- 类 :: 静态方法
- 类 :: 实例方法
(1)对象::实例方法
注意:Lambda 表达式体中调用方法的参数列表、返回类型必须和函数式接口中抽象方法保持一致
@Testpublic void test01(){PrintStream ps = System.out;Consumer<String> con1 = (s) -> ps.println(s);con1.accept("aaa");//对象::实例方法 表示Consumer<String> con2 = ps::println;con2.accept("bbb");}
(2)类::静态方法
@Testpublic void test02(){Comparator<Integer> com1 = (x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y);System.out.println(com1.compare(1, 2));//类::静态方法 表示Comparator<Integer> com2 = Integer::compare;System.out.println(com2.compare(2, 1));}
(3)类::实例方法
注意:Lambda 参数列表中的第一个参数是方法的调用者,第二个参数是方法的参数时,才能使用 类::实例方法
@Testpublic void test03(){BiPredicate<String, String> bp1 = (x, y) -> x.equals(y);System.out.println(bp1.test("a","b"));//类::实例方法 表示BiPredicate<String, String> bp2 = String::equals;System.out.println(bp2.test("c","c"));}
3.2 构造器引用
语法格式:
类名::new
类名::new
注意:需要调用的构造器的参数列表要与函数式接口中抽象方法的参数列表保持一致
@Testpublic void test04(){Supplier<List> sup1 = () -> new ArrayList();//类名::new 表示Supplier<List> sup2 = ArrayList::new;}
3.3 数组引用
语法格式:
Type::new
Type::new
@Testpublic void test05() {Function<Integer,String[]> fun=x ->new String[x];String[] str=fun.apply(3);//Type::new 表示Function<Integer,String[]> fun2=String[]::new;String[] str2=fun.apply(4);}

