二值化图像 binarizeImage(table,number)免费
格式 : table = binarizeImage( { 范围, 颜色+偏色 }, 步数值 )
适用场景 : 文字识别/A星寻路
关联叉叉官方函数: getColorRGB
关联其他函数:ptable
function binarizeImage(t,P)local P = P or 1 --[[遍历步数1像素]]local getColorRGB = getColorRGB --[[定义取色函数]]local rect = t.rect or {0,0,0,0}local diff = t.diff or {"0x000000-0x000000"}local color = {} --[[diff参数数值化]]local tab = {} --[[二值化存储]]for k,v in pairs(diff) doif color[k]==nil thenlocal rgb_1 = tonumber(string.sub(v,1,8)) --[[参数颜色]]local rgb_2 = tonumber(string.sub(v,10,17)) --[[参数偏色]]color[k] = {lr = rgb_1/0x10000, --[[颜色rgb]]lg = rgb_1%0x10000/0x100,lb = rgb_1%0x100,sr = rgb_2/0x10000, --[[偏色rgb]]sg = rgb_2%0x10000/0x100,sb = rgb_2%0x100,}endendkeepScreen(true) --[[保持屏幕,只在一张图片获取颜色]]for y=rect[2],rect[4],P dolocal y1 = math.floor((y - rect[2])/P) + 1 --坐标位置初始化tab[y1] = {}for x=rect[1],rect[3],P dolocal x1 = math.floor((x - rect[1])/P) + 1 --坐标位置初始化for i = 1,#color do --[[diff多参数循环]]local lr,lg,lb = color[i].lr,color[i].lg,color[i].lblocal sr,sg,sb = color[i].sr,color[i].sg,color[i].sblocal r,g,b = getColorRGB(x,y) --[[获取颜色RGB,搭配保持屏幕函数提高效率]]if math.abs(lr-r) > sr or math.abs(lg-g) > sg or math.abs(lb-b) > sb thentab[y1][x1] = 0 --[[不匹配]]elsetab[y1][x1] = 1 --[[匹配]]breakendendendendkeepScreen(false) --[[关闭保持屏幕]]return tabend
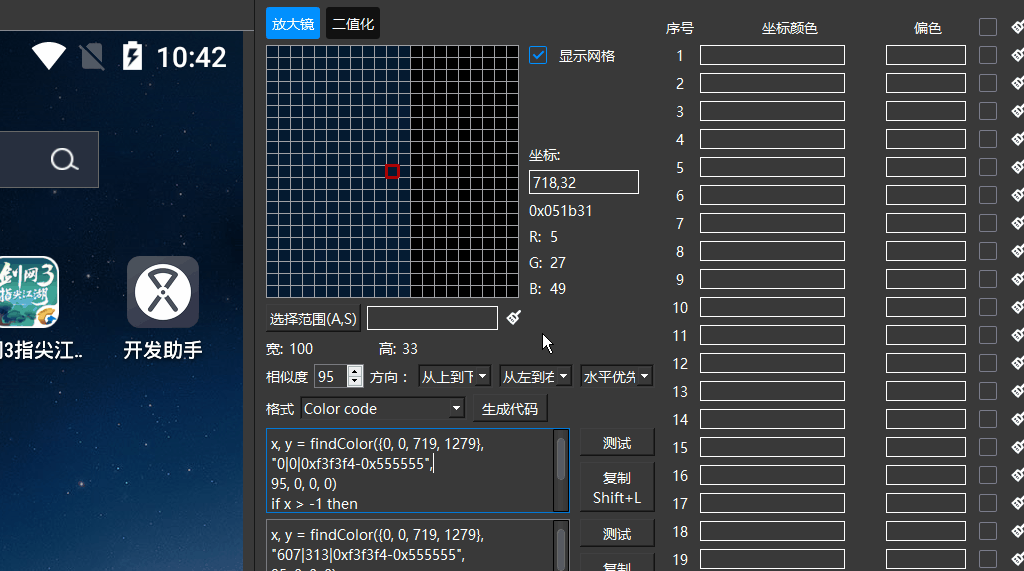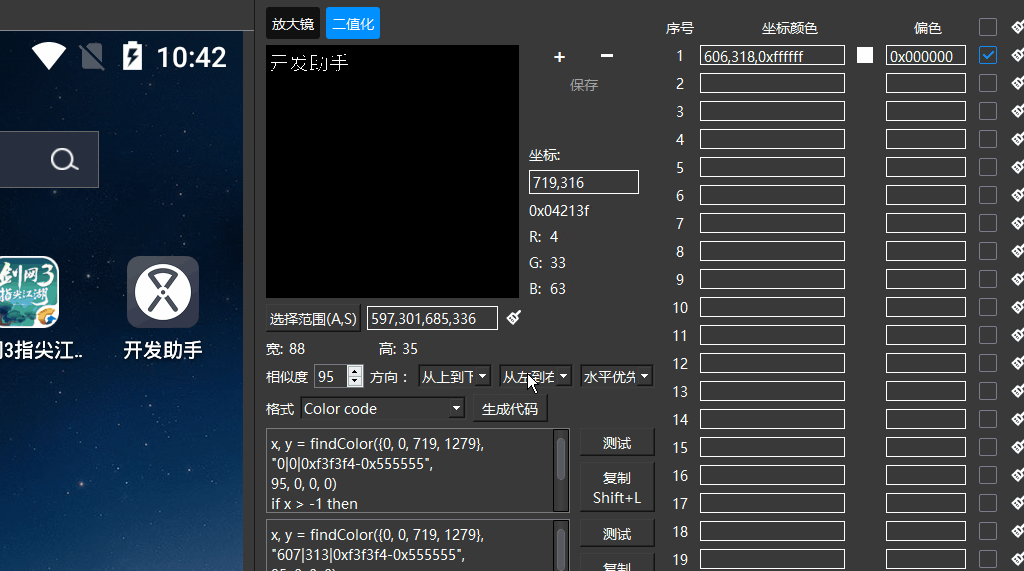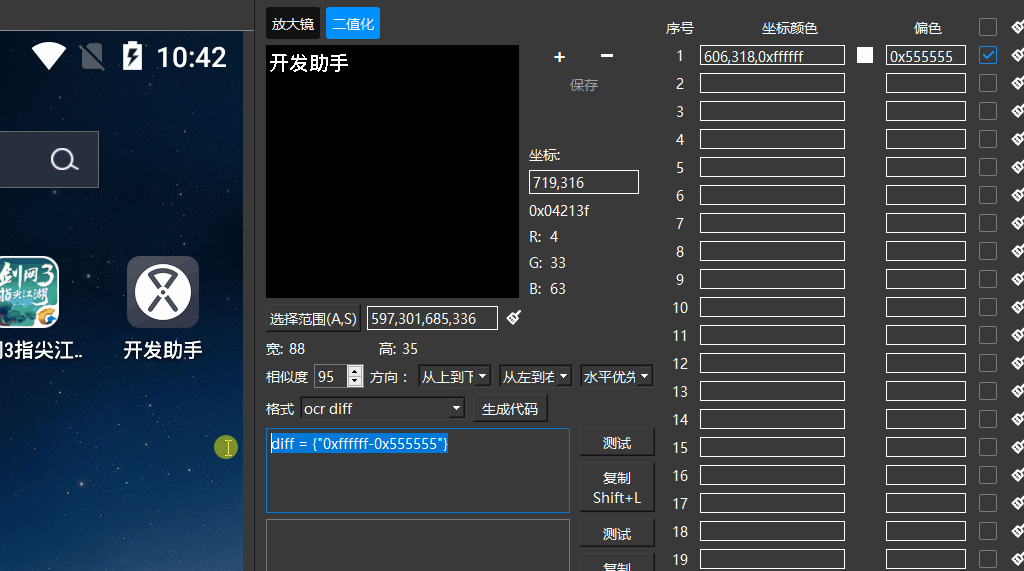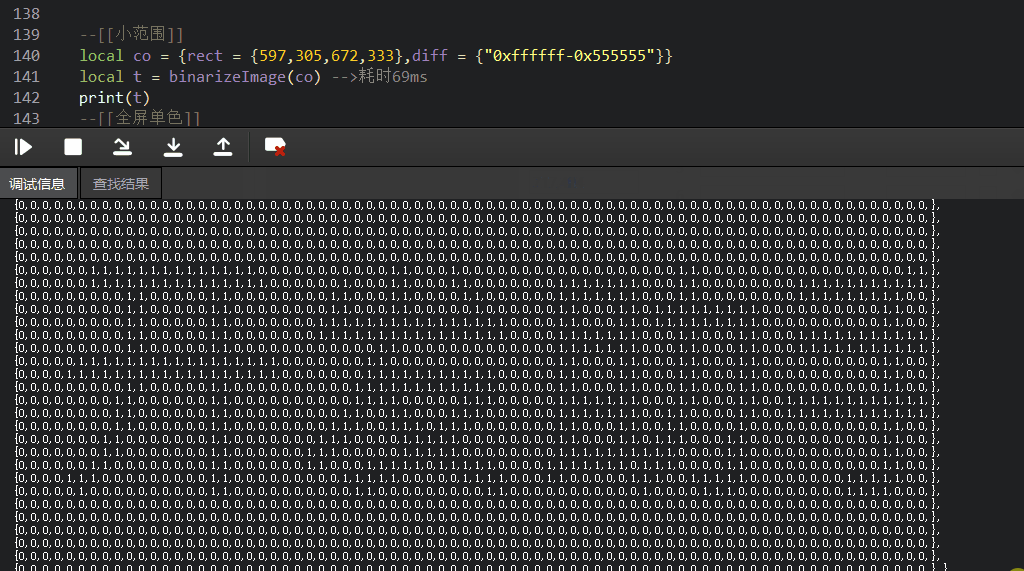
--[[小范围数据测试]]local t = {rect = {597,305,672,333},diff = {"0xf3f3f4-0x555555"}} --[[支持多颜色,但是会消耗更多比色时间]]local t = binarizeImage(t,1) -->耗时0.07秒ptable(t)
--[[大范围数据测试]]--[[720*1280全屏单色]]local t = {rect = {0, 0, 719, 1279},diff = {"0xf3f3f4-0x555555"}}local t = binarizeImage(t,1) -->耗时3.16秒--[[720*1280全屏多色]]local t = {rect = {0, 0, 719, 1279},diff = {"0xf3f3f4-0x555555","0xf3f3f4-0x555555"}}local t = binarizeImage(t,1) -->耗时5秒
二值化7201280范围一共是921600个像素点需要运算,必要时,我们需要缩放比例来提高效率。
*缩放原理:
跳跃式遍历,当步数为2的时候,会略过1个像素点,以此类推。
--[[720*1280全屏单色]]local t = {rect = {0, 0, 719, 1279},diff = {"0xf3f3f4-0x555555"}} --[[支持多颜色,耗时=颜色*n个]]local t = binarizeImage(t,2) -->耗时0.83秒--[[720*1280全屏多色]]local t = {rect = {0, 0, 719, 1279},diff = {"0xf3f3f4-0x555555","0xf3f3f4-0x555555"}}local t = binarizeImage(t,2) -->耗时1.4秒
高级:ffi.C函数
使用Lua实现二值化算法比较容易,适合新手入门学习,但是实际运用效率极低,对于后期需要全屏图像处理极不友好,此时学会思路,我们可以利用Luaffi库来调用C语言重新实现二值化算法。
--binarizeImage.luabinarizeImage = function(self,tab)self.pixel_wand = self.pixel_wand or ffi.gc(lib.NewPixelWand(), lib.DestroyPixelWand)local myffi = ffi.load('binarizeImage')ffi.cdef [[int main(int *rect,int *diff,int *wand,int *pixel_wand,int (*Magick)(),double (*R)(),double (*G)(),double (*B)());int *_BINARIZE_Image;int Freememory(int*a);]]--------------------颜色-偏色-----------------------------------------------local color={}local diff=tab.diff --颜色-偏色for k,v in pairs(diff) dolocal rgb_1 = tonumber(string.sub(v,1,8)) --[[参数颜色]]local rgb_2 = tonumber(string.sub(v,10,17)) --[[参数偏色]]color[k] = {rgb_1/0x10000, --[[颜色rgb]]rgb_1%0x10000/0x100,rgb_1%0x100,rgb_2/0x10000, --[[偏色rgb]]rgb_2%0x10000/0x100,rgb_2%0x100,}endlocal t ={}for k,v in pairs(color) do --{r,g,b,sr,sg,sb}if type(v)=="table" thenlocal p = ffi.cast('float*', ffi.new("float[20]",v)) --指针地址table.insert(t,tonumber(p))endendlocal diff = ffi.new("int[10]", t) --转换成{指针地址1,指针地址2}--------------------范围-----------------------------------------------------local rect = tab.rectlocal rect = ffi.cast('int*', ffi.new("int[10]",rect))myffi.main(rect,diff,self.wand,self.pixel_wand,lib.MagickGetImagePixelColor,lib.PixelGetRed,lib.PixelGetGreen,lib.PixelGetBlue) --C函数计算完毕返回数组local ti={} --创建可视化二值化表,开销时间从这里开始local i=0local rect = tab.rectfor y=1,rect[4]-rect[2] doti[y]={}for x=1,rect[3]-rect[1] doti[y][x]=0if myffi._BINARIZE_Image[i]==0 thenti[math.floor(i/(rect[3]-rect[1]))+1][x]=0elseti[math.floor(i/(rect[3]-rect[1]))+1][x]=1endi=i+1endendmyffi.Freememory(myffi._BINARIZE_Image) --释放堆内存-- ptable(ti)return tiend
--binarizeImage.c#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>/* #include <string.h> */#include <stdint.h>int *_BINARIZE_Image;int Freememory(int*a);int main(int *rect,int *diff,int *wand,int *pixel_wand,int (*Magick)(),double (*R)(),double (*G)(),double (*B)()) {_BINARIZE_Image = malloc(sizeof(int) * 5000*5000);//申请堆超大内存if(_BINARIZE_Image==NULL) {printf("申请堆内存失败\n");} else {int x,y;int j=0;for(y = 0; y<rect[3]-rect[1]; y++) { //遍历图片指定范围像素点for(x = 0; x<rect[2]-rect[0]; x++) {//---------------------获取r g b sr sg sb--------------------int i;for(i=0; i<10; i++) { //最多十个颜色if ((float *)(uintptr_t)diff[i]==NULL) {break; //如果等于nil值就退出} else {float *p =(float *)(uintptr_t)diff[i]; //获取lua表指针地址int lr=p[0]; //脚本颜色int lg=p[1];int lb=p[2];int sr=p[3]; //脚本偏色int sg=p[4];int sb=p[5];//---------------------获取当前图片r g b--------------------Magick(wand,x,y,pixel_wand);int r=R(pixel_wand)*255;int g=G(pixel_wand)*255;int b=B(pixel_wand)*255;//---------------------获取当前图片r g b--------------------if( abs(lr-r)>sr || abs(lg-g)>sg || abs(lb-b)>sb ) {_BINARIZE_Image[j]=0; //不匹配} else {_BINARIZE_Image[j]=1; //匹配break;}}}j++;//---------------------获取r g b sr sg sb--------------------}}}return 0;}int Freememory(int*a) { //释放内存free(a);a = NULL;return 0;}

3.png
--调用方法:local magick=require"magick.wand"local ffi = require"ffi"local img = magick.load_image("3.png") --创建图片对象t={rect = {0, 0, 38, 55},diff={"0x000000-0x555555"}} --范围,颜色-偏色ptable(img:binarizeImage(t)) --调用binarizeImage函数

C函数经过提前编译成二进制文件来进行运算,5000*5000分辨率耗时:0.02秒,基本没什么时间消耗,但是lua要打印出上面这个表则需要创建表,开销时间很大。实际我们不需要打印表,直接用c函数去计算,效率可提高10000倍以上。
 献出心脏。。
献出心脏。。


