前言
java中得复制,到底有哪些? 浅拷贝和深拷贝,有什么区别呢? 我们平时习惯属性间得复制,beanUtils.copyproperties,属于哪种类型得复制? 我们常用得数组间得复制转换,又分为哪些? 再IO中,零拷贝又是什么意思?
复制有哪些类型?
将一个对象的引用复制给另外一个对象,一共有三种方式。
第一种方式是直接赋值,
第二种方式 是浅拷贝,
第三种是深拷贝。
浅拷贝
对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型进行引用传递般的拷贝,此为浅拷贝
如何实现浅拷贝?
类实现implements Cloneable接口,然后重写clone方法
package com.haoker.copy;/*** @ClassName SimpleCopy* @Description TODO* @Author 豪* @Date 2021/8/3 23:44* @Version I. 0**/public class SimpleCopy {public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {PersonDest2 personDest2 = new PersonDest2(1, "12345", 21);Person p = new Person(23, "zhang",personDest2);Person p1 = (Person) p.clone();System.out.println(p.getPersonDest2());System.out.println(p1.getPersonDest2());}}class Person implements Cloneable{//private Integer age;private int age;//阿里规范中规定pojo类中的属性强制使用包装类型,这里只是测试private String name;private PersonDest2 personDest2;public Person(Integer age, String name,PersonDest2 personDest2) {super();this.age = age;this.name = name;this.personDest2 = personDest2;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public PersonDest2 getPersonDest2() {return personDest2;}public void setPersonDest2(PersonDest2 personDest2) {this.personDest2 = personDest2;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return super.toString();}@Overrideprotected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {return super.clone();}}
深拷贝
对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型,创建一个新的对象,并复制其内容,此为深拷贝。
如何实现深拷贝?
1、与通过重写clone方法实现浅拷贝的基本思路一样,只需要为对象图的每一层的每一个对象都实现Cloneable接口并重写clone方法,最后在最顶层的类的重写的clone方法中调用所有的clone方法即可实现深拷贝。简单的说就是:每一层的每个对象都进行浅拷贝=深拷贝。
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.io.Serializable;/* 通过序列化实现深拷贝 */public class DeepCopyBySerialization {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {Age a=new Age(20);Student stu1=new Student("摇头耶稣",a,175);//通过序列化方法实现深拷贝ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(bos);oos.writeObject(stu1);oos.flush();ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()));Student stu2=(Student)ois.readObject();System.out.println(stu1.toString());System.out.println(stu2.toString());System.out.println();//尝试修改stu1中的各属性,观察stu2的属性有没有变化stu1.setName("大傻子");//改变age这个引用类型的成员变量的值a.setAge(99);stu1.setLength(216);System.out.println(stu1.toString());System.out.println(stu2.toString());}}/** 创建年龄类*/class Age implements Serializable{//年龄类的成员变量(属性)private int age;//构造方法public Age(int age) {this.age=age;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String toString() {return this.age+"";}}/** 创建学生类*/class Student implements Serializable{//学生类的成员变量(属性),其中一个属性为类的对象private String name;private Age aage;private int length;//构造方法,其中一个参数为另一个类的对象public Student(String name,Age a,int length) {this.name=name;this.aage=a;this.length=length;}//eclipe中alt+shift+s自动添加所有的set和get方法public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Age getaAge() {return this.aage;}public void setaAge(Age age) {this.aage=age;}public int getLength() {return this.length;}public void setLength(int length) {this.length=length;}//设置输出的字符串形式public String toString() {return "姓名是: "+this.getName()+", 年龄为: "+this.getaAge().toString()+", 长度是: "+this.getLength();}}
2、使用序列化。可以先使对象实现 Serializable 接口,然后把对象(实际上只是对象的一个拷贝)写到一个流里,再从流里读出来,便可以重建对象
/*** 使用java的序列化实现深层复制*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T extends Serializable> T deepClone(T a){T t = null;if(a != null){try{ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);oos.writeObject(a);oos.flush();oos.close();byte[] arrByte = baos.toByteArray();ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(arrByte);ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);t = (T)ois.readObject();ois.close();}catch(Exception e){}}return t;}
数组间得复制,常用得哪几种?
1、利用for循环依次检索
package com.haoker.ArraysCopy;/*** 功能描述:通过循环赋值* @author: 豪* @date: 2021/8/3 23:59**/public class Arrays {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arrays1 = {3,4,6,8,9};int[] ret = copyArray(arrays1);System.out.println("拷贝后:");for (int x:ret) {System.out.print(" "+x+" ");}}public static int[] copyArray(int[]a){int[] ret = new int[a.length];for(int i = 0; i<ret.length; i++){ret[i]=a[i];}//利用for循环return ret;//返回数组}}
2、利用System.arraycopy()方法
package com.haoker.ArraysCopy;/*** 功能描述:利用System.arraycopy()方法* @author: 豪* @date: 2021/8/3 23:59**/public class SystemArraycopy {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arrays1 = {3,4,6,8,9};int[] ret = copyArray(arrays1);System.out.println("拷贝后:");for (int x:ret) {System.out.print(" "+x+" ");}}public static int[] copyArray(int[]a){int[] ret = new int[a.length];//参数一:被拷贝得源数组//参数二:被拷贝得源数组下标开始得位置//参数三:目标数组//参数四:目标数组下标开始得位置//参数五:复制多少长度System.arraycopy( a,1,ret,0,ret.length-1);return ret;}}
3、利用Arrays.copyof()方法,底层还是System.arraycopy方法
package com.haoker.ArraysCopy;import java.util.Arrays;/*** 功能描述:利用Arrays.copyof()方法* @author: 豪* @date: 2021/8/3 23:59**/public class ArraysCopyof {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arrays1 = {3,4,6,8,9};System.out.println("拷贝后:");copyArray(arrays1);}public static void copyArray(int[]a){int[] ret =Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length-1);for (int x:ret) {System.out.print(" "+x+" ");}}}
4、通过clone()
package com.haoker.ArraysCopy;import java.util.Arrays;/*** 功能描述:通过clone()方法* @author: 豪* @date: 2021/8/3 23:59**/public class ArraysClone {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arrays1 = {3,4,6,8,9};System.out.println("拷贝后:");copyArray(arrays1);}public static void copyArray(int[]a){int[] ret =a.clone();for (int x:ret) {System.out.print(" "+x+" ");}}}
常用属性间得复制,beanUtils.copyproperties,属于哪种类型复制?
浅拷贝,因为复制对象得时候,源对象进行改变后,复制过来得值也会跟着变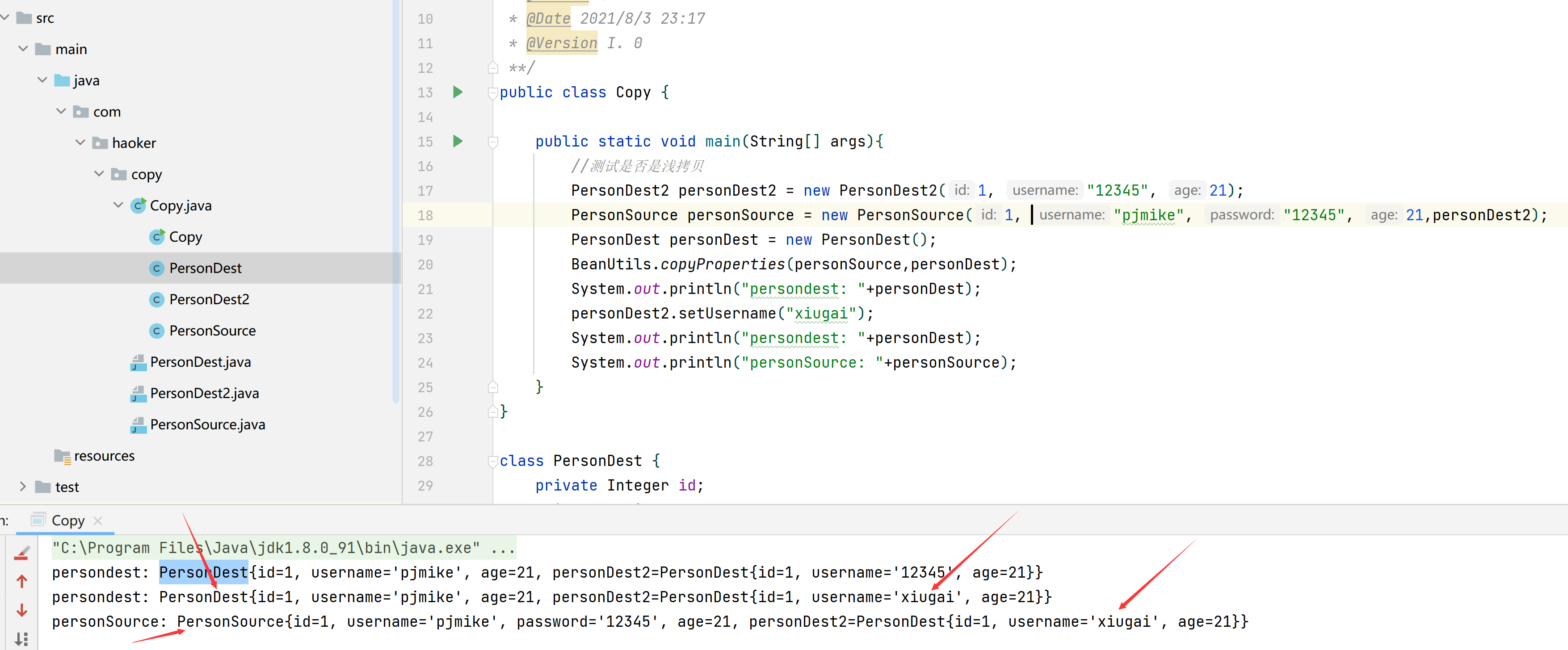
package com.haoker.copy;import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;/*** @ClassName Copy* @Description TODO* @Author 豪* @Date 2021/8/3 23:17* @Version I. 0**/public class Copy {public static void main(String[] args){//测试是否是浅拷贝PersonDest2 personDest2 = new PersonDest2(1, "12345", 21);PersonSource personSource = new PersonSource(1, "pjmike", "12345", 21,personDest2);PersonDest personDest = new PersonDest();BeanUtils.copyProperties(personSource,personDest);System.out.println("persondest: "+personDest);personDest2.setUsername("xiugai");System.out.println("persondest: "+personDest);System.out.println("personSource: "+personSource);}}class PersonDest {private Integer id;private String username;private Integer age;private PersonDest2 personDest2;// getters/setters omiitedpublic PersonDest() {}public PersonDest(Integer id, String username, Integer age) {this.id = id;this.username = username;this.age = age;}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getUsername() {return username;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public PersonDest2 getPersonDest2() {return personDest2;}public void setPersonDest2(PersonDest2 personDest2) {this.personDest2 = personDest2;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "PersonDest{" +"id=" + id +", username='" + username + '\'' +", age=" + age +", personDest2=" + personDest2 +'}';}}class PersonDest2 {private Integer id;private String username;private Integer age;// getters/setters omiitedpublic PersonDest2() {}public PersonDest2(Integer id, String username, Integer age) {this.id = id;this.username = username;this.age = age;}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getUsername() {return username;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "PersonDest{" +"id=" + id +", username='" + username + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}class PersonSource {private Integer id;private String username;private String password;private Integer age;private PersonDest2 personDest2;public PersonSource() {}public PersonSource(Integer id, String username, String password, Integer age,PersonDest2 personDest2) {this.id = id;this.username = username;this.password = password;this.age = age;this.personDest2 = personDest2;}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getUsername() {return username;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public String getPassword() {return password;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public PersonDest2 getPersonDest2() {return personDest2;}public void setPersonDest2(PersonDest2 personDest2) {this.personDest2 = personDest2;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "PersonSource{" +"id=" + id +", username='" + username + '\'' +", password='" + password + '\'' +", age=" + age +", personDest2=" + personDest2 +'}';}}

