- 一、排序算法
- 二、查找算法
- 三、回溯、贪心和动态规划
- 回溯算法思想
- leetcode 112 号算法题:路径总和
- leetcode 113 号算法题:路径总和 II
- leetcode 46 号算法题:全排列
- leetcode 47 号算法题:全排列 II
- leetcode 77 号算法题:组合
- leetcode 39 号算法题:组合总和
- leetcode 40 号算法题:组合总和 Ⅱ
- leetcode 216 号算法题:组合总和 Ⅲ
- leetcode 78 号算法题:子集
- leetcode 90 号算法题:子集Ⅱ
- leetcode 17 号算法题:电话号码的字母组合
- leetcode 93 号算法题:复原 IP 地址
- leetcode 22 号算法题:括号生成
- leetcode 51 号算法题:N 皇后
- leetcode 37 号算法题:数独问题
- 贪心算法思想
- 动态规划算法思想
- leetcode 509 号算法题:斐波那契数
- leetcode 322 号算法题:零钱兑换
- leetcode 64 号算法题:最小路径和
- leetcode 53 号算法题:最大子数组之和
- leetcode 647 号算法题:回文子串
- leetcode 5 号算法题:最长回文串
- leetcode 131 号算法题:分割回文串
- leetcode 516 号算法题:最长回文子序列
- leetcode 300 号算法题:最长上升子序列
- leetcode 1143 号算法题:最长公共子序列
- leetcode 72 号算法题:编辑距离
- leetcode 44 号算法题:通配符匹配
- leetcode 10 号算法题:正则表达式匹配
- leetcode 486 号算法题:预测赢家
- leetcode 877 号算法题:石子游戏
- 0-1 背包问题
- 总结
- 回溯算法思想
- 四、刷题总结
一、排序算法
1.快速排序
(挖坑排序法经典讲解:https://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6684558)
基本思想:
1.先从数列中取出一个数作为基准数。
2.分区过程,将比这个数大的数全放到它的右边,小于或等于它的数全放到它的左边。
3.再对左右区间重复第二步,直到各区间只有一个数。
挖坑填数+分治法=快速排序算法
快排示例:
以一个数组作为示例,取区间第一个数为基准数。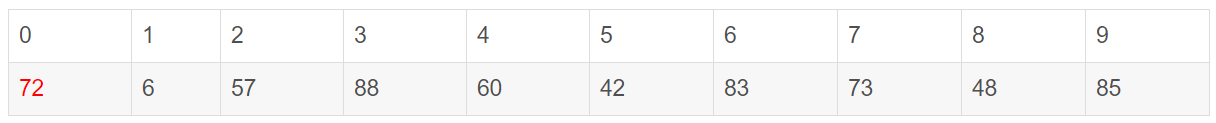
初始时,i = 0; j = 9; X = a[i] = 72;//X就是取的基准
由于已经将a[0]中的数保存到X中,可以理解成在数组a[0]上挖了个坑,可以将其它数据填充到这来。从j开始向前找一个比X小的数。当j=8,符合条件,将a[8]挖出再填到上一个坑a[0]中。a[0]=a[8]; i++; 这样一个坑a[0]就被搞定了,但又形成了一个新坑a[8],这怎么办?简单,再找数字来填a[8]这个坑。这次从i开始向后找一个大于X的数,当i=3,符合条件,将a[3]挖出再填到上一个坑中a[8]=a[3]; j—;
数组变为: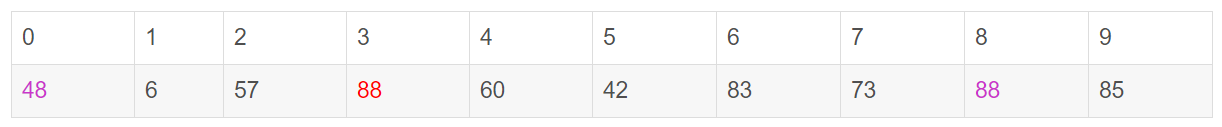 i = 3; j = 7; X=72
i = 3; j = 7; X=72
再重复上面的步骤,先从后向前找,再从前向后找。
从j开始向前找,当j=5,符合条件,将a[5]挖出填到上一个坑中,a[3] = a[5]; i++;
从i开始向后找,当i=5时,由于i==j退出。
此时,i = j = 5,而a[5]刚好又是上次挖的坑,因此将X填入a[5]。
数组变为: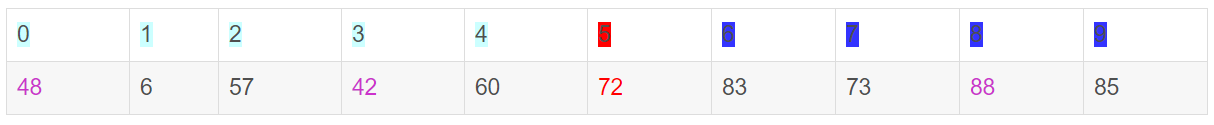
可以看出a[5]前面的数字都小于它,a[5]后面的数字都大于它。因此再对a[0…4]和a[6…9]这二个子区间重复上述步骤就可以了。
对挖坑填数进行总结
1.i =L; j = R; 将基准数挖出形成第一个坑a[i]。
2.j—由后向前找比它小的数,找到后挖出此数填前一个坑a[i]中。
3.i++由前向后找比它大的数,找到后也挖出此数填到前一个坑a[j]中。
4.再重复执行2,3二步,直到i==j,将基准数填入a[i]中。
照着这个总结很容易实现挖坑填数的代码:
public int AdjustArray(int s[], int l, int r){ //返回调整后基准数的位置int i = l, j = r;int x = s[i]; //s[l]即s[i]就是第一个坑while (i < j){while(i < j && s[j] >= x) // 从右向左找小于x的数来填s[i]j--;if(i < j){s[i] = s[j]; //将s[j]填到s[i]中,s[j]就形成了一个新的坑i++;}while(i < j && s[i] < x)// 从左向右找大于或等于x的数来填s[j]i++;if(i < j){s[j] = s[i]; //将s[i]填到s[j]中,s[i]就形成了一个新的坑j--;}}//退出时,i等于j。将x填到这个坑中。s[i] = x;return i;}
再写分治法的代码:
void quick_sort(int s[], int l, int r){if (l < r){//l>=r则表示细分到了1个元素int i = AdjustArray(s, l, r);//先成挖坑填数法调整s[]quick_sort(s, l, i - 1); // 递归调用quick_sort(s, i + 1, r);}}
这样的代码显然不够简洁,对其组合整理下:
//快速排序private void quickSort(int[] data,int left,int right){if(left<right){//细分为每个数组只有一个值的情况了(left==right)int i=left;int j=right;int temp=data[i];//让最左边的为第一个坑,并保留这个位置上的原来的元素while (i<j){while(i<j && data[j]>=temp) j--;//找到从右往左第一个比坑小的if(i<j) {data[i]=data[j];i++;}while(i<j && data[i]<=temp) i++;//找到从左往右第一个比坑大的if(i<j){data[j]=data[i];j--;}}//跳出时为i==j,则把temp放进这个坑里(一个while只是一趟的把一个数组划分为两个分别大和小的数组)data[i]=temp;quickSort(data, left, i-1);quickSort(data, i+1, right);}}
快速排序还有很多改进版本,如随机选择基准数,区间内数据较少时直接用另的方法排序以减小递归深度。
注1,有的书上是以中间的数作为基准数的,要实现这个方便非常方便,直接将中间的数和第一个数进行交换就可以了。
2.归并排序
基本思想:
归并示例:
递归分解+合并数列=归并排序
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。
首先考虑下如何将将二个有序数列合并。这个非常简单,只要从比较二个数列的第一个数,谁小就先取谁,取了后就在对应数列中删除这个数。然后再进行比较,如果有数列为空,那直接将另一个数列的数据依次取出即可。以下为合并两个有序数列:
//将有序数组a[]和b[]合并到c[]中void MemeryArray(int a[], int n, int b[], int m, int c[]){int i, j, k;i = j = k = 0;while (i < n && j < m){if (a[i] < b[j])c[k++] = a[i++];//要么同时移动c和aelsec[k++] = b[j++]; //要么同时移动c和b}while (i < n)c[k++] = a[i++];//将剩余的部分直接接到合并数组中while (j < m)c[k++] = b[j++];}
可以看出合并有序数列的效率是比较高的,可以达到O(n)。
解决了上面的合并有序数列问题,再来看归并排序,其的基本思路就是将数组分成二组A,B,如果这二组组内的数据都是有序的,那么就可以很方便的将这二组数据进行排序。如何让这二组组内数据有序了?
可以将A,B组各自再分成二组。依次类推,当分出来的小组只有一个数据时,可以认为这个小组组内已经达到了有序,然后再合并相邻的二个小组就可以了。这样通过先递归的分解数列,再合并数列就完成了归并排序。
public static void main (String[] args){int a[]={1,5,9,8,9,4,2,34,2,3,56,723,0,34};//测试数据int[] temp = new int[a.length];mergesort(a, 0, a.length-1, temp);for(int num :a )System.out.print(num + " ");}//将有二个有序数列a[first...mid]和a[mid+1...last]合并void mergearray(int a[], int first, int mid, int last, int temp[]){int i = first, j = mid + 1;//两个数列的首指针下标int m = mid,n = last;s//两个数列的尾指针下标int k = 0;//合并后的数列的首指针下标while (i <= m && j <= n){if (a[i] <= a[j])temp[k++] = a[i++];elsetemp[k++] = a[j++];}while (i <= m)temp[k++] = a[i++];while (j <= n)temp[k++] = a[j++];for (i = 0; i < k; i++)a[first + i] = temp[i];//将排好序的数列替换掉原始数组的内容}//递归和合并数列void mergesort(int a[], int first, int last, int temp[]){if (first < last){//递归的终止条件:就是分出来的小组只有一个数据就停止int mid = (first + last) / 2;mergesort(a, first, mid, temp); //不断递归左边,最终得到左边有序mergesort(a, mid + 1, last, temp); //不断递归左边,最终得到右边有序if(a[mid]<a[mid+1]) return;//如果已经是有序,则不需要继续合并mergearray(a, first, mid, last, temp); //最后再将二个有序数列合并}//然后继续向上合并}
归并排序的效率是比较高的,设数列长为N,将数列分开成小数列一共要logN步,每步都是一个合并有序数列的过程,时间复杂度可以记为O(N),故一共为O(NlogN)。因为归并排序每次都是在相邻的数据中进行操作,所以归并排序在O(NlogN)的几种排序方法(快速排序,归并排序,希尔排序,堆排序)也是效率比较高的。
注:有的书上是在mergearray()合并有序数列时分配临时数组,但是过多的new操作会非常费时。因此作了下小小的变化。只在MergeSort()中new一个临时数组。后面的操作都共用这一个临时数组。
二、查找算法
1.二分查找
1.1经典二分问题
基本思想:
二分查找是一种基于比较目标值和数组中间元素的教科书式算法。针对元素有序的(升序)整型数组
- 如果目标值等于中间元素,则找到目标值。
- 如果目标值较小,证明目标值小于中间元素及右边的元素,继续在左侧搜索。
如果目标值较大,证明目标值大于中间元素及左边的元素,继续在右侧搜索。
算法代码描述:
初始化指针 left = 0, right = n - 1。
当 left <= right:比较中间元素 nums[pivot] 和目标值 target 。如果 target = nums[pivot],返回 pivot。
- 如果 target < nums[pivot],则在左侧继续搜索 right = pivot - 1。
如果 target > nums[pivot],则在右侧继续搜索 left = pivot + 1。
经典二分问题:
给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target 。写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。【存在就返回存在的那个下标】
java代码实现:
class Solution {public int search(int[] nums, int target) {int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;//分别准备好左右端点while (left <= right) {//循环二分int pivot = left + (right - left) / 2;//取中点if (nums[pivot] == target) return pivot;//找到答案并返回if (target < nums[pivot]) right = pivot - 1;//向左继续找else left = pivot + 1;//向右继续找}return -1;//未找到,返回-1}}
1.2 基础二分小变形1
将目标数插入到第一个比目标值大的数左边
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
思路:我们注意,这一题和上一题的区别在于,这一题并不存在‘没找到’这种情况,因为要插入到”第一个比目标值大的数“的左边,返回这样一个插入位置,你不可能”找不到“,不可返回-1。
事实上,我们的目标也再不是找到一个相同的数字,而是找到第一个比目标值大的数,也就是插入位置。
代码的内部逻辑是”一路找到最后,返回的一定是答案“,而上段代码的逻辑是”边找边判断,找到最后还没有找到,就返回-1“。代码实现
public class Solution {public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {int left = 0;while (left <= right) {int mid = (left + right) / 2;if (nums[mid] < target) {//此处注意不需要等号,加等号是加在最右边,不加等号是加在最左边left = mid + 1;} else {right = mid - 1;}}return left;}}
提醒:所以,如果你是一个想注重细节,做到写二分代码不出错,那么你就需要关心最后返回值,while结束条件,while内部是否加判断等等这些细节了。
1.3基础二分小变形2
查找某个目标值的边界
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(logn) 级别。
如果数组中不存在目标值,返回 [-1, -1]。示例 1:输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8输出: [3,4]
- 示例 2:输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6输出: [-1,-1]
思路:两个二分,稍微改一下,就可以找到第一个target或最后一个target;
- 本元素和前面一个元素不相等,才代表找到了最左边的目标元素。
-
代码实现
class Solution {public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {int[] ans=new int[2];ans[0]=searchRangeLeft(nums,target);ans[1]=searchRangeRight(nums,target);return ans;}public int searchRangeLeft(int[] nums, int target) {int left=0;int right=nums.length-1;while(left<=right){int mid=(left+right)/2;if(nums[mid]>target){//小于中间值,往左边查找right=mid-1;}else if(nums[mid]<target){//大于中间值,往右边查找left=mid+1;}else if(mid==0 || nums[mid-1]!=target){//mid==0是为了防止mid-1越界,同时也是右边界//中间值等于目标值,前一个值不等于目标值,查找到了最左边 或者 已经查找到最左边return mid;}else{right=mid-1;//中间值等于目标值,前一个值还等于目标值,继续向左缩小目标范围}}return -1;}public int searchRangeRight(int[] nums, int target) {int left=0;int right=nums.length-1;while(left<=right){int mid=(left+right)/2;if(nums[mid]>target){right=mid-1;}else if(nums[mid]<target){left=mid+1;}else if(mid==nums.length-1 || nums[mid+1]!=target){//mid==len-1是为了防止mid+1越界,同时也是左边界return mid;}else{left=mid+1;}}return -1;}}
1.4泛化二分的概念
与有序无序无关
简单来说,我百度百科对二分的定义就是在顺序存储结构(数组)有序的情况下进行二分查找。
从第四节开始,我们介绍的就不是传统意义上的二分查找了,不局限于”有序“,甚至不局限于线性结构,while循环里判断向左还是向右搜索的条件也不会这么单一,而更可能是这样:
while (范围没有缩小为0) {
if (满足某种条件) {
排除一半答案
} else {
排除另一半答案
}
}
我们的思想是:只要可以通过正确逻辑,用二分思想正确的缩小查找范围,都称之为二分。
下面就来体会一下什么是二分思想:
我们正在玩一个猜数字游戏。 游戏规则如下:我从 1 到 n 选择一个数字。 你需要猜我选择了哪个数字。每次你猜错了,我会告诉你这个数字是大了还是小了。
你调用一个预先定义好的接口 guess(int num),它会返回 3 个可能的结果(-1,1 或 0):
-1 : 我的数字比较小
1 : 我的数字比较大
0 : 恭喜!你猜对了!
示例 :
输入: n = 10, pick = 6输出: 6代码实现
public class Solution extends GuessGame {public int guessNumber(int n) {int low = 1;int high = n;while (low <= high) {int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;int res = guess(mid);if (res == 0)return mid;else if (res < 0)high = mid - 1;elselow = mid + 1;}return -1;}}
这就是把条件抽象成一个接口,完全脱离了线性数据结构,更和有序无序没关系,只是二分的思想。
1.5在线性结构上二分的题目积累
例1:找峰值元素
峰值元素是指其值大于左右相邻值的元素。给定一个输入数组 nums,其中 nums[i] ≠ nums[i+1],找到峰值元素并返回其索引。数组可能包含多个峰值,在这种情况下,返回任何一个峰值所在位置即可。
示例 1:输入: nums = [1,2,3,1]输出: 2
解释: 3 是峰值元素,你的函数应该返回其索引 2。
示例 2:输入: nums = [1,2,1,3,5,6,4]输出: 1 或 5
解释: 你的函数可以返回索引 1,其峰值元素为 2;或者返回索引 5, 其峰值元素为 6。
说明:你的解法应该是 O(logN) 时间复杂度的。
思路:可以用二分的要求:线性表能够根据中间元素的特点推测它两侧元素的性质,以达到缩减问题规模的效果即可,不一定非要有序。具体到本题来说,我们如何做到搜索到任何一个“峰值”呢?请看图: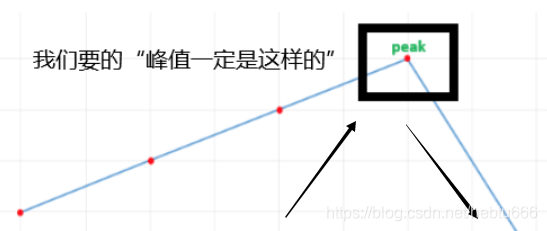
要先有上升的趋势,后有下降的趋势。更通俗一点就是说,要保证前一个数字比峰值小,后一个数字比峰值大,我们只要每次搜索都满足这个条件,搜到最后就一定可以找到某个峰值,因为从递增到递减,肯定是因为中间有峰值的存在所导致的。
我们看中点,如果中点向右有递增趋势,我们就继续搜索右边:
反之,有向左递增的趋势,我们就搜左边:
实现代码public class Solution {public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {int l = 0, r = nums.length - 1;while (l < r) {int mid = (l + r) / 2;if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1])r = mid;elsel = mid + 1;}return l;//最后缩小到l==r时,就找到了峰值}}
我们发现,这个题目的代码逻辑就是第二节的”一路找到最后,返回的一定是答案“,不同于最基础的二分”边找边判断,找到最后还没有找到,就返回-1“。我们是缩小范围到最后,找到了答案l。
例2:找原有序旋转数组的旋转后最小元素
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。请找出其中最小的元素。你可以假设数组中不存在重复元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,4,5,1,2]输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]输出: 0
分析:
如果数组没有翻转,即 nums[left] <= nums[right],则 nums[left] 就是最小值,直接返回。
如果数组翻转,需要找到数组中第二部分的第一个元素: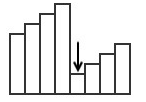 。
。
下面讨论数组翻转的情况下,如何收缩区间以找到这个元素:
若 nums[left] <= nums[mid],说明区间 [left,mid] 连续递增,则最小元素一定不在这个区间里,可以直接排除。因此,令 left = mid+1,在 [mid+1,right] 继续查找。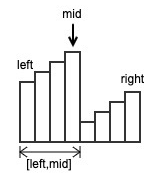
否则,说明区间 [left,mid] 不连续,则最小元素一定在这个区间里。因此,令 right = mid,在 [left,mid] 继续查找[left,right] 表示当前搜索的区间。
注意 right 更新时会被设为 mid 而不是 mid-1,因为 mid 无法被排除。
代码实现class Solution {public int findMin(int[] nums) {if(nums.length==1) return nums[0];if(nums[0]<nums[nums.length-1]) return nums[0];int left=0;int right=nums.length-1;int mid=0;while(left<right){mid=(left+right)/2;if(nums[mid]>=nums[0]){left=mid+1;}else{right=mid;}}return nums[right];//最后缩小到了left==right,就找到了最小值}}
例3:找原有序旋转数组是否存在某个目标值,并返回其索引
其它条件和例2一样,例3要搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
思路:先通过例2的方法找到分割点,再对左右某一边进行二分即可。
解答:可以发现的是,我们将数组从中间分开成左右两部分的时候,一定有一部分的数组是有序的。拿示例[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]来看,我们从 6 这个位置分开以后数组变成了 [4, 5, 6] 和 [7, 0, 1, 2] 两个部分,其中左边 [4, 5, 6] 这个部分的数组是有序的,其他也是如此。这启示我们可以在常规二分查找的时候查看当前 mid 为分割位置分割出来的两个部分 [l, mid] 和 [mid + 1, r] 哪个部分是有序的,并根据有序的那个部分确定我们该如何改变二分查找的上下界,因为我们能够根据有序的那部分判断出 target 在不在这个部分: 如果 [l, mid] 是有序数组,且 target 的大小满足 [nums[l],nums[mid-1]],则我们应该将搜索范围缩小至 [l, mid - 1],否则在 [mid + 1, r] 中寻找。
- 如果 [mid, r] 是有序数组,且 target 的大小满足 [nums[mid+1],nums[r]],则我们应该将搜索范围缩小至 [mid + 1, r],否则在 [l, mid - 1] 中寻找。
代码实现
public static int search(int[] nums, int target) {int n = nums.length;if (n == 0) {return -1;}if (n == 1) {return nums[0] == target ? 0 : -1;}int l = 0, r = n - 1;while (l <= r) {int mid = (l + r) / 2;if (nums[mid] == target) {//相等的时候返回return mid;}if (nums[0] <= nums[mid]) {//if (nums[0] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {//r = mid - 1;} else {l = mid + 1;}} else {//if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[n - 1]) {//l = mid + 1;} else {r = mid - 1;}}}return -1;}
1.6二维数组的二分查找
判断 m x n 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值
编写一个高效的算法来判断 m x n 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值。该矩阵具有如下特性:
每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。
每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
示例 1:
matrix = [
[1, 3, 5, 7],
[10, 11, 16, 20],
[23, 30, 34, 50]
]
target = 3
输出: true
示例 2:
matrix = [
[1, 3, 5, 7],
[10, 11, 16, 20],
[23, 30, 34, 50]
]
target = 13
输出: false
仔细观察我们发现,其实这个二维数组整体就是有序的,所以当成一维数组二分查找即可,但是要注意二维数组的操作,需要一点功底。
代码实现
class Solution {public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {return false;}int row = matrix.length;int col = matrix[0].length;int start = 0;int end = row * col - 1;while (start <= end) {int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;//正规的二分写法,避免溢出if (matrix[mid / col][mid % col] == target)return true;else if (matrix[mid / col][mid % col] > target)end = mid - 1;elsestart = mid + 1;}return false;}}
1.7二叉树上二分的题目积累
我们刚才学会了一些一维二维数组的二分操作,下面我们再去其它数据结构试试看,继续养成二分的思想。
例1:先看一道简单的在二叉树上查找值。
给定一个不为空的二叉搜索树和一个目标值 target,请在该二叉搜索树中找到最接近目标值 target 的数值。
注意:给定的目标值 target 是一个浮点数,题目保证在该二叉搜索树中只会存在一个最接近目标值的数。
示例:
输入: root = [4,2,5,1,3],目标值 target = 3.714286
4
/ \
2 5
/ \
1 3
输出: 4
思路:二分,当前节点比target大就往左边搜(因为右边的差距更大),当前节点比target小就往右搜(因为左边的差距更大)。
补充:二叉查找树它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
代码实现
public class MyTest {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeNode node1=new TreeNode(4);TreeNode node2=new TreeNode(2);node1.left=node2;node1.right=new TreeNode(5);node2.left=new TreeNode(1);node2.right=new TreeNode(3);int closest=closestSearch(node1,2.714286);System.out.println(closest);}private static int closestSearch(TreeNode root,double target){int val=root.val;int closest=root.val;//closest最近的while(root!=null){val=root.val;closest=Math.abs(val-target)<Math.abs(closest-target)?val:closest;//上次的差值和这次的比较root=root.val>target?root.left:root.right;}return closest;}}class TreeNode {int val;TreeNode left;TreeNode right;TreeNode(int x){val = x;}}
例2:给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ /
4 5 6
输出: 6
思路:如果不考虑最后一层,节点数完全可以算出来,每一层分别为1,2,4,8….你会发现是2的n次方,那么总和也很好求,所以问题就在于如何知道最后一层有多少节点,换句话说,最后一层的最右边的那个节点在哪里?我们需要二分搜索。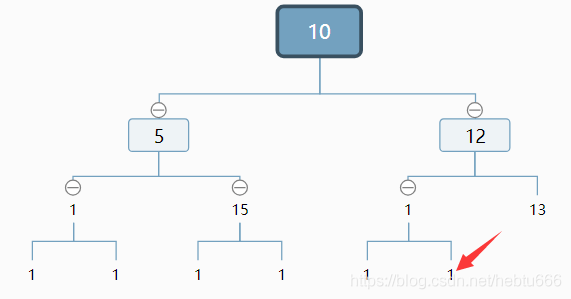
目标:找箭头指向的结点。
我们采用二分法:
1)找到右子树的最左结点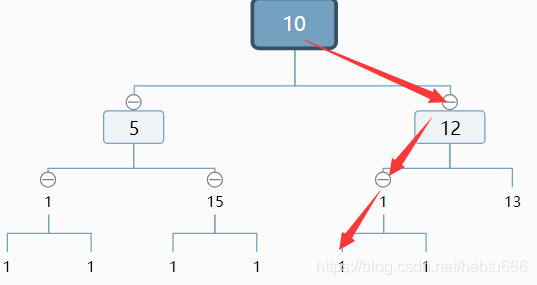
我们知道总深度为4,如果右子树深度为3,说明 图中最后的1是存在的(说明最后一行最右结点一定来自右子树),否则,如果我们修改一下如下图:
图中最后的1是存在的(说明最后一行最右结点一定来自右子树),否则,如果我们修改一下如下图: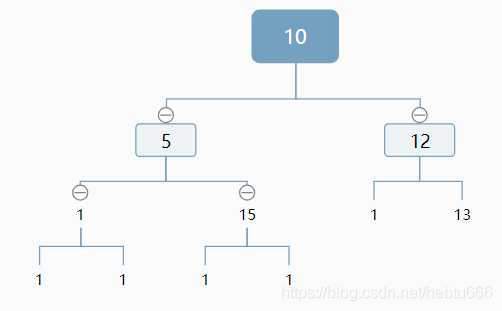
右子树深度为2!=4-1,不存在最后一行的结点。(说明最后一行最右结点一定来自左子树).
2)判断之后,如果是这种情况,我们排除了左子树,计算排除的结点个数,并对右子树(如图2)做相同的处理。 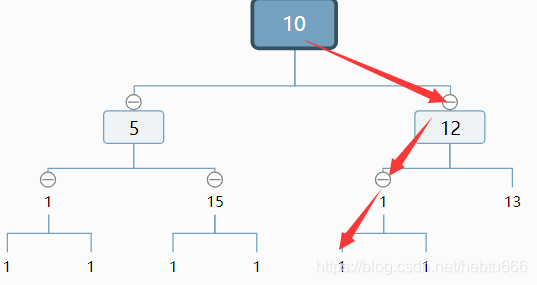
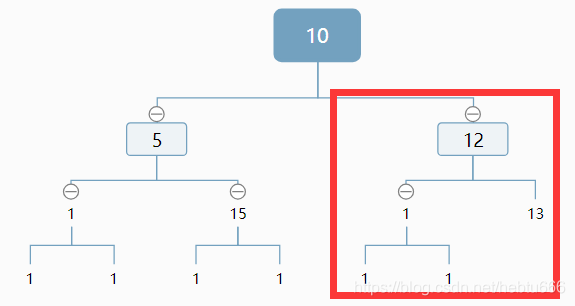
更新结点数(未被框起的部分,满二叉树公式+1)+1是根结点
3)对方框内重复此过程。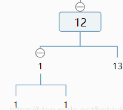
我们继续看右子树,发现右子树深度为1!=3-1.
说明最深层最右结点来自于左子树。所以对左子树重复上述过程
我们发现,右子树深度=1=2(整棵树深度)-1,说明最深层最右结点来自于右子树,所以对右子树重复此过程。 最终找到它。
最终找到它。
代码实现
public class TestStaticClass {public static class Node {public int value;public Node left;public Node right;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}//返回结点个数public static int nodeNum(Node head) {if (head == null) {return 0;}return bs(head, 1, mostLeftLevel(head, 1));}//返回根为node,当前层数为l,总深度为h的结点个数public static int bs(Node node, int l, int h) {if (l == h) {return 1;//到达最后一层}if (mostLeftLevel(node.right, l + 1) == h) { //右子树最深一行最左不为空return (1 << (h - l)) + bs(node.right, l + 1, h); //右bs+左子树结点个数} else { //右子树最深一行最左为空return (1 << (h - l - 1)) + bs(node.left, l + 1, h);//左bs+右子树结点个数}}//计算树的高度public static int mostLeftLevel(Node node, int level) {while (node != null) {level++;node = node.left;}return level - 1;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(1);head.left = new Node(2);head.right = new Node(3);head.left.left = new Node(4);head.left.right = new Node(5);head.right.left = new Node(6);System.out.println(nodeNum(head));}}
补充:
1.满二叉树公式为 (2^k) -1 【k是树的层数】
2.关于使用static关键字修饰类:
java里面static一般用来修饰成员变量或函数。但有一种特殊用法是用static修饰内部类,普通类是不允许声明为静态的,只有内部类才可以。被static修饰的内部类可以直接作为一个普通类来使用,而不需实例一个外部类(见如下代码):需要注意的是当一个内部类没有使用static修饰的时候,是不能直接使用内部类创建对象,须要先使用外部类对象点new内部类对象及(外部类对象.new 内部类())
1、被static修饰的内部类可以直接作为一个普通类来使用,而不需实例一个外部类class OuterClass {public static class InnerClass{public InnerClass(){System.out.println("============= 我是一个内部类'InnerClass' =============");}public void test(){}}}public class TestStaticClass {public static void main(String[] args) {new OuterClass.InnerClass();// 不需要new一个InnerClasnew OuterClass.InnerClass().test();}}2、如果没有用static修饰InterClass,则只能按如下方式调用:需要先new 一个外部类实例OuterClass oc = new OuterClass(); 在使用外部类实例点内部类实例oc.new InnerClass();class OuterClass {public class InnerClass{public InnerClass(){System.out.println("============= 我是一个内部类'InnerClass' =============");}public void test(){}}}public class TestStaticClass {public static void main(String[] args) {new OuterClass().new InnerClass();// OutClass需要先生成一个实例,然后再new一个InnerClass();new OuterClass().new InnerClass().test();}}
1..8数学中的二分
实现 int sqrt(int x) 函数。计算并返回 x 的平方根,其中 x 是非负整数。由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留整数的部分,小数部分将被舍去。
示例 1:
输入: 4输出: 2
示例 2:
输入: 8输出: 2
说明: 8 的平方根是 2.82842…,
由于返回类型是整数,小数部分将被舍去。
思路依旧是二分,格式和上文都一样。
代码实现
public class MyTest {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = mySqrt(8);System.out.println(i);}public static int mySqrt(int x) {long left = 0;long right = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// MAX_VALUE=0x7fffffff;while (left < right) {// >>>表示无符号右移,也叫逻辑右移,即若该数为正,则高位补0,而若该数为负数,则右移后高位仍补0long mid = (left + right + 1) >>> 1;long square = mid * mid;if (square > x) {right = mid - 1;} else {left = mid;}}return (int) left;//left==right时跳出循环}}
1.9最大化或最小化问题
如果在求解最大最小问题中,能比较简单的判断某个解是否满足条件(这里的简单一般指的是o(n)及以下,视具体数据范围而定),使用二分搜索答案就能很好的解决问题。
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1064
题目大意:有n条绳子,长度分别为L[i]。如果从他们中切割出k条长度相同的绳子的话,这k条绳子每条最长能有多长?(答案保留小数点后两位,规定1单位长度的绳子最多可以切割成100份)。
思路:二分搜索答案,每条最短0,最大设置一个较大的数,然后开始二分答案并依次判断,判断也很简单,判断每个绳子的长度整除答案的累加和是不是大于k就好了。
代码实现
补充:有n个牛栏,选m个放进牛,相当于一条线段上有 n 个点,选取 m 个点,使得相邻点之间的最小距离值最大
思路:和上一道题类似,二分答案,判断答案也很简单,贪心即可,遍历,遇到大于枚举的距离就放一只牛,看最后能不能放得下。
代码实现
三、回溯、贪心和动态规划
回溯、贪心和动态规划三类算法思想是层层递进,环环相扣的,如果想学习好的话,就应该放在一起系统的学习,否则,你很难学会他们
如果你能系统的完成下面的 36 道算法面试题的话,那么对于回溯、贪心和动态规划的问题,就会很容易的解答了:
回溯算法思想
- leetcode 112 号算法题:路径总和
- leetcode 113 号算法题:路径总和 II
- leetcode 46 号算法题:全排列
- leetcode 47 号算法题:全排列 II
- leetcode 77 号算法题:组合
- leetcode 39 号算法题:组合总和
- leetcode 40 号算法题:组合总和 Ⅱ
- leetcode 216 号算法题:组合总和 Ⅲ
- leetcode 78 号算法题:子集
- leetcode 90 号算法题:子集Ⅱ
- leetcode 17 号算法题:电话号码的字母组合
- leetcode 93 号算法题:复原 IP 地址
- leetcode 22 号算法题:括号生成
- leetcode 51 号算法题:N 皇后
- leetcode 37 号算法题:数独问题
贪心算法思想
- leetcode 455 号算法题:分发饼干
- leetcode 322 号算法题:零钱兑换
- leetcode 45 号算法题:跳跃游戏 Ⅱ
- leetcode 1578 号算法题:避免重复字母的最小删除成本
- leetcode 402 号算法题:移掉K位数字
动态规划算法思想
- leetcode 509 号算法题:斐波那契数
- leetcode 322 号算法题:零钱兑换
- leetcode 64 号算法题:最小路径和
- leetcode 53 号算法题:最大子数组之和
- leetcode 647 号算法题:回文子串
- leetcode 5 号算法题:最长回文串
- leetcode 131 号算法题:分割回文串
- leetcode 516 号算法题:最长回文子序列
- leetcode 300 号算法题:最长上升子序列
- leetcode 1143 号算法题:最长公共子序列
- leetcode 72 号算法题:编辑距离
- leetcode 44 号算法题:通配符匹配
- leetcode 10 号算法题:正则表达式匹配
- leetcode 486 号算法题:预测赢家
- leetcode 877 号算法题:石子游戏
- 0-1 背包问题
你可以按照上面的顺序来刷这些题目,注意,一定要按照 回溯,然后 贪心,最后才 动态规划 的顺序来刷题,我相信你能系统的学会回溯、贪心和动态规划
题解
回溯算法思想
leetcode 112 号算法题:路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum ,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1: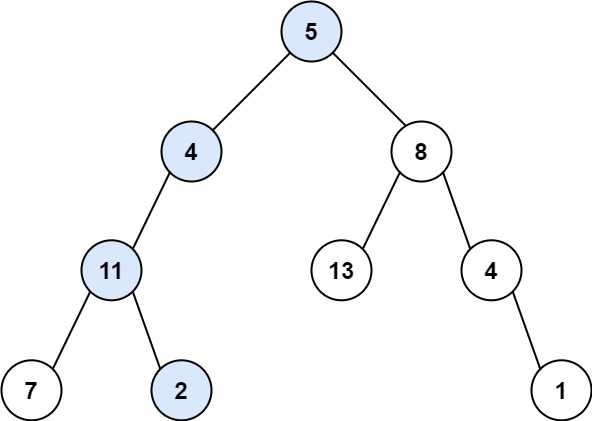
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
//深度优先搜索class Solution {//只有深度遍历的每一层都返回true才会最终返回true(从最深处逐级往上)public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if(root==null)//如果这个成立,说明是像题干中的4的左节点一样的节点,4并不是叶子节点,防止没到叶子节点但累计和到了目标和的情况return false;if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)//只有是叶子节点return targetSum==root.val;return hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val)||hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum-root.val);}}或class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {return dfs(root, targetSum, 0);}private boolean dfs(TreeNode node,int targetSum,int nodeValSum){if(node==null)return false;if(node.left==null&&node.right==null)return (nodeValSum+node.val)==targetSum;return dfs(node.left,targetSum,nodeValSum+node.val)||dfs(node.right,targetSum,nodeValSum+node.val);}}或//广度优先搜索class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if(root==null) return false;LinkedList<TreeNode> nodeQue=new LinkedList<>();LinkedList<Integer> valQue=new LinkedList<>();nodeQue.addLast(root);valQue.addLast(root.val);while (!nodeQue.isEmpty()){TreeNode node=nodeQue.pollFirst();Integer value = valQue.pollFirst();if(node.left==null&&node.right==null){//才是叶子节点if(value==targetSum)return true;continue;//当前节点都到叶子节点了,就不往下走了,而是继续下一个节点的判断}if(node.left!=null){nodeQue.addLast(node.left);valQue.addLast(node.left.val+value);}if(node.right!=null){nodeQue.addLast(node.right);valQue.addLast(node.right.val+value);}}return false;}}
leetcode 113 号算法题:路径总和 II
//深度优先class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root,int targetSum) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();if(root==null) return res;LinkedList<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();dfs(root, targetSum,res, path);return res;}private void dfs(TreeNode node,int targetSum,List<List<Integer>> res, LinkedList<Integer> path){if(node==null) return;path.addLast(node.val);if(node.left==null&&node.right==null&&targetSum==node.val)res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));dfs(node.left,targetSum-node.val,res,path);dfs(node.right,targetSum-node.val,res,path);path.removeLast();}}或//广度优先public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return list;List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();int pathSum = 0;TreeNode lastVisited = null;TreeNode curr = root;while (curr != null || !s.isEmpty()){//把每个节点都当做根节点处理,并且把这个根节点的所有子节点都加入到栈中//所有节点入栈都从这里添加,一条路径所有节点的累加和都在这里进行while (curr != null){// 1. 遍历搜索左边的节点,一直到叶子节点s.push(curr);// 将节点压入栈中path.add(curr.val);// 将当前的节点加入当前的路径中pathSum += curr.val;// 累计计算当前 path 的总和curr = curr.left;}// 2. 访问左节点的右子树:先拿到左节点,这里使用 peek() 的原因:如果这个左节点有右子树的话,我们就不用再一次 push 到栈中curr = s.peek();if (curr.right != null && curr.right != lastVisited){// 条件:有右子树,并且右子树还没有访问过curr = curr.right;// 访问右子树continue; // 跳出外面的循环,来处理当前左节点的右子树//这里是为了把所有节点都当做根节点处理,即把当前节点放到while (curr!=null){这个循环中去处理}//能走到这里的路径一定是一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,从这以下的代码都是对叶子节点的操作// 3. 检查是否符合路径和的条件:节点的左右子节点都为 null,并且路径总和等于目标值 sumif (curr.left == null && curr.right == null && pathSum == sum){// 当前路径符合条件,加入到返回结果中list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));}s.pop();// 出栈当前的节点,因为已经处理完了lastVisited = curr; // 标记当前节点已经被访问,免得在这里被重复访问if (curr.right != nullpathSum -= curr.val; // 当前路径总和减去当前的节点值path.remove(path.size() - 1);// 当前路径中删除掉最后一个节点(也就是当前节点)curr = null; // 将当前的节点设置为 null,这是为了下次循环的时候从栈中拿到节点来进行处理,也是防止再次进去 while (curr != null){这个循环中}return list;}
leetcode 46 号算法题:全排列
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
题解: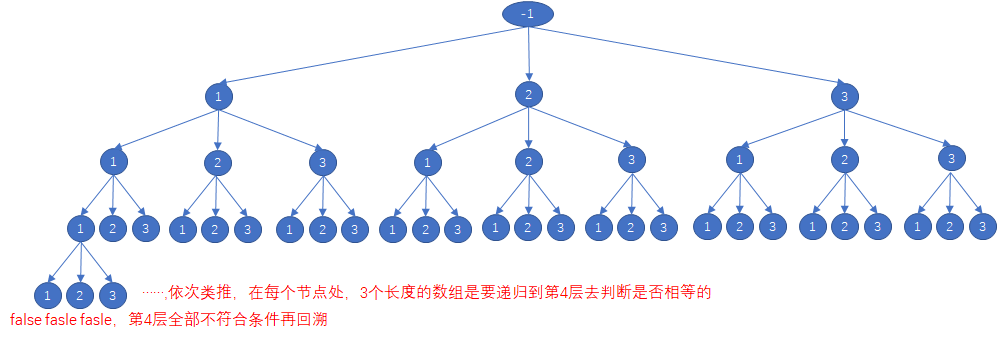
//过程1:可以选取重复数字的排列public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums, -1, path, res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int index,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {return;}if (index != -1) path.add(nums[index]);if (path.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){dfs(nums, i, path, res);}if (index != -1) path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯的过程中,将当前的节点从 path 中删除}//过程2:合并回溯条件和添加排列(但是每种排列都被重复添加了多次)public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums, -1, path, res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int index,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}if (index != -1) path.add(nums[index]);for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){dfs(nums, i, path, res);}if (index != -1) path.remove(path.size() - 1);// 回溯的过程中,将当前的节点从 path 中删除}//过程3:去除过程2中的重复,回到过程1中的可以选取重复数字的排列,总结出回溯算法框架代码public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums, -1, path, res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int index,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){path.add(nums[i]);//添加当前节点dfs(nums, i, path, res);path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯的过程中,将当前的节点从 path 中删除}}过程4:找到全排列组合(利用contains方法来进行判断,其中,index也是不需要的方法参数,可以去掉)public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums, path, res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){//这个循环时间复杂度为O(N^2),for循环O(n),contains()方法O(n)if(path.contains(nums[i])) continue;path.add(nums[i]);//添加当前节点dfs(nums, path, res);path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯的过程中,将当前的节点从 path 中删除}}//过程5:从过程4的时间复杂度O(N!*N^2)优化到了O(N!*N)public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();boolean[] used=new boolean[nums.length];dfs(nums, path, res,used);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res,boolean[] used) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){//这个循环时间复杂度为O(N),for循环O(n),判断为O(1)if(used[i]) continue;path.add(nums[i]);//添加当前节点used[i]=true;dfs(nums, path, res,used);path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯的过程中,将当前的节点从 path 中删除used[i]=false;}}
leetcode 47 号算法题:全排列 II
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
//整体思路用一句话表示,两数相同时,前面的数据没插入,后面数据也不会插入第二条由以下条件进行判断,两数相同时(nums[i] == nums[i - 1]),当前一个数没有递归时(!vis[i - 1]),则当前数据不递归(continue),这条规则保证了递归过程中,相同数据加入递归的顺序始终为坐标位置的顺序,即相同数据不排序(当然第二条的前提是数组必须排序,使相同的数据相邻)class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();boolean[] used=new boolean[nums.length];Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(res,path,nums,used);return res;}private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> path,int[] nums,boolean[] used){if(path.size()==nums.length){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){//当前元素被用过了就跳过//走到后面这个判断条件一定是used[i]==false,即当前元素没有被用过,且if(used[i] || (i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&!used[i-1]))continue;path.add(nums[i]);used[i]=true;dfs(res,path,nums,used);path.remove(path.size()-1);used[i]=false;}}}或class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();boolean[] used=new boolean[nums.length];Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(res,path,nums,used);return res;}private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> path,int[] nums,boolean[] used){if(path.size()==nums.length){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}int prev=Integer.MAX_VALUE;for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){if(used[i] || prev==nums[i])continue;path.add(nums[i]);used[i]=true;dfs(res,path,nums,used);path.remove(path.size()-1);used[i]=false;prev=nums[i];}}}
leetcode 77 号算法题:组合
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 … n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
示例:
输入: n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();dfs(n,k,path,res);return res;}private void dfs(int n,int k, List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res){if(path.size()==k){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(path.size()>0&&path.get(path.size()-1)>=i)continue;path.add(i);dfs(n, k, path, res);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}
leetcode 39 号算法题:组合总和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
题解:
在当前的函数中,每次我们可以选择跳过不用第 index 个数,即执行 dfs(target, path, index + 1)。
也可以选择使用第 index 个数,即执行 dfs(target - candidates[index ], path, index ),注意到每个数字可以被无限制重复选取,因此搜索的下标仍为 index。
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();dfs(candidates, target, res, path, 0);return res;}public void dfs(int[] candidates,int target,List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> path,int index) {if (index==candidates.length) {return;}if (target==0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}dfs(candidates,target,res,path,index+1);// 直接跳过if (target-candidates[index]>=0) {// 选择当前数path.add(candidates[index]);dfs(candidates,target-candidates[index],res,path,index);path.remove(path.size() - 1);}//此处是target <= 0时,就自然而然的结束了这个方法,所以不用加在递归条件里面}}或class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();dfs2(candidates,target,0,path,res,0);return res;}private void dfs2(int[] candidates, int target,int pathSum,List<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res,int index){if(index==candidates.length||pathSum>target)return;if(target==pathSum){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}dfs2(candidates, target, pathSum, path, res, index+1);if(pathSum<target){path.add(candidates[index]);dfs2(candidates, target, pathSum+candidates[index], path, res, index);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}
leetcode 40 号算法题:组合总和 Ⅱ
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();LinkedList<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();Arrays.sort(candidates);// 排序方便进行剪枝dfs(res,path,candidates,0,target);return res;}private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res,Deque<Integer> path,int[] candidates,int index,int target){if (target==0){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for (int i=index;i<candidates.length;i++){// 大剪枝:减去 candidates[i] 小于 0,减去后面的 candidates[i + 1]、candidates[i + 2] 肯定也小于 0,因此用 breakif (target-candidates[i]<0) break;// 小剪枝:同一层相同数值的结点,从第 2 个开始,候选数更少,结果一定发生重复,因此跳过,用 continueif (i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {continue;}path.addLast(candidates[i]);dfs(res,path,candidates,i+1,target-candidates[i]);path.removeLast();}}或class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();LinkedList<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();Arrays.sort(candidates);// 排序方便进行剪枝dfs(res,path,candidates,0,target);return res;}private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res,Deque<Integer> path,int[] nums,int index,int target){if (index>nums.length) return;if (target==0){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}List<Integer> pre=new ArrayList<>(nums.length);for (int i=index;i<nums.length;i++){// 此处遍历决定的是每一个位置的数字的值if (pre.contains(nums[i])) continue;if (target-nums[i]<0) break; // 剪枝pre.add(nums[i]);path.addLast(nums[i]);dfs(res,path,nums,i+1,target-nums[i]);path.removeLast();}}}
leetcode 216 号算法题:组合总和 Ⅲ
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
说明:
所有数字都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]
示例 2:
输入: k = 3, n = 9
输出: [[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();dfs(n,k,path,res);return res;}private void dfs(int n, int k, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if(path.size()>k||n<0){return;}if(path.size()==k&&n==0){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=1;i<=9;i++){if(path.size()>0&&path.get(path.size()-1)>=i)continue;path.add(i);dfs(n-i, k, path, res);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}
leetcode 78 号算法题:子集
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(nums,0,path,res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int index, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if(index==nums.length){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}dfs(nums, index+1, path, res);path.add(nums[index]);dfs(nums, index+1, path, res);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}或class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(nums,0,path,res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int index,List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if(path.size()<=nums.length){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){if(path.size()>0&&path.get(path.size()-1)>=nums[i]) continue;path.add(nums[i]);dfs(nums, index+1,path, res);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}或class Solution {List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) {path.clear();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {//这里n是固定的if ((mask & (1 << i)) != 0) {path.add(nums[i]);}}res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}return res;}}
leetcode 90 号算法题:子集Ⅱ
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中可能包含重复元素,请你返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。返回的解集中,子集可以按 任意顺序 排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,2]
输出:[[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(nums,0,path,res);return res;}private void dfs(int[] nums, int index,List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if(path.size()<=nums.length){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}List<Integer> pre=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=index;i<nums.length;i++){if((path.size()>0&&path.get(path.size()-1)>nums[i])||pre.contains(nums[i])) continue;pre.add(nums[i]);path.add(nums[i]);dfs(nums, i+1, path, res);path.remove(path.size()-1);}}}
leetcode 17 号算法题:电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例 1:
输入:digits = “23”
输出:[“ad”,”ae”,”af”,”bd”,”be”,”bf”,”cd”,”ce”,”cf”]
class Solution {public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {List<String> res=new ArrayList<>();if(digits==null||digits.length()==0)return res;HashMap<Character,String> map=new HashMap<>();map.put('2', "abc");map.put('3', "def");map.put('4', "ghi");map.put('5', "jkl");map.put('6', "mno");map.put('7', "pqrs");map.put('8', "tuv");map.put('9', "wxyz");dfs(digits,0,map,new StringBuilder(),res);return res;}private void dfs(String digits,int index,HashMap<Character,String> map,StringBuilder builder,List<String> res) {if(builder.length()==digits.length()){res.add(builder.toString());}else {char ch = digits.charAt(index);String str = map.get(ch);int len=str.length();for(int i=0; i<len;i++){builder.append(str.charAt(i));dfs(digits, index+1, map, builder, res);builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length()-1);}}}}或class Solution {public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {List<String> res=new ArrayList<>();if(digits==null||digits.length()==0)return res;HashMap<Character,String> map=new HashMap<>();map.put('2', "abc");map.put('3', "def");map.put('4', "ghi");map.put('5', "jkl");map.put('6', "mno");map.put('7', "pqrs");map.put('8', "tuv");map.put('9', "wxyz");dfs(digits,0,map,"",res);return res;}private void dfs(String digits, int index, HashMap<Character,String> map, String str, List<String> res) {if(str.length()==digits.length()){res.add(str);}else {char ch = digits.charAt(index);String temp = map.get(ch);for(char strToCh:temp.toCharArray()){dfs(digits, index+1, map, str+strToCh, res);}}}}
leetcode 93 号算法题:复原 IP 地址
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能从 s 获得的 有效 IP 地址 。你可以按任何顺序返回答案。有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 ‘.’ 分隔。
例如:”0.1.2.201” 和 “192.168.1.1” 是 有效 IP 地址,但是 “0.011.255.245”、”192.168.1.312” 和 “192.168@1.1” 是 无效 IP 地址。
示例 1:
输入:s = “25525511135”
输出:[“255.255.11.135”,”255.255.111.35”]
class Solution {public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();int len=s.length();//要分割的字符串长度if (len<4||len>12) { //如果长度不够或者过大,则不搜索return res;}Deque<String> path=new ArrayDeque<>(4);//存放每一个符合规则的ip地址int splitTimes=0;//已经分割成ip地址的段数dfs(s,len,splitTimes,0,path,res);return res;}//判断 s 的子区间 [left, right] 是否能够成为一个 ip 段。判断的同时顺便把类型转了private int judgeIfIpSegment(String s,int left,int right){int len=right-left + 1;if(len>1&&s.charAt(left)=='0') {//大于1位的时候,不能以0开头return -1;}int res=0;for (int i=left;i<=right;i++) { //转成int类型res=res*10+s.charAt(i)-'0';}if (res>255) {//大于255不是合法的 ip 段数值return -1;}return res;}private void dfs(String s,int len,int split,int begin,Deque<String> path,List<String> res) {if (begin==len) {//到达字符串末尾if (split==4) {//并且分隔成为了4段的ipres.add(String.join(".", path));}return;}// 看到剩下位数的不够或者超出了,就退出(剪枝),len-begin表示剩余的还未分割的字符串的位数if (len-begin<(4-split)||len-begin >3*(4-split)) {return;}for (int i=0;i<3;i++) {//每个ip地址段都可以取1-3位的数字if (begin+i>=len) {//剩下的数字不够取了,则结束break;}int ipSegment=judgeIfIpSegment(s,begin,begin + i);if (ipSegment!=-1) { // 在判断是 ip 段的情况下,才去做截取path.addLast(ipSegment + "");dfs(s,len,split + 1,begin+i+1,path,res);path.removeLast();}}}}或public class Solution {static final int SEG_COUNT=4;List<String> res=new ArrayList<>();int[] segments=new int[SEG_COUNT];public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {dfs(s,0,0);return res;}public void dfs(String s,int segId,int segStart) {if (segId==SEG_COUNT) {// 如果找到了 4 段 IP 地址if (segStart==s.length()) {//并且遍历完了字符串,那么就是一种答案StringBuffer ipAddr=new StringBuffer();for (int i=0;i<SEG_COUNT;i++) {ipAddr.append(segments[i]);if (i!=SEG_COUNT-1) {//不是最后一段的话,就加上ip地址的分割符号 .ipAddr.append('.');}}res.add(ipAddr.toString());}return;}if (segStart==s.length()) { //能走到这,说明还没有找到4段IP地址,但已经遍历完了字符串,那么提前回溯return;}if (s.charAt(segStart)=='0') {//由于不能有前导零,如果当前数字为 0,那么这一段 IP 地址只能为 0segments[segId] = 0;dfs(s,segId+1,segStart+1);}int addr=0; //一般情况,枚举每一种可能性并递归for (int segEnd=segStart;segEnd<s.length();segEnd++) {addr =addr*10+(s.charAt(segEnd)-'0');if(addr>0&&addr<=0xFF){segments[segId]=addr;dfs(s,segId+1,segEnd + 1);}else{break;}}}}
leetcode 22 号算法题:括号生成
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/generate-parentheses/solution/pei-yang-chou-xiang-si-wei-hui-su-jie-fa-7dwu/
数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
示例 1:
输入:n = 3
输出:[“((()))”,”(()())”,”(())()”,”()(())”,”()()()”]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1
输出:[“()”]
提示:
1 <= n <= 8
class Solution {public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {List<String> res=new ArrayList<>();if(n<1) return res;dfs(n,"",res,0,0);return res;}private void dfs(int n,String path,List<String> res,int open,int close){if(close>open||open>n)return;if(2*n==path.length()){res.add(path);return;}dfs(n, path+"(", res,open+1,close);dfs(n, path+")", res,open,close+1);}}或class Solution {public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {List<String> res=new ArrayList<>();if(n<1) return res;dfs(n,"",res,0,0);return res;}private void dfs(int n,String path,List<String> res,int open,int close){if(2*n==path.length()){res.add(path);return;}if(open<n)dfs(n, path+"(", res,open+1,close);if(close<open)dfs(n, path+")", res,open,close+1);}}
leetcode 51 号算法题:N 皇后
//找到所有的n皇后摆放位置class Solution {private void check(int[] array,int max,int n,List<int[]> res){//放置第n个皇后if(n==max){res.add(Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length));return;}for(int i=0;i<max;i++){//放置第n个皇后时:从这行0-max处一次放置,看是否会冲突array[n]=i;if(judge(array,n)){//当前位置不冲突,则放置下一个皇后check(array,max,n+1,res);}}}private boolean judge(int[] array,int n){//判断当前皇后放在此处(这行的第n个位置)是否冲突for(int i=0; i<n;i++){//与前n-1个皇后的位置进行比较,看是否冲突//array[i] == array[n] 看是否在同一列上//Math.abs(n - i) == Math.abs(array[n] - array[i]) 看是否在同一斜线上if (array[i]==array[n]||Math.abs(n-i)==Math.abs(array[n]-array[i])){return false;}}return true;}}
class Solution {public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {int[] array=new int[n];List<List<String>> res=new ArrayList<>();check(array, n, 0, res);return res;}private void check(int[] array,int max,int n,List<List<String>> res){//放置第n个皇后if(n==max){List<String> path=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=0;i<max;i++){char[] chars=new char[max];Arrays.fill(chars, '.');chars[array[i]]='Q';path.add(new String(chars));}res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<max;i++){//放置第n个皇后时:从这行0-max处一次放置,看是否会冲突array[n]=i;if(judge(array,n)){//当前位置不冲突,则放置下一个皇后check(array,max,n+1,res);}}}private boolean judge(int[] array,int n){//判断当前皇后放在此处(这行的第n个位置)是否冲突for(int i=0; i<n;i++){//与前n-1个皇后的位置进行比较,看是否冲突//array[i] == array[n] 看是否在同一列上//Math.abs(n - i) == Math.abs(array[n] - array[i]) 看是否在同一斜线上if (array[i]==array[n]||Math.abs(n-i)==Math.abs(array[n]-array[i])){return false;}}return true;}}或class Solution {public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {List<List<String>> res=new ArrayList<>();char[][] board=new char[n][n];for (int i=0;i<board.length;i++) {Arrays.fill(board[i],'.');}check(board, 0, res);return res;}private void check( char[][] board,int index,List<List<String>> res){if(index==board.length){List<String> temp=new ArrayList<>();for (int i=0;i<board.length;i++) {temp.add(new String(Arrays.copyOf(board[i],board.length)));}res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));return;}for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++){//列if(isVisited(board,index,i,'Q'))continue;board[index][i]='Q';check(board, index+1, res);board[index][i]='.';}}private boolean isVisited(char[][] board, int row, int col, char target) {for (int i=0; i<row; i++) {if(board[i][col]==target)return true;}if(row>0&&col>0) {for (int i=row-1,j=col-1;i>=0&&j>=0;i--,j--) { //左上角if (board[i][j] == target)return true;}}if(row>0){for(int i=row-1,j=col+1;i>=0&&j<board.length;i--,j++){ //右上角if(board[i][j]==target)return true;}}return false;}}
leetcode 37 号算法题:数独问题
class Solution {public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {backtrack(board, 0, 0);}private boolean backtrack(char[][] board,int i,int j){//i是行,j是列if(j==board[0].length){return backtrack(board, i+1, 0);}if(i==board.length){return true;}if(board[i][j]!='.'){return backtrack(board, i, j+1);}for(char ch='1';ch<='9';ch++){if(isVisited(board,i,j,ch)) {continue;}board[i][j]=ch;if(backtrack(board, i, j+1))return true;board[i][j]='.';}return false;}private boolean isVisited(char[][] board,int m,int n,char target) {for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++){if(board[m][i]==target)return true;if(board[i][n]==target)return true;if(board[(m/3)*3+i/3][(n/3)*3+i%3]==target)return true;}return false;}}
贪心算法思想
leetcode 455 号算法题:分发饼干
leetcode 322 号算法题:零钱兑换
leetcode 45 号算法题:跳跃游戏 Ⅱ
leetcode 1578 号算法题:避免重复字母的最小删除成本
leetcode 402 号算法题:移掉K位数字
动态规划算法思想
leetcode 509 号算法题:斐波那契数
leetcode 322 号算法题:零钱兑换
leetcode 64 号算法题:最小路径和
leetcode 53 号算法题:最大子数组之和
leetcode 647 号算法题:回文子串
leetcode 5 号算法题:最长回文串
leetcode 131 号算法题:分割回文串
leetcode 516 号算法题:最长回文子序列
leetcode 300 号算法题:最长上升子序列
leetcode 1143 号算法题:最长公共子序列
leetcode 72 号算法题:编辑距离
leetcode 44 号算法题:通配符匹配
leetcode 10 号算法题:正则表达式匹配
leetcode 486 号算法题:预测赢家
leetcode 877 号算法题:石子游戏
0-1 背包问题
总结
1.深度优先搜索遍历二叉树的所有路径
//深度优先遍历public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();LinkedList<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();dfs(root,path,res);return res;}private void dfs(TreeNode node,LinkedList<Integer> path,List<List<Integer>> res){if(node==null) return;path.addLast(node.val);if(node.left==null&&node.right==null){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}dfs(node.left, path, res);dfs(node.right, path, res);path.removeLast();}或List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();LinkedList<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root) {dfs(root);return res;}private void dfs(TreeNode node){if(node==null) return;path.addLast(node.val);if(node.left==null&&node.right==null){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}dfs(node.left);dfs(node.right);path.removeLast();}//广度优先遍历public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();TreeNode curr=root;TreeNode lastVisited=null;while (curr!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){while (curr!=null){stack.add(curr);path.add(curr.val);curr=curr.left;}curr=stack.peek();if(curr.right!=null&&curr.right!=lastVisited){curr=curr.right;continue;}if(curr.right==null&&curr.left==null){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}path.remove(path.size()-1);curr=stack.pop();lastVisited=curr;curr=null;}return res;}
四、刷题总结
1.关于递归反转链表
private ListNode traverse(ListNode head) {//反转整个链表if(head.next==null)return head;ListNode last=traverse(head.next);head.next.next=head;head.next=null;return last;}ListNode after;private ListNode traverse(ListNode head,int m) {//反转链表的前n个节点if(m==1){after=head.next;return head;}ListNode last=traverse(head.next,m-1);head.next.next=head;head.next=after;return last;}private ListNode traverse(ListNode head,int m,int n) {//反转链表 m-n 之间的节点if(m==1){return traverse(head,n);}head.next=traverse(head.next,m-1,n-1);return head;}

