17.1 动态存储分配
- 需要的头文件
- 对应的函数
- malloc:分配内存块,但不初始化
- calloc:分配内存块,并且对内存块进行清除
- realloc:调整先前分配的内存块
- 返回值 void * :即一个内存地址
-
17.2 动态分配字符串
使用 malloc 函数为字符串分配内存时,复制操作会把 malloc 的通用指针转换成为对应类型的,当然最好自己强制转换(1)
- 使用 malloc 分配一个字符串(2)
// 1#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(){int *p;p = (int *)malloc(1000);}// 2#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <stdlib.h>char *concat(char *s1,char *s2);int main(){char *p = concat("abc","def");printf("%s",p);return 0;}char *concat(char *s1,char *s2){char *result=NULL;result = (char *)malloc(strlen(s1)+strlen(s2)+1);// 如果 result 为空就退出strcpy(result,s1);strcat(result,s2);return result;}// 输出abcdef
17.3 动态分配数组
- 使用 malloc 进行动态分配(1)
// 1#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(){int n;int *a;printf("输入你想要的数组大小:");scanf("%d",&n);a = (int *)malloc(n*sizeof(int));printf("%d",sizeof(a)); // 8return 0;}
17.4 释放存储
- free 函数:free(void *ptr)
p = malloc(...);q = malloc(...);p = q;free(p);
17.5 realloc() 函数
- 【作用】:实现对内存大小的重新分配
- 【函数原型】:
_void* realloc (void* ptr, size_t size);_- 【参数解释】ptr 指向要重新分配的空间,size 重新分配的大小
- 【注意】
- ptr 为 null ,即表示新开辟一个空间,和 malloc 相同
- size 为 null ,即新空间大小为空,和 free 相同
- ptr 在重新分配完成后会被回收
- 新的内存空间地址,可能和原来一样,也可能不一样
#include <stdio.h>#include <stlib.h>int main(){// 先动态分配一个内存地址及其对应的内存空间int *test = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*10);printf("%d\n",test);// 用新指针指以下int *re = test;// 重新分配内存空间test = (int *)realloc(re,sizeof(int)*100);printf("%d",test);return 0;}
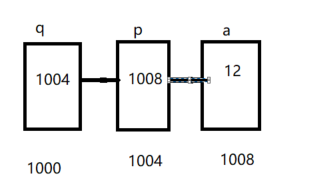
17.6 指向指针的指针
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int a = 12;int *p = &a;int **q = &p;printf("%d",**q); // 12return 0;}