简介
fail-fast 机制,即快速失败机制,是java集合(Collection)中的一种错误检测机制
- 当在迭代集合的过程中该集合在结构上发生改变的时候,就有可能会发生fail-fast,即抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
- fail-fast机制并不保证在不同步的修改下一定会抛出异常,它只是尽最大努力去抛出,所以这种机制一般仅用于检测bug
案例
出现场景
迭代器每次next()/hasNext()时都会判断modCount!=expectedmodCount
- modCount:列表在结构上被修改的次数
- expectedmodCount:预期列表结构被修改次数
- 如果二者不相等就抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
- 这两个在遍历前是相等的,如果循环中执行了add,remove,clear操作都会修改modCount,set操作不会修改modCount
使用foreach语法糖时,不能add,remove,clear也是一样的道理,foreach底层就是iterator
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.addAll(Arrays.asList("A","B","C"));System.out.println("list = " + list);Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){String elem = it.next();list.remove(elem);// it.remove();}System.out.println("list = " + list);}
解决方案
iterator迭代器自带的remove
遍历过程中使用迭代器的remove方法,删除当前元素(每次remove后会重新给expectedModCount赋值)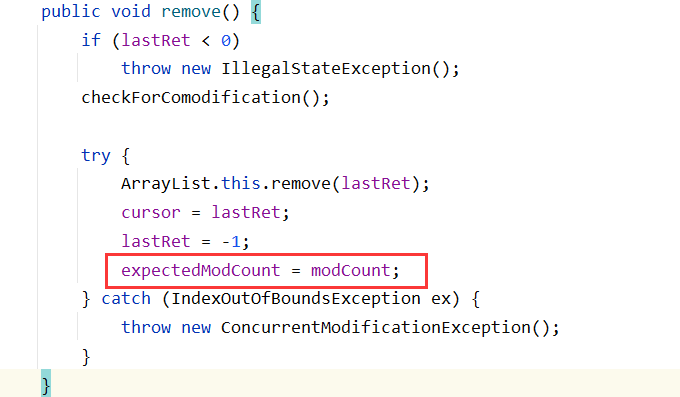
CopyOnWriteArrayList
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();list.addAll(Arrays.asList("A","B","C"));System.out.println("list = " + list);Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){list.remove(it.next());}System.out.println("list = " + list);}
CopyOnWriteArrayList的删除操作
- 加锁
- 找到需删除元素的索引位置
- 新建一个比原容器容量少1的新容器
- 复制原容器删除位置之前的全部元素到新容器中
- 复制原容器删除位置之后的全部元素到新容器中
- 原容器的引用指向新容器,丢弃原容器
- 解锁
//不加锁,只是用来查询一些必要信息public boolean remove(Object o) {Object[] snapshot = getArray();int index = indexOf(o, snapshot, 0, snapshot.length);return (index < 0) ? false : remove(o, snapshot, index);}// o:要删除的元素; snapshot:列表快照; index:o在列表中的索引位置private boolean remove(Object o, Object[] snapshot, int index) {// 加锁final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {Object[] current = getArray();int len = current.length;// remove(Object o)并发执行了,这里进行检查,查到要删除元素真正的索引if (snapshot != current) findIndex: {int prefix = Math.min(index, len);// 容器在index索引前面的结构发生了变化for (int i = 0; i < prefix; i++) {// prefix前有索引位置元素发生变化,如果该位置元素变成我们需要的,// 直接返回这个位置if (current[i] != snapshot[i] && eq(o, current[i])) {index = i;break findIndex;}}// 当前容器长度<=该元素索引位置,说明当前容器不存在该元素if (index >= len)return false;// index位置元素是我们需要的,找到需要的元素索引if (current[index] == o)break findIndex;// 遍历当前容器,查找我们要删除元素的索引index = indexOf(o, current, index, len);if (index < 0)return false;}// 新建一个比原容器容量少1的新容器Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1];// 复制原容器删除位置之前的全部元素到新容器中System.arraycopy(current, 0, newElements, 0, index);// 复制原容器删除位置之后的全部元素到新容器中System.arraycopy(current, index + 1,newElements, index,len - index - 1);// 原容器的引用指向新容器setArray(newElements);return true;} finally {// 解锁lock.unlock();}}// 原容器的引用指向新容器final void setArray(Object[] a) {array = a;}

