在node中,我们在用户模块中直接获取通过require('fs')获取并使用该模块的函数进行文件的操作。这里的fs模块并不是内建的原生模块。它也是通过编写javaScript的方式去实现。这种模块在node里面称为native模块。
native模块也称为内建javaScript模块(名字有点混淆,下面统一使用内建javaScript模块)。在node.js中内建javaScript模块最终并不是以文件的形式的存在。在node的工程目的lib目录下。是内建javaScript模块的存放目录。在打包构建的时候在经过gyp构建工具的js2c.py的python脚本处理后。生成node_javaScript.cc源文件。下面是pyp生成配置配置。
action: 针对输入的文件,定义了一组自定义的构建动作
'actions': [{'action_name': 'node_js2c','process_outputs_as_sources': 1,'inputs': [# Put the code first so it's a dependency and can be used for invocation.'tools/js2c.py','<@(library_files)','config.gypi'],'outputs': ['<(SHARED_INTERMEDIATE_DIR)/node_javascript.cc',],'action': ['python', '<@(_inputs)','--target', '<@(_outputs)',],},],
js2c.py部分代码。通过读取文件内容最终插入到模板中。
TEMPLATE = """
#include "env-inl.h"
#include "node_native_module.h"
#include "node_internals.h"
namespace node {{
namespace native_module {{
{0}
void NativeModuleLoader::LoadJavaScriptSource() {{
{1}
}}
UnionBytes NativeModuleLoader::GetConfig() {{
return UnionBytes(config_raw, {2}); // config.gypi
}}
}} // namespace native_module
}} // namespace node
"""
我们以fs.js和 internal\bootstrap\loaders.js为例子。
|- lib |- internal |- bootstrap |- loaders.js |- fs.js
最终生成的node_javaScript.cc文件。
/*代码有省略*/
#include "env-inl.h"
#include "node_native_module.h"
#include "node_internals.h"
namespace node {
namespace native_module {
static const uint8_t fs_raw[] = { 47, 47, 32, 67,111,112,121,114,105,103,104,116, 32, 74,111,121,101,110/*省略部分代码*/};
static const uint8_t internal_bootstrap_loaders_raw [] = { 32, 32, 34,118, 56, 95,117,115,101, 95,115,105,112,104/*省略部分代码*/};
static const uint8_t config_raw[] = {56, 95,117,115,101, 95,115,105,112,104/*省略部分代码*/}
void NativeModuleLoader::LoadJavaScriptSource() {
source_.emplace("fs", UnionBytes{fs_raw, 62403});
source_.emplace("internal/bootstrap/loaders", UnionBytes{internal_bootstrap_loaders_raw, 11349});
}
UnionBytes NativeModuleLoader::GetConfig() {
return UnionBytes(config_raw, 3317); // config.gypi
}
}
}
node\src\node_native_module.h文件
// 内容有省略
using NativeModuleRecordMap = std::map<std::string, UnionBytes>;
class NativeModuleLoader {
private:
NativeModuleRecordMap source_;
}
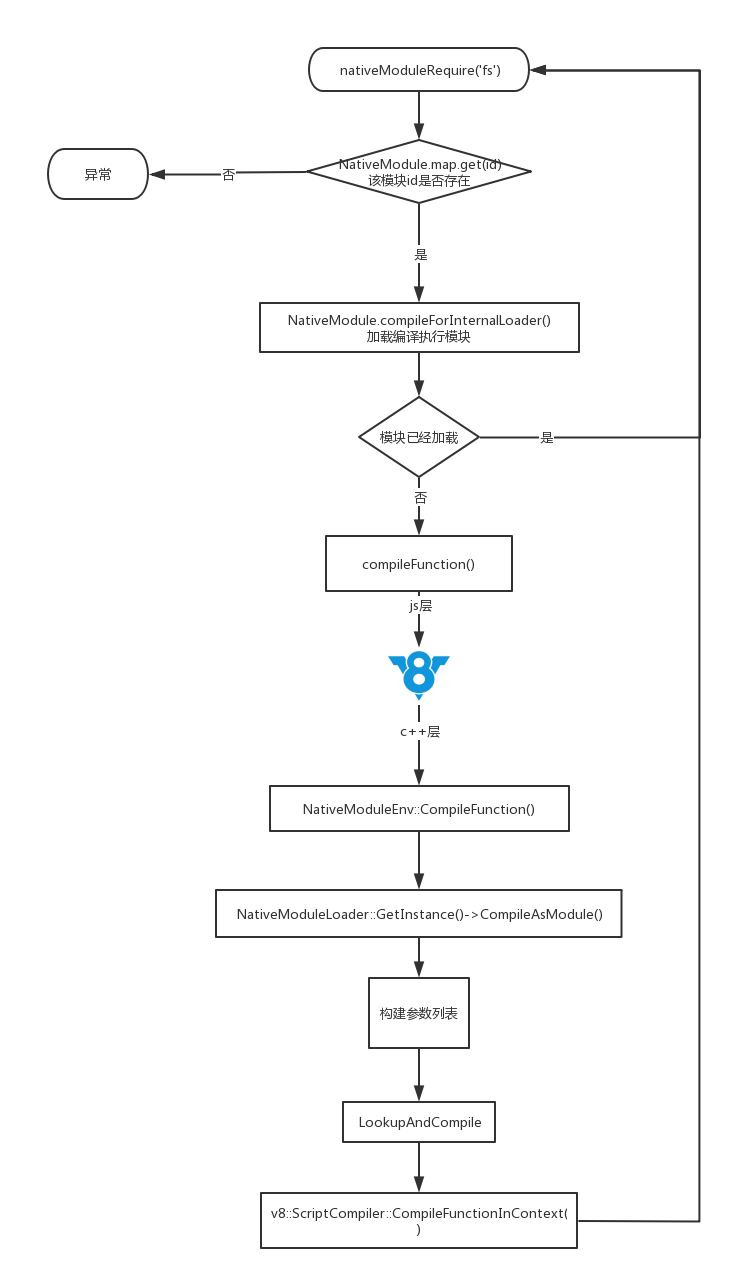
在此可以知道。source_是一个map。key为lib目录文件相对于lib目录的绝对路径。value为文件的ASCII编码的二进制数据。node内建的javaScript文件最终以二进制的方式存储在NativeModuleLoader中。当我们获取内建javaScipr模块的时候最终也是通过NativeModuleLoader去获取。最终在编译构建后。内建的javaScript文件被包含在node.exe中。因此获取内建模块会更快。下面我们看一下一个内建javaScript的加载流程。
在内建模块中我们知道通过执行internal\bootstrap\loaders.js 文件后。导出来的native_module_require函数正是获内建javaScript模块的的函数。
// 内容有省略
const loaderId = 'internal/bootstrap/loaders';
// 获取内建模块native_module
const {
moduleIds,
compileFunction
} = internalBinding('native_module');
// moduleIds 是一个数组。存储着内建模块在源码相对于lib目录的相对路径。并却省略了后缀名。例如 ['internal\bootstrap\loaders', 'fs']
// compileFunction 是一个以模块id为参数。返回内建模块的javaScript包装函数。
const getOwn = (target, property, receiver) => {
return ObjectPrototypeHasOwnProperty(target, property) ?
ReflectGet(target, property, receiver) :
undefined;
};
// 对内建javaScript模块的分装
class NativeModule {
// 构建一个map, key为 模块id, value为 nativeModuale对象
static map = new SafeMap(
ArrayPrototypeMap(moduleIds, (id) => [id, new NativeModule(id)])
);
constructor(id) {
this.filename = `${id}.js`;
this.id = id;
// 判断是否能在用户模块获取。
// 在 internal/**目录下的文件不能在用户模块中使用。
this.canBeRequiredByUsers = !StringPrototypeStartsWith(id, 'internal/');
// 在模块中的exports对象
this.exports = {};
// 模块标记。
this.loaded = false;
this.loading = false;
//省略代码
}
// 判断是否存在某个内建javaScript模块
static exists(id) {
return NativeModule.map.has(id);
}
// 判断某个内建javaScript模块能被用户模块获取
static canBeRequiredByUsers(id) {
const mod = NativeModule.map.get(id);
return mod && mod.canBeRequiredByUsers;
}
// 编译执行内建模块。
compileForInternalLoader() {
if (this.loaded || this.loading) {
return this.exports;
}
const id = this.id;
this.loading = true;
try {
const requireFn = StringPrototypeStartsWith(this.id, 'internal/deps/') ?
requireWithFallbackInDeps : nativeModuleRequire;
// 通过模块id去查找某个内建javaScript模块。并把它包赚成一个javaScript函数。编译并返回。
const fn = compileFunction(id);
// 执行某个内建模块。
fn(this.exports, requireFn, this, process, internalBinding, primordials);
this.loaded = true;
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
ArrayPrototypePush(moduleLoadList, `NativeModule ${id}`);
return this.exports;
}
}
const loaderExports = {
// 获取内建模块。在上面内建模块中已做讲解
internalBinding,
// 内建javaScript模块的封装
NativeModule,
// 获取内建javaScript模块的require函数。
require: nativeModuleRequire
};
// 获取原生模块
function nativeModuleRequire(id) {
if (id === loaderId) {
return loaderExports;
}
const mod = NativeModule.map.get(id);
if (!mod) throw new TypeError(`Missing internal module '${id}'`);
return mod.compileForInternalLoader();
}
function requireWithFallbackInDeps(request) {
if (!NativeModule.map.has(request)) {
request = `internal/deps/${request}`;
}
return nativeModuleRequire(request);
}
// Pass the exports back to C++ land for C++ internals to use.
return loaderExports;
NativeModule是一个对内建javaScript模块的封装。负责内建模块的构建,和加载。最后把内建模块模块引用,缓存记录在NativeModule对象上。NativeModule 的编译模块通过内建原生模块native_module获取了compileFunction 和 moduleIds。node_native_module_env.cc是注册为native_module的的注册模块。
// 获取moduleId列表
void NativeModuleEnv::ModuleIdsGetter(Local<Name> property,
const PropertyCallbackInfo<Value>& info) {
Isolate* isolate = info.GetIsolate();
std::vector<std::string> ids = NativeModuleLoader::GetInstance()->GetModuleIds();
// 把std::vector<T> 列表转换成v8的javaScript数组并作为返回值。
info.GetReturnValue().Set( ToV8Value(isolate->GetCurrentContext(), ids).ToLocalChecked());
}
void NativeModuleEnv::CompileFunction(const FunctionCallbackInfo<Value>& args) {
Environment* env = Environment::GetCurrent(args);
// 获取模块id
node::Utf8Value id_v(env->isolate(), args[0].As<String>());
const char* id = *id_v;
NativeModuleLoader::Result result;
// 获取模块包装函数。
MaybeLocal<Function> maybe = NativeModuleLoader::GetInstance()->CompileAsModule( env->context(), id, &result);
// 把当前模块记录到缓存中
RecordResult(id, result, env);
Local<Function> fn;
if (maybe.ToLocal(&fn)) {
args.GetReturnValue().Set(fn);
}
}
void NativeModuleEnv::Initialize(Local<Object> target,
Local<Value> unused,
Local<Context> context,
void* priv) {
Environment* env = Environment::GetCurrent(context);
// 对对象属性 moduleIds 设置了getter属性访问器.setter为nullptr。
target->SetAccessor(env->context(),
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), "moduleIds"),
ModuleIdsGetter,
nullptr,
MaybeLocal<Value>(),
DEFAULT,
None,
SideEffectType::kHasNoSideEffect).Check();
// compileFunction模块编译函数
env->SetMethod(target, "compileFunction", NativeModuleEnv::CompileFunction);
}
NODE_MODULE_CONTEXT_AWARE_INTERNAL(native_module, node::native_module::NativeModuleEnv::Initialize)
native_module并没有真正的逻辑,最终全部指向了NativeModuleLoader。下面我们详细介绍一下NativeModuleLoader类。在上面我们可以知道NativeModuleLoader的私有属性source_保存了内建javaScript模块的模块id和模块的源代码的衍射。NativeModuleLoader在node中以单例的方式使用。通过静态函数NativeModuleLoader::NativeModuleLoader()访问。
// 内容有省略
class NativeModuleLoader {
public:
// 没有public默认构造函数。不能通过构造函数去创建对象
NativeModuleLoader(const NativeModuleLoader&) = delete;
// 删除了默认的赋值构造函数。
NativeModuleLoader& operator=(const NativeModuleLoader&) = delete;
private:
// 允许友元类访问
friend class NativeModuleEnv;
friend class CodeCacheBuilder;
NativeModuleLoader();
static NativeModuleLoader* GetInstance();
// 获取模块id列表
std::vector<std::string> GetModuleIds();
v8::MaybeLocal<v8::Function> CompileAsModule(v8::Local<v8::Context> context, const char* id, Result* result);
// 模块实例
static NativeModuleLoader instance_;
// 内建javaScript的模块id与模块源码的map
NativeModuleRecordMap source_;
}
native_module 最终通过NativeModuleLoader::GetInstance()->GetModuleIds()去获取moduleIds 。
std::vector<std::string> NativeModuleLoader::GetModuleIds() {
std::vector<std::string> ids;
// 遍历source的map对象。获取模块的id。并存放在 std::vector<std::string>里面
ids.reserve(source_.size());
for (auto const& x : source_) {
ids.emplace_back(x.first);
}
return ids;
}
native_module通过 NativeModuleLoader::GetInstance()->CompileAsModule( env->context(), id, &result);编译内建javaScript模块。
MaybeLocal<Function> NativeModuleLoader::CompileAsModule(
Local<Context> context,
const char* id,
NativeModuleLoader::Result* result) {
Isolate* isolate = context->GetIsolate();
// 构建参数列表,在内建的javaScript模块可以获取到以下参数
std::vector<Local<String>> parameters = {
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "exports"),
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "require"),
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "module"),
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "process"),
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "internalBinding"),
FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "primordials")};
// 查找并编译模块
return LookupAndCompile(context, id, ¶meters, result);
}
// 查找并编译模块。
MaybeLocal<Function> NativeModuleLoader::LookupAndCompile(
Local<Context> context,
const char* id,
std::vector<Local<String>>* parameters,
NativeModuleLoader::Result* result) {
Isolate* isolate = context->GetIsolate();
EscapableHandleScope scope(isolate);
Local<String> source;
// 加载内建javaScript源码。在根据模块id在source_ 查找
if (!LoadBuiltinModuleSource(isolate, id).ToLocal(&source)) {
return {};
}
// 模块名称为 "node" + 模块id
std::string filename_s = std::string("node:") + id;
Local<String> filename =
OneByteString(isolate, filename_s.c_str(), filename_s.size());
ScriptOrigin origin(isolate, filename, 0, 0, true);
ScriptCompiler::CachedData* cached_data = nullptr;
// 构建缓存
{
Mutex::ScopedLock lock(code_cache_mutex_);
auto cache_it = code_cache_.find(id);
if (cache_it != code_cache_.end()) {
// Transfer ownership to ScriptCompiler::Source later.
cached_data = cache_it->second.release();
code_cache_.erase(cache_it);
}
}
const bool has_cache = cached_data != nullptr;
ScriptCompiler::CompileOptions options =
has_cache ? ScriptCompiler::kConsumeCodeCache
: ScriptCompiler::kEagerCompile;
ScriptCompiler::Source script_source(source, origin, cached_data);
// 以函数的方式去编译
MaybeLocal<Function> maybe_fun =
ScriptCompiler::CompileFunctionInContext(context,
&script_source,
parameters->size(),
parameters->data(),
0,
nullptr,
options);
Local<Function> fun;
if (!maybe_fun.ToLocal(&fun)) {
return MaybeLocal<Function>();
}
*result = (has_cache && !script_source.GetCachedData()->rejected)
? Result::kWithCache
: Result::kWithoutCache;
std::unique_ptr<ScriptCompiler::CachedData> new_cached_data(
ScriptCompiler::CreateCodeCacheForFunction(fun));
CHECK_NOT_NULL(new_cached_data);
{
Mutex::ScopedLock lock(code_cache_mutex_);
code_cache_.emplace(id, std::move(new_cached_data));
}
return scope.Escape(fun);
}
} // namespace native_module
通过构建参数列表对模块做了包装。这也是我们能在内建javaScript模块中能直接获取。require,export等参数。我们以lib/fs.js为例子。最终生成的模块。最终生成模块名称为node:fs.js的文件名。并放回包装号的v8的javaScript函数放回到javaScript环境中。
/*
* @params exports{Object} 模块导出对象
* @params require{Function} require函数,该函数并不是我们在用户模块的require,它是用来获取其他内建javaScript模块
* @params module{Object} 模块对象
* @params process{Object} 进程对象
* @params internalBinding{Function} 用于获取内建原生模块的函数
* @params primordials{Object} 标准javaScript内置全局对象上的原型上的对象或者函数的引用对象集。
*/
function anonymity(esports,require,module, process, internalBinding,primordials ) {
// lib/fs.js 模块的内容
}
所以一个内建javaScript的加载流程为。