ECMA 基础(一)
European Computer Manufactures Association
ECMAScript是 JavaScript所基于的脚本语言。Ecma国际组织 负责将 ECMAScript标准化。
欧洲计算机制造联合会,位于日内瓦,致力于评估,开发,认可电信,制定了计算机标准List 清,ECMA-262 脚本语言的规范 ECMAScript里的ES5和ES6标准
ECMAScript 历史:
- 1997 年 1.0
- 1998 年 2.0
- 1999 年 3.0 通行标准
- 2007 年 4.0 草案(
mozilla支持,google,firefox,microsoft不支持) - 2008 年 4.0 中止,把容易改善的部分归纳到 3.1,激进部分(
Harmony),更名为ECMAScript5 - 2009 年 5.0 正式发布,
Harmony分成两部分,不怎么激进部分(JS.Next),比较激进部分(JS.Next.Next) - 2011 年,5.1 发布,成为
ISO国际标准 - 2013 年,
ES6不再增添内部,直接用JS.Next,ES7 用JS.Next.Next,ES6草案发布 - 2015 年,
ES6正式发布又名为ECMAScript2015
内核
| 浏览器 | 内核 |
|---|---|
| IE | trident |
| chrome | webkit blink |
| safari | webkit |
| firefox | gecko |
| opera | presto |
浏览器历史
- 1990 年,蒂姆 伯纳斯 李 超文本分享资讯的人,
world wide web移植到C libwww/nexus,允许别人浏览他人编写的网站 - 1993 年,美国伊利诺大学
NCSA组织(马克 安德森),开发了MOSIAC浏览器,可以显示图片,图形化浏览器 - 1994 年,马克 安德森 和 吉姆 克拉克(硅图
SGI) 成立MOSIAC communication corporation(因为商标纠纷而倒闭)插曲,MOSIAC属于伊利诺大学并将商标转让给spy glass公司(做数据的),在没办法的情况下改名为Netscape communication corporation网景公司,并开发了netscape navigator浏览器(流行了 10 年) - 1996 年,微软收购了
spy glass,开发了Internet Exploror 1.0,IE3 开发了Jscript(实现网页动态交互) - 1996 年,网景公司
Brendan eich在netscape navigator开发出了livescript(JavaScript前身) - 1996 年,
Java有一定的知名度了,网景livescript不温不火,和SUN公司商量合作推广和宣传产品,livescript发展更名为JavaScript - 2001 年,
IE6 XP诞生,带来JavaScript的生命-JS引擎 - 2003 年,
Mozilla公司(早期互联网电子开发)firefox也是根据netscape navigator改版的 - 2008 年,谷歌基于
webkit blink内核加上gears(离线上网功能) ,开发出chrome浏览器(V8 引擎-JS引擎),直接翻译机器码,且独立于浏览器运行,并提出渐进式APP(Progressive Web APP) - 2009 年,甲骨文
Oracle收购了SUN公司,JavaScript的所有权给了甲骨文
编程语言
是用来定义计算机程序的形式语言。它是一种被标准化的交流技巧,用来向计算机发出指令,一种能够让程序员准确地定义计算机所需要使用数据的计算机语言,并精确地定义在不同情况下所应当采取的行动。
计算机不能直接理解高级语言,只能直接理解机器语言,所以必须要把高级语言翻译成机器语言,计算机才能执行高级语言编写的程序。
编译与解释语言的区别:
一个是编译,一个是解释。两种方式只是翻译的时间不同。编译型语言写的程序执行之前,需要一个专门的编译过程,把程序编译成为机器语言的文件,比如exe文件,以后要运行的话就不用重新翻译了,直接使用编译的结果就行了(exe文件),因为翻译只做了一次,运行时不需要翻译,所以编译型语言的程序执行效率高,但也不能一概而论,部分解释型语言的解释器通过在运行时动态优化代码,甚至能够使解释型语言的性能超过编译型语言。
解释则不同,解释性语言的程序不需要编译,省了道工序,解释性语言在运行程序的时候才翻译,比如解释性basic语言,专门有一个解释器能够直接执行basic程序,每个语句都是执行的时候才翻译。这样解释性语言每执行一次就要翻译一次,效率比较低。解释是一句一句的翻译。
解释型语言的好处就是不需要根据不同的系统平台进行移植
脚本语言(前后端都有):
JavaScript客户端脚本PHP服务器脚本
脚本语言 -> 脚本引擎 -> 解释器
JavaScript编程语言 4 要素:
- 变量
- 数据结构
- 函数
- 运算能力
JavaScript 概念
JavaScript分为:
- 文档对象模型 (
DOM) -document object model(W3C规范) - 浏览器对象模型(
BOM) -browser object model(没有规范) ESMAScript
关于 ESMAScript:
语法,变量,关键字,保留字,值,原始类型,引用类型运算,对象,继承,函数
线程
- 单线程
- 多线程
JavaScript引擎为单线程 -> 模拟多线程
单线程的机制是轮转时间片,短时间内轮流执行多个任务的片段
- 任务 1,任务 2
- 切分任务 1,任务 2
- 随机排列这些任务片段,组成队列
- 按照这个队列顺序将任务片段送进
JS进程 JS线程执行一个又一个的任务片段
引用
- 外部文件
- 内部脚本代码块
//外部文件<script type="text/javascript" src="js/index.js"></script>
//内部文件<script type="text/javascript">document.write('I am a inner JS');</script>
变量
变量是一个容器用于存储数据后续使用
声明变量 var
- 声明变量
- 变量赋值
var a; //声明变量aa = 3; //变量赋值var a = 3; //变量声明并赋值
//单一声明var x = 1,y = 2;
企业开发命名规范:
- 不能以数字开头
- 能字母
_,$开头 - 字母
_,$数字 - 不能关键字
- 不能保留字
- 语义化
- 结构化(
js_header js-header) - 小驼峰
- 英语写法
- 避免拼音
优先级:
运算 > 赋值
var x = 3,y = 4;var z = x + y;console.log(z);7
JS 值
JavaScript语言是动态语言也是脚本语言也是解释型语言也是弱类型语言(根据值的类型成为被赋值的变量)
Java语言是静态语言也是编译型语言也是强类型语言
原始值
基本数据类型有Number,String,Boolean,undefined,null
Number
var a = 1;var a = 3.14;
String
var str = 'i love programing';
Boolean
布尔值(布尔发明),计算机里,非真即假,非假即真。
truefalse
var a = true;console.log(a);//true
undefined
- 系统会给一个未赋值的变量自动赋值为
undefined,类型也是undefined - 函数没有传入实参时,参数为
undefined - 函数没有返回值时,默认返回
undefined
var a = undefined;console.log(a);//undefined
var a;console.log(a);//undefined
undefined既是一个原始数据类型,也是一个原始值数据undefined是全局对象上的一个属性window.undefinedundefined不可写writable: falseundefined不可配置configurable: falseundefined不可枚举enumerable: falseundefined不可重新定义defineProperty- 全局下,
undefined无法作为一个变量使用 - 局部作用域下,
undefined可以作为一个变量使用,说明undefined不是 JS 的保留字和关键字
注:
void(0) === undefined
null
空值,它的作用在于
- 初始化组件
- 销毁函数
引用值
引用值有object,array,function,date,RegExp等
堆栈
- 栈内存
Stack - 堆内存
Heap
如何存储原始值?
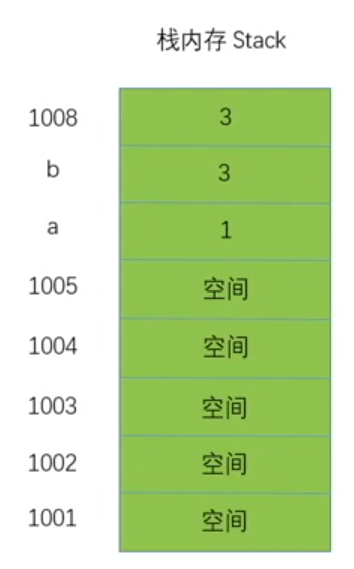
栈内存先进后出
var a = 3;var b = a;a = 1;console.log(b); //3
存储步骤:
- 往内存空间最里面声明变量 a 并在空间里存入值 3(
var a = 3) - 往内存空间最里面的上一位声明变量 b 并在空间里存入值 3(
var b = a) - 往内存空间最里面的上上一位开辟空间里存入值 1(
a = 1)
说明原始值数据是永久保存且不可改变的,例如手机相机电脑内存删除内容其实数据仍保留
如何存储引用值?
值,指针存储在栈 Stack内存 指向 堆内存 Heap地址
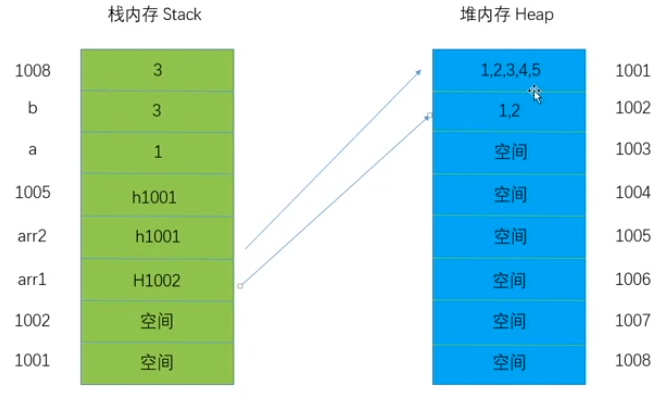
var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];var arr2 = arr1;console.log(arr1 + '' + arr2);//1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3, 4
指向相同地址的情况:
var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];var arr2 = arr1;arr1.push(5);console.log(arr1); //1, 2, 3, 4, 5console.log(arr2); //1, 2, 3, 4, 5
指向不同地址的情况:
var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];var arr2 = arr1;arr1 = [1, 2];console.log(arr1); //1, 2console.log(arr2); //1, 2, 3, 4, 5
规范
- 结束语句写分号
for,if,switch,function语句可以不加分号- 单一声明模式可以不加分号
var a = 1, b = 2; - 符号两边加空格
+,=
错误
- 语法问题:如有错误,代码一句都不执行
Uncaught SyntaxError 通用问题:中断执行
- 引用错误
Uncaught ReferenceError - 类型错误
Uncaught TypeError
- 引用错误
多个代码块之间的错误不影响下面代码块的执行
<script type="text/javascript">console.log(1) ;</script><script type="text/javascript">console.log(1);</script>
运算符
+,-,*,/,%,()
加号运算符
var a = 1,b = 2,c;c = a + b;console.log(c); //3
var a = 1,b = 2,d = 3,c;c = a + b * d;console.log(c); //7
优先级:括号运算 > 普通运算 > 赋值
var a = 1,b = 2,d = 3,var c = (a + b) * d;console.log(c); //9//计算机步骤://1.声明变量//2.变量a的值和变量b的值相加,与变量d的值相乘得到结果//3.将该结果赋值给变量c
字符串拼接,任何数据类型的值 + 字符串 = 字符串
var a = 1,b = 2,c;c = 1 + 'str'; //console.log(c); 1strc = 'str' + 'str'; //console.log(c); strstrc = 'str' + undefined; //console.log(c); strundefinedc = 'str' + null; //console.log(c); strnullc = 'str' + true; //console.log(c); strtruec = 'str' + NaN; //console.log(c); strNaNc = 'str' + 1 + 1; //console.log(c); str11c = 'str' + (1 + 1); //console.log(c); str2c = 1 + 1 + 'str' + (1 + 1); //console.log(c); 2str2
减号运算符
减号 加 字符串会先转为数字
var num = '123';console.log(typeof(- num) + ':' + - num); //number : -123
var num = 'abc';console.log(typeof(- num) + ':' + - num); //number : NaN
除号运算符
//除法var a = 10,b = 2,c;c = a / b; console.log(c); //5c = 0 / 0; console.log(c); //NaN -> Not a Number 数字类型console.log(1 / 0); //Infinity 正无穷 数字类型console.log(-1 / 0); //-Infinity 负无穷 数字类型
余号运算符
console.log(5 % 2); //1 5-(2*2)=1console.log(5 % 3); //2 5-(1*3)=2console.log(4 % 6); //4 前面比后面小,取前面
交换值的问题:
方法一
var a = 1,b = 2;//a b的值交换var c = a, //c = 1a = b, //a = 2b = c; //b = 1console.log(a, b); //2 1
方法二
var a = 1,b = 2;//a b的值交换a = a + b; //a = 3b = a - b; //b = 3 - 2 = 1a = a - b; //a = 3 - 1 = 2console.log(a, b); //2 1
++&--
//var a = 1; a = a + 1; => a++var a = 1;console.log(a++); //1 先打印后运算console.log(a); //2console.log(++a); //2 先运算赋值再打印console.log(a = a + 1); //2
var a = 5;console.log(a--); //5 先打印后运算console.log(a); //4console.log(--a); //4 先运算赋值再打印
var a = 5,b;b = a++ + 1;console.log(b, a); //6 6
var a = 5,b;b = ++a + 1;console.log(b, a); //7 6
var a = 5,b;b = a-- + --a; //5 + 3console.log(b, a); //8 3
var a = 5,b;b = --a + --a; //4 + 3console.log(b, a); //7 3
var a = 5,b;b = --a + a++; //4 + 4console.log(b, a); //8 5
比较运算符
>大于<小于>=大于等于<=小于等于==相等===全等!=不相等!==不全等
number比较 number
var bool = 1 > 2;console.log(bool); //false
var bool = 1 < 2;console.log(bool); //true
number比较 string,string先转化成 number再进行比较
var bool = 1 > '2';console.log(bool); //false
var bool = 1 < '2';console.log(bool); //true
string比较 string,寻找对应 ASCII码的十进制数字对比,多个字符的,从左到右依次对比,直到比较出 ASCII码的大小为止
var bool = 'a' > 'b';//a -> 97(ASCII码对应的十进制数字)//b -> 98(ASCII码对应的十进制数字)console.log(bool); //false
var bool = 'a' < 'b';console.log(bool); //true
为什么 4.5 > 11? 因为 ASCII码对应 ASCII码的十进制数字
var bool = '4.5' > '11';//先比较前面的4 和 1 然后再逐个往后对比//显然4(52) > 1(49),对比结束//4 -> 52(ASCII码对应的十进制数字)//1 -> 49(ASCII码对应的十进制数字)console.log(bool); //true
var bool = '4.5' < '11';console.log(bool); //false
var bool = '1.5' > '11';//先比较前面的1 和 1 然后再逐个往后对比//首先1(52) = 1(52)//然后.(46) < 1(52)console.log(bool); //false
==,相等是不看数据类型的,全等需要看数据类型是否相等的
var bool = 1 == 1;console.log(bool); //true
var bool = 1 == '1';console.log(bool); //true
var bool = 1 === '1';console.log(bool); //false
!=,
var bool = 1 != 1;console.log(bool); //false
var bool = 1 != 2;console.log(bool); //true
var bool = 1 != '1';console.log(bool); //true
NaN与包括自己在内任何东西都不相等
var bool = NaN == NaN;console.log(bool); //false
if语句
判断分支之if语句
if(条件){语句;}
- 在条件中
&&就是并且,&&两边都必须满足条件即可 ||就是或者,||两边有一边满足条件即可
查询成绩等级:
var score = 63;if (score >= 90) {console.log('您的成绩等级为A');}if (score >= 80 && score < 90) {console.log('您的成绩等级为B');}if (score >= 70 && score < 80) {console.log('您的成绩等级为C');}if (score >= 60 && score < 70) {console.log('您的成绩等级为D');}if (score < 60) {console.log('您的成绩等级为不合格');}
以上的if语句不管是否匹配成功条件都要继续往下匹配,造成性能影响,可以改为以下写法
var score = 63;if (score >= 90 && score <= 100) {console.log('您的成绩等级为A');} else if (score >= 80 && score < 90) {console.log('您的成绩等级为B');} else if (score >= 70 && score < 80) {console.log('您的成绩等级为C');} else if (score >= 60 && score < 70) {console.log('您的成绩等级为D');} else if (score < 60 && score >= 0) {console.log('您的成绩等级为不合格');} else {console.log('您的成绩出现异常');}
switch语句
判断分支之switch语句
switch(变量){case 值:语句;default:语句;}
注:
case相当于 当值为 ,default相当于else
var city = window.prompt('请输入您所在的地区');switch (city) {case '北京':console.log('15k');case '上海':console.log('13k');case '深圳':console.log('12k');case '广州':console.log('11k');default:console.log('9k');}//输入北京 print15k13k12k11k9k
如果缺少break断开,代码会执行往下执行,所以加上break匹配到条件就不会往下执行
var city = window.prompt('请输入您所在的地区');switch (city) {case '北京':console.log('15k');break;case '上海':console.log('13k');break;case '深圳':console.log('12k');break;case '广州':console.log('11k');break;default:console.log('9k');}//输入北京 print15k
关于适用性:
- 有值范围的或者条件是多个的用
if语句恰当 - 定值或者多个以上的用
switch语句比较好
三目运算符
三元运算符
var a = 5;if (a > 0) {console.log('大于0');} else {console.log('小于0');}a > 0 ? console.log('大于0'): console.log('小于0');
简写
a > 0 ? str = '大于0' : str = '小于0';
var str = a > 0 ? '大于0' : '小于0';
嵌套写法
var a = 5,str = '';if (a > 0) {if (a > 3) {str = '大于3';} else {str = '小于等于3';}} else {str = '小于0'}str = a > 0 ? (a > 3 ? '大于3' : '小于等于3') : '小于0'console.log(str);
逻辑运算
假包括:undefined,null,NaN,空字符串,0,false
除以上假的都为真
与&&
核心:
遇到真就往后走
var a = 1 && 2;console.log(a); //2
遇到假或走到最后就返回当前的值
var a = 1 && 2 && undefined && 10;console.log(a); //undefined
总结:
当&&前面和后面都满足条件才能使if语句(为真)继续进入往下执行
//1 && 1 返回1 真//0 && 1 返回0 假//1 && 0 返回0 假//0 && 0 返回0 假//if(... && ...){}
或||
核心:
遇到假就往后走
var b = 1 || 2;console.log(b); //1
遇到真或者走到最后就返回当前的值
var b = 0 || null || 1 || 0;console.log(b); //1
总结:
当||前面或后面有一个能满足条件if语句(为真)条件就可继续进入往下执行
//1 || 1 返回1 真//0 || 1 返回1 真//1 || 0 返回1 真//0 || 0 返回0 假if(... || ...){}
非!
var a = !1;console.log(a); //falsevar a = !!1;console.log(a); //true
注释
- 行注释
- 块注释
正确写法:
/*** 123* 345*/
错误写法:
/*123345*/
循环语句
多次执行相同代码
if & while语句
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {console.log(i);}//1//2//3
步骤
1.声明变量 i = 0;2.if(i < 3){console.log(i); //0}3.i++;4.if(i < 3){console.log(i); //1}5.i++;...6.if(i < 3){ 不满足条件 停止循环console.log(i); //1}
换种写法:
var i = 0;for(; i < 3;){console.log(i);i++;}
写法类似于while循环:
var i = 0;while(i < 3){console.log(i);i++;}
说明for循环可以转换为while循环
死循环:
var i = 0;//1 条件永远满足会一直执行while(1){console.log(i);i++;}
没有条件的情况也是死循环:
var i = 1;for(; i;){console.log(1);i++;}
跳出死循环并打印 1-10
var i = 1;for (; i;) {console.log(i);i++;if (i == 11) {i = 0; //or break}}
从 0 开始做加法,加到什么时候总和是小于 100 的
var sum = 0;for (var i = 0; i < 100; i++) {sum += i;if (sum > 100) {break;}console.log(i, sum);}
100 以内的数 跳过可以被 7 整除 或个位数是 7 的数
for (var i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {if (i % 7 == 0 || i % 10 == 7) {} else {console.log(i);}}
continue可以直接跳过循环打印结果
for (var i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {if (i % 7 == 0 || i % 10 == 7) {continue;}console.log(i);}
打印 0-9
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {console.log(i);}
打印 1-10
for (var i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {console.log(i);}
打印 0-9 的和
var sum = 0;for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {sum += i;}console.log(sum); //45
可以被 4,5,6 整除的数
for (var i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {if (i % 4 == 0 || i % 5 == 0 || i % 6 == 0) {console.log(i);}}
面试题:打印 0-100 的数,且又条件如下:
()只能有一句,不能写比较{}不能出现i++和i--
var i = 101;//i-- 如果到0就会自动结束循环//只能写分号中间,条件判断语句 0的时候就为falsefor (; i--;) {console.log(i);}
do while语句
特点:无论条件是否成立都要先执行
var i = 0;while (i < 10) {console.log(i);i++;}
var i = 0;do {console.log('我要开始循环了', i);i++;} while (i < 10);
10 的 n 次方
//10 100 1000 10000 100000var n = 5;var num = 1;for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {num *= 10; //num = num * 10}console.log(num); //100000
n 的阶乘
var n = 5;var num = 1;for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {num *= i; //num = num * i}console.log(num); //120
运算题:
求数字 789 反转后的数字 987
知识拓展:
被除数:789 除数:10 商数:78 余数:9
- 公式 1:除数 * 商数 + 余数 = 被除数
公式 2(被除数%除数 ):
- 商数 = 被除数 / 除数 (取整数)
- 余数 = 被除数 / 除数 (取小数 * 除数)
var num = 789;var a = num % 10; //789 % 10 = 9var b = (num - a) % 100 / 10; //(789 - 9) % 100 = 80var c = (num - a - b * 10) / 100; //(789 - 9 - 80) % 100 = 7console.log(a); //9console.log(b); //8console.log(c); //7console.log('' + a + b + c); //987
打印三个数中的最大的数
var a = 1,b = 2,c = 3;if (a > b) {if (a > c) {console.log(a);} else {console.log(c);}} else {if (b > c) {console.log(b);} else {console.log(c);}}//3
打印 100 以内的质数
质数:除了 1 和此整数自身外,没法被其他自然数整除的数。
100 以内的素数素数的规律如下:
- 个位是偶数的只有 2;
- 个位是 5 的只有 5;
- 个位是 1 的有 11、31、41、61、71,共 5 个;
- 个位是 3 的有 3、13、23、43、53、73、83,共 7 个;
- 个位是 7 的有 7、17、37、47、67、97,共 6 个;
- 个位是 9 的有 19、29、59、79、89,共 5 个。
注:个位十位数字相同的除了 11 外,其它都不是素数。
100 以内的素数共 25 个,如下: 2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,
47,53,59,61,67,71,73,79,83,89,97
//仅仅能被1 和自己整除的数var c = 0;//i 必须以2开始因为质数第一位是2//i < 100 100以内不包括100for (var i = 2; i < 100; i++) {//j 必须以1开始因为i % j 的时候i必须大于jfor (var j = 1; j <= i; j++) {//第1轮 2 % 1 == 0//第2轮 2 % 2 == 0//第3轮 2 % 3 == 2 跳出//第4轮 3 % 1 == 0//第5轮 3 % 2 == 1//第6轮 3 % 3 == 0//第7轮 3 % 4 == 3 跳出//第8轮 4 % 1 == 0//第9轮 4 % 2 == 0//第10轮 4 % 3 == 1//第11轮 4 % 4 == 0//第12轮 4 % 5 == 0//第13轮 5 % 1 == 0//第14轮 5 % 2 == 1//第14轮 5 % 3 == 2//第15轮 5 % 4 == 1//第16轮 5 % 5 == 0//第17轮 5 % 6 == 5 跳出//...if (i % j == 0) {c++;//第1轮 c = 0//第2轮 c = 1//第3轮 c = 2//第4轮 c = 0//第5轮 c = 1//第6轮 c = 1//第7轮 c = 2//第8轮 c = 0//第9轮 c = 1//第10轮 c = 2//第11轮 c = 2//第12轮 c = 3//第13轮 c = 0//第13轮 c = 1//第13轮 c = 1//第14轮 c = 1//第15轮 c = 1//第16轮 c = 1//第17轮 c = 2//...}}console.log(i, j, c);if (c == 2) {console.log('质数为:' + i);//2 3 5}c = 0;}
显式类型转换
任何 typeof的 typeof的结果都为 string
console.log(typeof (a)); //'undefined'console.log(typeof (123)); //'number'console.log(typeof ('')); //stringconsole.log(typeof (typeof (a))); //stringconsole.log(typeof (typeof (123))); //string
JS 的typeof()可能返回的值有:object/boolean/number/string/undefined/function
//JS的typeof可能返回的值有哪些?//object/boolean/number/string/undefinedconsole.log(typeof ('abc')); //stringconsole.log(typeof (1)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (true)); //booleanconsole.log(typeof (undefined)); //undefinedconsole.log(typeof (null)); //objectconsole.log(typeof ({})); //objectconsole.log(typeof ([])); //objectconsole.log(typeof (function () {})); //function
显式类型转换
number()
var a = '123';console.log(Number(a)); //123console.log(Number(a) + '-' + typeof (Number(a))); //123-numberconsole.log(typeof (Number(a)) + '-' + Number(a)); //number-123
Number()对字符串,undefined转化为NaN,对布尔值先转化为 0 或 1 再转化为数字,对null转为 0
console.log(Number('true')); //NaNconsole.log(Number(true)); //1console.log(Number(false)); //0console.log(Number(null)); //0console.log(Number(undefined)); //NaNconsole.log(Number('3.14')); //3.14console.log(typeof (NaN)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (1)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (0)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (0)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (NaN)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (3.14)); //numberconsole.log(typeof (Number('true')) + '-' + Number('true')); //number-NaNconsole.log(typeof (Number(true)) + '-' + Number(true)); //number-1console.log(typeof (Number(false)) + '-' + Number(false)); //number-0console.log(typeof (Number(null)) + '-' + Number(null)); //number-0console.log(typeof (Number(undefined)) + '-' + Number(undefined)); //number-NaNconsole.log(typeof (Number('3.14')) + '-' + Number('3.14')); //number-3.14
parseInt()
parseInt()把一个数转化整形,对true,false,null,字符串,undefined都转换为NaN
var a = '3.14';console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-3
var a = '123';console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-123var a = 'true';console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaNvar a = true;console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaN 这里parseInt()不管布尔值是否先转换为1,而是直接整形为NaNvar a = false;console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaN 这里parseInt()不管布尔值是否先转换为1,而是直接整形为NaNvar a = NaN;console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaNvar a = undefined;console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaNvar a = null;console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaNvar a = '123';console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-123var a = '';console.log(typeof (parseInt(a)) + '-' + parseInt(a)); //number-NaN
parseInt()如果是字符串开头得到的是NaN,数字开头得到截取数字开头的数字
var a = 'b';console.log(parseInt('abc123')); //NaNconsole.log(parseInt('123abc')); //123
关于十六进制:
0123456789abcdef
16 进制 -> 颜色值 16 值 HEX 颜色值 #fff or #f0f0f0
parseFloat()
console.log(parseFloat('3.14')); //3.14
保留小数点后两位
var num = parseFloat('3.1415926');console.log(num.toFixed(2)); //3.14(str) 四舍五入
string()
console.log(String(123)); //'123'console.log(typeof (String(123))); //stringconsole.log(typeof ('' + 123)); //stringconsole.log(typeof (123 + '')); //string
toString()
var str = '3.14';console.log(str.toString()); //3.14
undefined和null没有toString()方法
var str = undefined;var str = null;console.log(str.toString()); //报错
toString(radix)可以填写进制参数,以十进制为基础转化为目标进制
var str = '100';//以二进制为基础转化为十进制的数console.log(parseInt(str, 2)); //4//以十进制为基础转化为十六进制的数console.log(parseInt(str, 2).toString(16)); //4
Boolean()
console.log(Boolean(1)); //trueconsole.log(Boolean(null)); //falseconsole.log(Boolean(false)); //falseconsole.log(Boolean(undefined)); //falseconsole.log(Boolean(NaN)); //falseconsole.log(Boolean(0)); //falseconsole.log(Boolean('')); //false
隐式类型转换
加减乘除余
加号会将字符串转为数字
var a = '123'; //Number(a);a++;console.log(a); //124
字符串拼接会隐式将数字转变为字符串再拼接
var a = 'a'+ 1; //String(1);console.log(a); //a1
乘除余减都会由 string 转 number 的过程
var a = '3'* 2;console.log(a); //6
比较运算
遇到比较运算符先转换为 number
var a = '1' > 2;console.log(a); //falsevar a = 1 > '2';console.log(a); //false
两个字符串相比较的时候会转化为 ASCII 码
var a = 'a' > 'b';console.log(a); //false
相等==
var a = 1 == '1';console.log(a); //true
不等!=
var a = 1 != '2';console.log(a); //true
全等===不进行数据类型转换
var a = 1 === '1';console.log(a); //false
NaN不等于任何东西,连自己都不等
var a = NaN == NaN;console.log(a); //falsevar a = NaN === NaN;console.log(a); //false
//2 > 1 => true = 1 > 3 => falsevar a = 2 > 1 > 3;console.log(a); //false
//2 > 1 => true = 1 == 1 => truevar a = 2 > 1 == 1;console.log(a); //true
undefined跟数字相比较都为 false,null跟数字相比较都为 false,undefined跟null是相等关系但不是全等关系
var a = undefined > 0;console.log(a); //falsevar a = undefined < 0;console.log(a); //falsevar a = undefined == 0;console.log(a); //falsevar a = null > 0;console.log(a); //falsevar a = null < 0;console.log(a); //falsevar a = null == 0;console.log(a); //falsevar a = undefined == null;console.log(a); //true//undefined和null并不是一个数据类型var a = undefined === null;console.log(a); //false
isNaN()
可以判断是否为 非数字,都需要先进行Number()再判断
console.log(isNaN(NaN)); //trueconsole.log(isNaN(123)); //false//Number('123') => 123console.log(isNaN('123')); //falseconsole.log(isNaN('a')); //true//null => 0 不是非数字console.log(isNaN(null)); //false//Number(undefined) => NaNconsole.log(isNaN(undefined)); //true
ASCII 码
UNICODE码涵盖 ASCII码
注: 可以用
charCodeAt()方法查询
- 表 1 字符为一个字节对应 0-127
- 表 2 字符为两个字节对应 128-255
语法
//index 字符串中某个位置的数字,即字符在字符串中的下标。stringObject.charCodeAt(index);
严格模式
ES5开始有严格模式和非严格模式,IE9及以下不支持严格模式
'use strict'
//自己函数或模块里面写function test() {//最上一行'use strict';}
with改变作用域,在严格模式下不能用,性能低
// 'use strict';var a = 1;var obj = {a: 2};//with(作用域名称){}//严格模式不能使用with表达式function test() {var a = 3;with(test) {console.log(a); //3}with(obj) {console.log(a); //2}with(window) {console.log(a); //1}}test();
caller, callee,这些属性都不通过
'use strict';//caller calleefunction test1() {console.log(arguments.callee);}test1(1, 2, 3);//Uncaught TypeError: 'caller', 'callee', and 'arguments' properties may not be accessed on strict modefunction test2() {test3();}function test3() {console.log(arguments.caller);}//Uncaught TypeError: 'caller', 'callee', and 'arguments' properties may not be accessed on strict mode
严格模式下必须声明变量
'use strict';a = 1;//Uncaught ReferenceError: a is not defined
重复赋值报错
'use strict';var a = b = 1;//Uncaught ReferenceError: b is not defined
严格模式下函数内部this指向undefined,实例化后this指向对象本身
'use strict';//非严格模式指向windowfunction test() {console.log(this);}test(); //undefinednew test(); //test{}
call/apply
// 'use strict';function test() {console.log(this);}//非严格模式call()test.call(1); //指向包装类Number()对象test.call({}); //指向test对象//严格模式call()test.call(1); //指向1test.call({}); //指向{}
函数参数不能重复
'use strict';function test(a, a) {console.log(a);}test(1, 2);//非严格模式//2//严格模式//Uncaught SyntaxError: Duplicate parameter name not allowed in this context
对象属性名不允许重复
'use strict';var obj = {a: 1,a: 2}console.log(obj.a);//非严格模式//2//严格模式//2 不报错
错误信息
SyntaxError语法错误- 变量名不规范
- 关键字赋值
- 基本的语法错误
ReferenceError引用错误- 变量或者函数未被声明
- 给无法被赋值的对象赋值
RangeError范围错误TypeError类型错误URIError URI错误EvalErroreval函数执行错误
- 人为抛出的错误
//变量名不规范var 1 = 1;//Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected numbervar 1ab = 1;function 1 test() {}//Uncaught SyntaxError: Invalid or unexpected token
//关键字赋值new = 5;//Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token '='function = 1;//Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token '='
//基本的语法错误var a = 5://Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token ':'
//变量或者函数未被声明test();//Uncaught ReferenceError: test is not definedconsole.log(a);//Uncaught ReferenceError: a is not defined
//给无法被赋值的对象赋值var a = 1 = 2;console.log(a) = 1;//Uncaught SyntaxError: Invalid left-hand side in assignment
//RangeError范围错误//数组长度赋值为负数var arr = [1, 2, 3];arr.length = -1;console.log(arr);//Uncaught RangeError: Invalid array length//对象方法参数超出可行范围var num = new Number(66.66);console.log(num.toFixed(-1));//Uncaught RangeError: toFixed() digits argument must be between 0 and 100
//TypeError 类型错误//调用不存在的方法123();//Uncaught TypeError: 123 is not a functionvar obj = {};obj.say();//Uncaught TypeError: obj.say is not a function//实例化原始值var a = new 'string';var a = new 123;//Uncaught TypeError: "string" is not a constructor
关于 URL:
//URIError URI错误//URI: UNIFORM RESOURCE IDENTIFIER 统一资源标识符//URL: UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR 统一资源定位符//URN: UNIFORM RESOURCE NAME 统一资源名称//URL和URN属于URI//URL: http://www.baidu.com/news#today 协议+域名+资源空间// ftp://www.baidu.com/ftp#developer//URN: www.baidu.com/ftp#developer 代表资源唯一的标识 -> ID// href="tel:13900000000"
//URLError URI错误var myUrl = 'http://www.baidu.cin?name=哈哈哈';//把中文字转化为中文编码字符var newUrl = encodeURI(myUrl);console.log(newUrl);//http://www.baidu.cin?name=%E5%93%88%E5%93%88%E5%93%88//把中文编码字符转化为中文字var newNewUrl = decodeURI(newUrl);console.log(newNewUrl);//http://www.baidu.cin?name=哈哈哈var str = decodeURI('%fsdcf%');//Uncaught URIError: URI malformed
//人为抛出的错误var error = new Error();var error2 = new SyntaxError();var error3 = new ReferenceError();var error4 = new TypeError();
异常捕获
try..catch..手动抛出错误方法来避免程序遇到错误终止执行
//try正常执行没有错误的时候不走catchtry {console.log('正常执行1');console.log(a);console.log(b);console.log('正常执行2');//捕获} catch (e) {console.log(e); //'ReferenceError: a is not defined'//不管有错没错都会执行} finally {console.log('正常执行3');}console.log('正常执行4');//正常执行1//'ReferenceError: a is not defined'//正常执行3//正常执行4
案例:
//JSON字符串var jsonStr = '';try {console.log('我要执行了!');var json = JSON.parse(jsonStr);console.log(json);} catch (e) {var errorTip = {name: '数据传输失败',errorCode: '10010'}console.log(errorTip);//{name: "数据传输失败", errorCode: "10010"}}
throw
//JSON字符串var jsonStr = '';try {if (jsonStr == '') {throw 'JSON字符串为空';}console.log('我要执行了!');var json = JSON.parse(jsonStr);console.log(json);} catch (e) {console.log(e); //JSON字符串为空var errorTip = {name: '数据传输失败',errorCode: '10010'}console.log(errorTip);//{name: "数据传输失败", errorCode: "10010"}}
垃圾回收
垃圾回收原理:
- 找出不再使用的变量
- 释放其占用内存
- 固定的时间间隔运行
//标记清除: mark and sweepfunction test() {var a = 0; //进入环境}test(); //a 标记为 离开环境//引用计数 reference counting//次数为0 回收function test() {var a = new Object(); //a = 1;var b = new Object(); //b = 1;var c = a; //a++ = 2var c = b; //a-- = 1//循环引用a.prop = b; //b = 2;b.prop = a; //b = 2;a = null;b = null;}

