概览

声明式编程思维

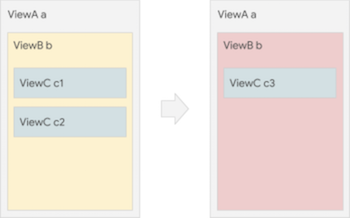
// Imperative styleb.setColor(red)b.clearChildren()ViewC c3 = new ViewC(...)b.add(c3)
// Declarative stylereturn ViewB( color: red, child: ViewC(...),)
直观认识State

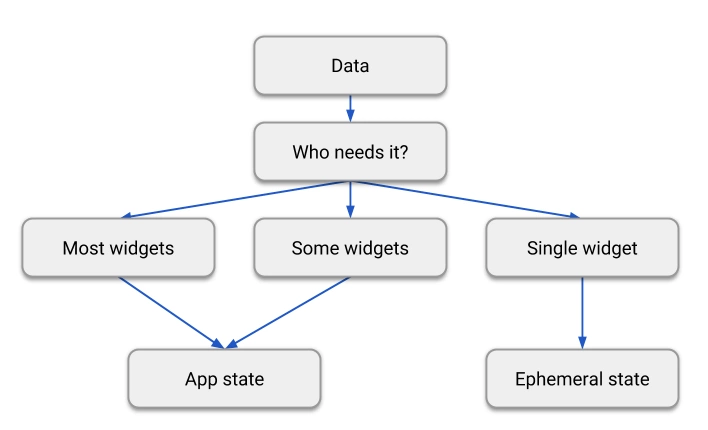
状态的分类
- 短暂状态 ephemeral state (əˈfem(ə)rəl)
- 应用状态 app state
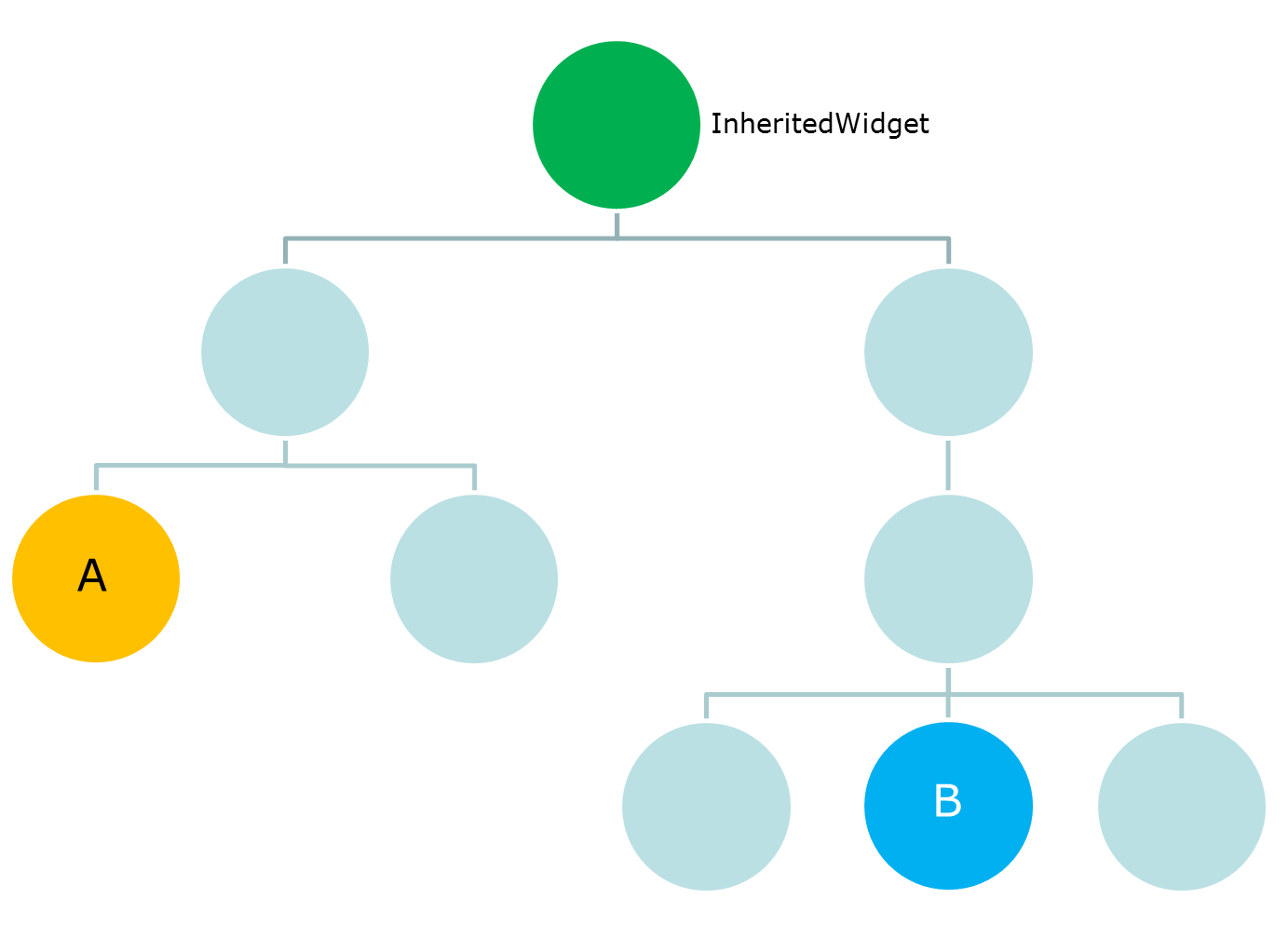
ShoppingCartDemo (使用InheritedWidget)
点击查看【bilibili】

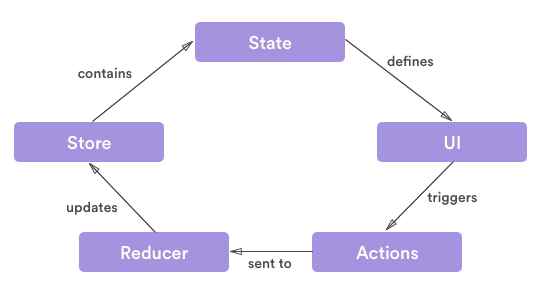
Redux
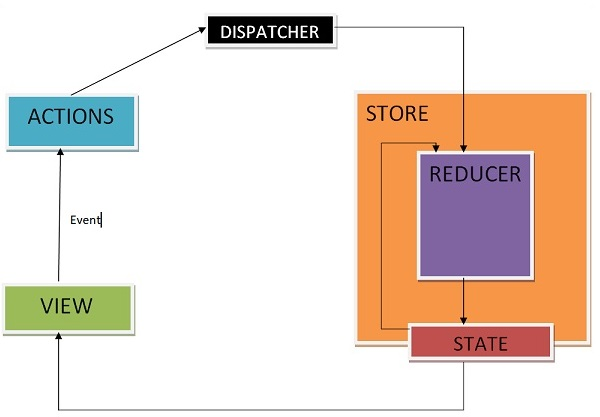
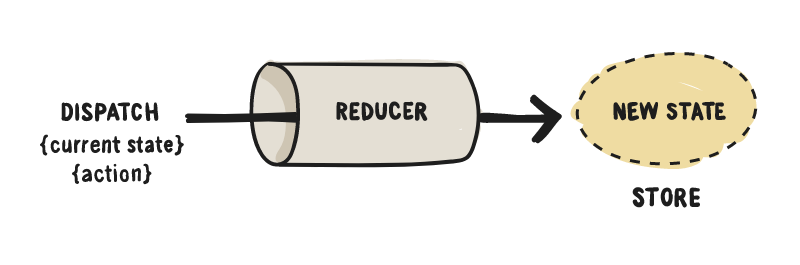
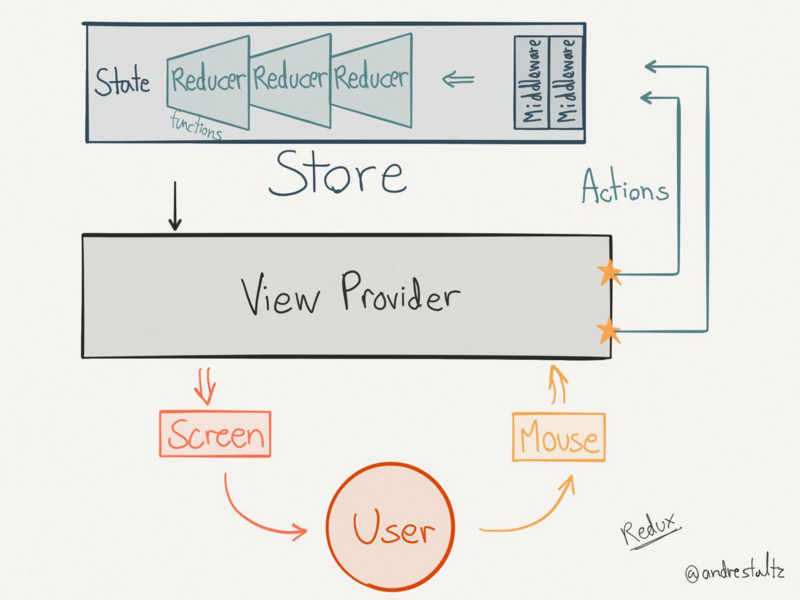
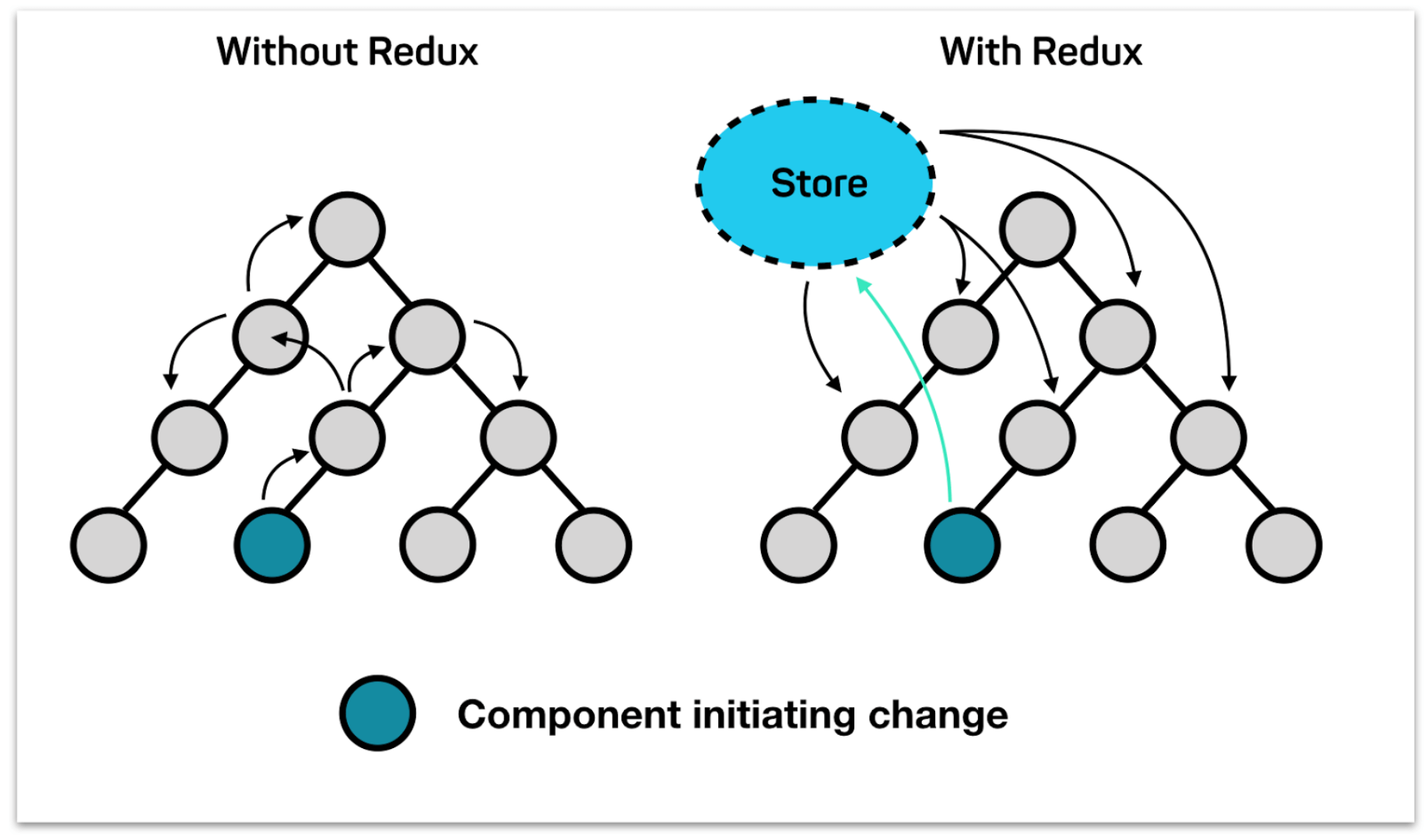
import 'dart:async';/// Defines an application's state change////// Implement this typedef to modify your app state in response to a given/// action.////// ### Example////// int counterReducer(int state, action) {/// switch (action) {/// case 'INCREMENT':/// return state + 1;/// case 'DECREMENT':/// return state - 1;/// default:/// return state;/// }/// }////// final store = new Store<int>(counterReducer);typedef Reducer<State> = State Function(State state, dynamic action);/// Defines a [Reducer] using a class interface.////// Implement this class to modify your app state in response to a given action.////// For some use cases, a class may be preferred to a function. In these/// instances, a ReducerClass can be used.////// ### Example////// class CounterReducer extends ReducerClass<int> {/// int call(int state, action) {/// switch (action) {/// case 'INCREMENT':/// return state + 1;/// case 'DECREMENT':/// return state - 1;/// default:/// return state;/// }/// }/// }////// final store = new Store<int>(new CounterReducer());abstract class ReducerClass<State> { /// The [Reducer] function that converts the current state and action into a /// new state State call(State state, dynamic action);}/// A function that intercepts actions and potentially transform actions before/// they reach the reducer.////// Middleware intercept actions before they reach the reducer. This gives them/// the ability to produce side-effects or modify the passed in action before/// they reach the reducer.////// ### Example////// loggingMiddleware(Store<int> store, action, NextDispatcher next) {/// print('${new DateTime.now()}: $action');////// next(action);/// }////// // Create your store with the loggingMiddleware/// final store = new Store<int>(/// counterReducer,/// middleware: [loggingMiddleware],/// );typedef Middleware<State> = dynamic Function( Store<State> store, dynamic action, NextDispatcher next,);/// Defines a [Middleware] using a Class interface.////// Middleware intercept actions before they reach the reducer. This gives them/// the ability to produce side-effects or modify the passed in action before/// they reach the reducer.////// For some use cases, a class may be preferred to a function. In these/// instances, a MiddlewareClass can be used.////// ### Example/// class LoggingMiddleware extends MiddlewareClass<int> {/// call(Store<int> store, action, NextDispatcher next) {/// print('${new DateTime.now()}: $action');////// next(action);/// }/// }////// // Create your store with the loggingMiddleware/// final store = new Store<int>(/// counterReducer,/// middleware: [new LoggingMiddleware()],/// );abstract class MiddlewareClass<State> { /// A [Middleware] function that intercepts a dispatched action dynamic call(Store<State> store, dynamic action, NextDispatcher next);}/// The contract between one piece of middleware and the next in the chain. Use/// it to send the current action in your [Middleware] to the next piece of/// [Middleware] in the chain.////// Middleware can optionally pass the original action or a modified action to/// the next piece of middleware, or never call the next piece of middleware at/// all.typedef NextDispatcher = dynamic Function(dynamic action);/// Creates a Redux store that holds the app state tree.////// The only way to change the state tree in the store is to [dispatch] an/// action. the action will then be intercepted by any provided [Middleware]./// After running through the middleware, the action will be sent to the given/// [Reducer] to update the state tree.////// To access the state tree, call the [state] getter or listen to the/// [onChange] stream.////// ### Basic Example////// // Create a reducer/// final increment = 'INCREMENT';/// final decrement = 'DECREMENT';////// int counterReducer(int state, action) {/// switch (action) {/// case increment:/// return state + 1;/// case decrement:/// return state - 1;/// default:/// return state;/// }/// }////// // Create the store/// final store = new Store<int>(counterReducer, initialState: 0);////// // Print the Store's state./// print(store.state); // prints "0"////// // Dispatch an action. This will be sent to the reducer to update the/// // state./// store.dispatch(increment);////// // Print the updated state. As an alternative, you can use the/// // `store.onChange.listen` to respond to all state change events./// print(store.state); // prints "1"class Store<State> { /// The [Reducer] for your Store. Allows you to get the current reducer or /// replace it with a new one if need be. Reducer<State> reducer; final StreamController<State> _changeController; State _state; List<NextDispatcher> _dispatchers; /// Creates an instance of a Redux Store. /// /// The [reducer] argument specifies how the state should be changed in /// response to dispatched actions. /// /// The optional [initialState] argument defines the State of the store when /// the Store is first created. /// /// The optional [middleware] argument takes a list of [Middleware] functions /// or [MiddlewareClass]. See the [Middleware] documentation for information /// on how they are used. /// /// The [syncStream] argument allows you to use a synchronous /// [StreamController] instead of an async `StreamController` under the hood. /// By default, the Stream is async. Store( this.reducer, { State initialState, List<Middleware<State>> middleware = const [], bool syncStream = false, /// If set to true, the Store will not emit onChange events if the new State /// that is returned from your [reducer] in response to an Action is equal /// to the previous state. /// /// Under the hood, it will use the `==` method from your State class to /// determine whether or not the two States are equal. bool distinct = false, }) : _changeController = StreamController.broadcast(sync: syncStream) { _state = initialState; _dispatchers = _createDispatchers( middleware, _createReduceAndNotify(distinct), ); } /// Returns the current state of the app State get state => _state; /// A stream that emits the current state when it changes. /// /// ### Example /// /// // First, create the Store /// final store = new Store<int>(counterReducer, 0); /// /// // Next, listen to the Store's onChange stream, and print the latest /// // state to your console whenever the reducer produces a new State. /// // /// // We'll store the StreamSubscription as a variable so we can stop /// // listening later. /// final subscription = store.onChange.listen(print); /// /// // Dispatch some actions, and see the printing magic! /// store.dispatch("INCREMENT"); // prints 1 /// store.dispatch("INCREMENT"); // prints 2 /// store.dispatch("DECREMENT"); // prints 1 /// /// // When you want to stop printing the state to the console, simply /// `cancel` your `subscription`. /// subscription.cancel(); Stream<State> get onChange => _changeController.stream; // Creates the base [NextDispatcher]. // // The base NextDispatcher will be called after all other middleware provided // by the user have been run. Its job is simple: Run the current state through // the reducer, save the result, and notify any subscribers. NextDispatcher _createReduceAndNotify(bool distinct) { return (dynamic action) { final state = reducer(_state, action); if (distinct && state == _state) return; _state = state; _changeController.add(state); }; } List<NextDispatcher> _createDispatchers( List<Middleware<State>> middleware, NextDispatcher reduceAndNotify, ) { final dispatchers = <NextDispatcher>[]..add(reduceAndNotify); // Convert each [Middleware] into a [NextDispatcher] for (var nextMiddleware in middleware.reversed) { final next = dispatchers.last; dispatchers.add( (dynamic action) => nextMiddleware(this, action, next), ); } return dispatchers.reversed.toList(); } /// Runs the action through all provided [Middleware], then applies an action /// to the state using the given [Reducer]. Please note: [Middleware] can /// intercept actions, and can modify actions or stop them from passing /// through to the reducer. dynamic dispatch(dynamic action) { return _dispatchers[0](action); } /// Closes down the Store so it will no longer be operational. Only use this /// if you want to destroy the Store while your app is running. Do not use /// this method as a way to stop listening to [onChange] state changes. For /// that purpose, view the [onChange] documentation. Future teardown() async { _state = null; return _changeController.close(); }}
更多阅读












