1 获取连接Session
1.1 构造session对象
X DevAPI session是建立在传统mysql连接基础上的高层次会话,使用MySql X protocol,支持DevAPI中全部操作和部分SQL语言功能。
我们可以直接传递参数构造一个session对象,示例如下:
#include <iostream>#include <mysqlx/xdevapi.h>using namespace std;using namespace mysqlx;int main(){//利用大括号,session在括号结束时自动close连接并释放资源{Session sess("localhost", 33060, "barret", "newpasswd");Schema db = sess.getSchema("world_x"); //获取数据库// or Schema db(sess, "test");}}
也可以通过SessionSetting设置参数,再创建session对象:
SessionSettings settings(SessionOption::HOST,"localhost",SessionOption::PORT, 33060);settings.set(SessionOption::USER, "barret");settings.set(SessionOption::PWD, "newpasswd");Session mySession(settings);Schema myDb= mySession.getSchema("world_x");
我们可以用URI的格式尝试连接多个server,最后会返回按优先级排列的连接成功的session,URI格式如下:
user:password@[(address=[host]:[port], priority=value), (address=[host]:[port], priority=value) ..]
1.2 connection pooling
X DevAPI支持connection pooling,可以避免反复的创建释放数据库连接。connection pool的生命周期依赖Client对象,当Client对象析构时,pool就不复存在了。
pool的配置如下:
| Option | Meaning | Default |
|---|---|---|
| enabled | Connection pooling enabled. When the option is set to false, a regular, non-pooled connection is returned, and the other connection pool options listed below are ignored. | true |
| maxSize | The maximum number of connections allowed in the pool | 25 |
| maxIdleTime | The maximum number of milliseconds a connection is allowed to idle in the queue before being closed. A zero value means infinite. | 0 |
| queueTimeout | The maximum number of milliseconds a request is allowed to wait for a connection to become available. A zero value means infinite | 0 |
使用示例如下:
int main(){/*( "mysqlx://user:password@host_name/db_name",ClientOption::POOLING, true,ClientOption::POOL_MAX_SIZE, max_connections,ClientOption::POOL_QUEUE_TIMEOUT, std::chrono::seconds(100),ClientOption::POOL_MAX_IDLE_TIME, std::chrono::microseconds(1)*/Client cli("mysqlx://barret:shidandan1230@localhost/world_x", ClientOption::POOL_MAX_SIZE, 7);Session sess = cli.getSession();// use Session sess as usualcli.close(); // close all Sessions}
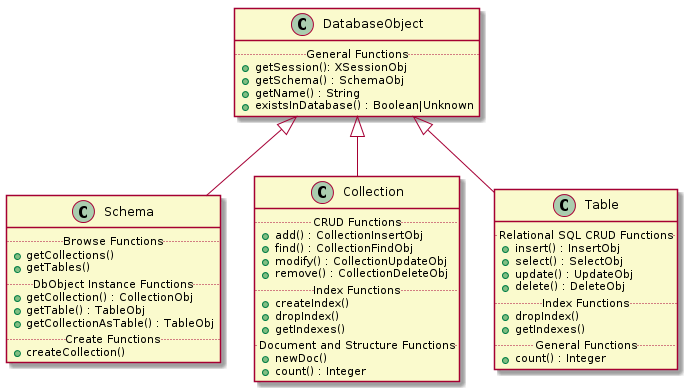
2 获取数据库对象Schema
通过session的函数getSchema()或getDefaultSchema()可以获取到Schema对象。可以把Schema当作是DB对象,Schema是访问操作数据表的基本结构。
简单示例如下:
int main(){Session sess("localhost", 33060, "barret", "newpasswd");//获取所有的数据库并打印namestd::list<Schema> schemaList = sess.getSchemas();cout << "Available schemas in this session:" << endl;for (Schema schema : schemaList){cout << schema.getName() << endl;}Schema db = sess.getSchema("world_x"); //获取指定数据库Table table = db.getTable("city");//获取表cout<<"row count of city table is "<<table.count()<<endl;}
3 执行原始SQL语句
通过session.sql()函数,我们可以执行原始的SQL语句:
//使用session的sql函数,执行原始SQL语句#include <iostream>#include <mysqlx/xdevapi.h>using namespace std;using namespace mysqlx;int main(){try{Session sess("localhost", 33060, "barret", "shidandan1230");cout << "Session accepted, creating collection..." << endl;sess.sql("use world_x").execute(); //使用url不需要这句//执行一个select语句并打印结果RowResult rs = sess.sql("SELECT ID, Name, CountryCode FROM city where ID <10").execute();for (auto it = rs.begin(); it != rs.end(); ++it){cout << (*it).get(0).get<int>() << " ";cout << (*it).get(1).get<std::string>() << " ";cout << (*it).get(2).get<std::string>();cout << endl;}}catch (const Error &e){cout << e.what() << endl;}return 0;}
4 CRUD基本函数
DevAPI提供了如下函数,用于对collection和table执行CRUD操作:
| Operation | Document | Relational |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Collection.add() | Table.insert() |
| Read | Collection.find() | Table.select() |
| Update | Collection.modify() | Table.update() |
| Delete | Collection.remove() | Table.delete() |
比如我们可以用select函数查询city table代替上一节中的原始sql示例:
//使用API提供的函数读取表内容,这里不是用原始SQL#include <iostream>#include <mysqlx/xdevapi.h>using namespace std;using namespace mysqlx;int main(){try{Session sess("localhost", 33060, "barret", "shidandan1230");cout << "Session accepted, creating collection..." << endl;Schema db = sess.getSchema("world_x");Table city = db.getTable("city"); //获取数据表RowResult rs = city.select("ID", "Name", "CountryCode").where("ID < 10").execute();for (auto it = rs.begin(); it != rs.end(); ++it){cout << (*it).get(0).get<int>() << " ";cout << (*it).get(1).get<std::string>() << " ";cout << (*it).get(2).get<std::string>();cout << endl;}}catch (const Error &e){cout << e.what() << endl;}return 0;}
Note: 默认的execute是同步操作,会一直阻塞等待SQL的执行结果。我们可以通过callbacks, Promises或explicitly waiting来实现异步执行。但是C++API并不支持异步,可以使用C#或java实现异步。
5 参数绑定
在使用CRUD各个函数时,我们可以使用bind()函数绑定SQL中的参数,这样就不需要费心的组装SQL字符串了。
对每一个参数,在CRUD函数中使用:name形式指定参数名,并在bind函数中通过name指定value(一般bind只能绑定一个参数,不需要考虑顺序)。
示例如下:
try{Session sess("localhost", 33060, "barret", "shidandan1230");cout << "Session accepted, creating collection..." << endl;Schema db = sess.getSchema("world_x");Table city = db.getTable("country"); //获取数据表//使用1,bind绑定参数// RowResult rs = city.select().where("Name = :param1").bind("param1", "China").execute();//使用2,可以通过bind和execute将一个操作重复执行多次:auto statement = city.select().where("Name = :param1");RowResult rs = statement.bind("param1", "China").execute();//打印结果rs = statement.bind("param1", "United States").execute();//打印结果}
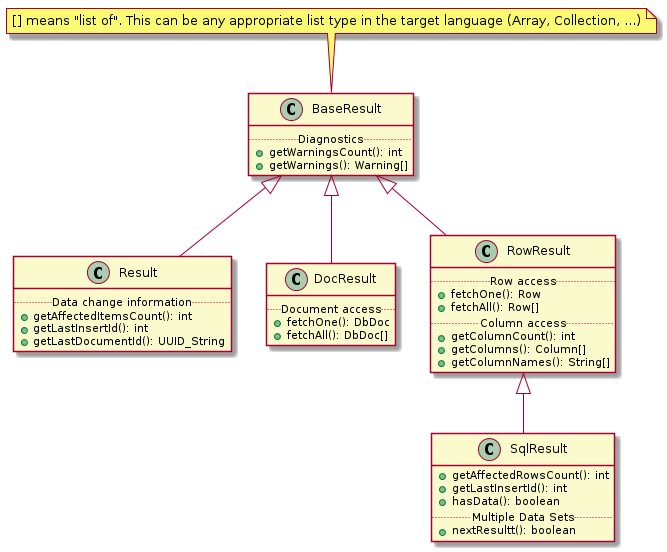
6 查询结果处理