开发环境
为了让成员的代码符合团队的规则,并且样式保持一致,建议使用 ESlint 和 Prettier。
1. ESLint
ESLint 是一个 JavaScript Lint,帮助我们规范代码质量,提高开发效率。
安装依赖
eslint:JavaScript 代码检测工具@typescript-eslint/parser:将 TS 转化成 ESTree,使能被 eslint 所识别@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin:TS 规则列表,其中的每一条规则都可进行打开或关闭yarn add eslint @typescript-eslint/parser @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin -D
配置 .eslintrc.js
module.export = { // 解析器 parser: "@typescript-eslint/parser", // 继承的扩展 extends: ["plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended", "react-app"], // 插件 plugins: ["@typescript-eslint", "react"], // 规则 rules: {} }2. Prettier
Prettier 能够统一团队的编码风格,统一的代码风格有助于保证代码的可读性。
安装依赖
prettier: 按配置格式化代码eslint-config-prettier: 将禁用任何可能干扰现有 prettier 规则的 linting 规则eslint-plugin-prettier: 将作为 ESlint 的一部分运行 Prettier 分析yarn add prettier eslint-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier -D配置 .eslintrc.js
module.export = { // 解析器 parser: "@typescript-eslint/parser", // 继承的扩展 extends: ["plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended", "react-app", "plugin:prettier/recommended"], // 插件 plugins: ["@typescript-eslint", "react"], // 规则 rules: {} }配置 .prettierrc
{ "singleQuote": true, "trailingComma": "es5", "printWidth": 80, "semi": true, "tabWidth": 4, "useTabs": false }3. VSCode 编辑器
在 workspace settings 中配置检测文件范围,确保 react 项目中.ts和.tsx文件有 lint 自动修复功能。{ "eslint.validate": [ "javascript", "javascriptreact", { "language": "typescript", "autoFix": true }, { "language": "typescriptreact", "autoFix": true } ] }
TS React 图谱
基础篇
实战篇
环境搭建
同上,第一篇幅。
组件与类型
- 函数组件
函数组件一般只需要约束 props 参数。
import React from 'react';
import { Button } from 'antd';
interface Greeting {
name: string;
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
}
const Welcome = (props: Greeting) => <Button>Hello {props.name}</Button>
export default Welcome
- 类组件
类组件除了需要约束 props 参数外,还需要给 state 进行定义。如果有可选参数,需要定义默认值,类组件中使用 static 关键字。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Button } from 'antd';
interface Greeting {
name: string;
firstName?: string;
lastName?: string;
}
interface WelcomeState {
count: number
}
class WelcomeClass extends Component<Greeting, WelcomeState> {
state: WelcomeState = {
count: 0
}
// 给可选参数定义默认值
static defaultProps = {
firstName: '',
lastName: ''
}
render() {
return (
<>
<p>你点击了 {this.state.count} 次</p>
<Button onClick={() => {this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1})}}>
Hello {this.props.name}
</Button>
</>
)
}
}
export default WelcomeClass;
- 高阶组件
高阶函数需要使用 ts 范型约束传进来的组件,使用类型断言来约束 props。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
interface Loading {
loading: boolean
}
function WelcomeHOC<P> (WrappedComponent: React.ComponentType<P>) {
return class extends Component<P & Loading> {
render () {
const { loading, ...props } = this.props;
return loading ? <div>Loading...</div> : <WrappedComponent { ...props as P } />;
}
}
}
export default WelcomeHOC
- hooks
hooks 函数组件需要约束 props 参数。
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react'
import { Button } from 'antd'
interface Greeting {
name: string
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
}
const WelcomeHooks = (props: Greeting) => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const [text, setText] = useState<string | null>(null)
useEffect(() => {
if (count > 5) {
setText('休息一下')
}
}, [count])
return (
<>
<p>你点击了 {count} 次 {text}</p>
<Button onClick={() => {setCount(count + 1)}}>
Hello {props.name}
</Button>
</>
)
}
WelcomeHooks.defaultProps = {
firstName: '',
lastName: ''
}
export default WelcomeHooks
事件与类型
// 普通原生事件,类型定义
export default class Button<P, S> extends React.Component<P, S> {
public handleClick = (e: React.MouseEvent) => {
console.log(e.screenX, e.screenY)
console.log(this.getVal(5))
}
private getVal = (x: number): number => {
return x * x
}
public render() {
return (
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>
content
</div>
)
}
}
class中推荐各种数据与方法的书写顺序
[
"public-static-field",
"protected-static-field",
"private-static-field",
"static-field",
"public-static-method",
"protected-static-method",
"private-static-method",
"static-method",
"public-instance-field",
"protected-instance-field",
"private-instance-field",
"public-field",
"protected-field",
"private-field",
"instance-field",
"field",
"constructor",
"public-instance-method",
"protected-instance-method",
"private-instance-method",
"public-method",
"protected-method",
"private-method",
"instance-method",
"method"
]
数据请求
// ajax.d.js
declare namespace Ajax {
export interface Data<T>{
pageObject: T[],
pageIndex: number,
pageSize: number,
totalPage: number,
totalCount: number,
}
export interface AjaxResponse{
code: number,
msg: string,
title?: string,
}
// boolean number string number object
export interface AjaxResponseStr<T> extends AjaxResponse{
data: T,
}
// 列表页
export interface AjaxResponseList<T> extends AjaxResponse {
data: Data<T>,
}
}
import 'whatwg-fetch';
import * as Antd from 'antd';
import queryString from 'query-string';
let baseUrl = 'http://boss-test.intra.xiaojukeji.com';
if (/boss-pre.am.intra.xiaojukeji.com/.test(location.host)) {
baseUrl = 'http://boss-pre.am.intra.xiaojukeji.com';
}
if (/boss.xiaojukeji.com/.test(location.host)) {
baseUrl = 'http://boss.xiaojukeji.com';
}
const { notification } = Antd;
const codeMessage = {
200: '服务器成功返回请求的数据。',
201: '新建或修改数据成功。',
202: '一个请求已经进入后台排队(异步任务)。',
204: '删除数据成功。',
400: '发出的请求有错误,服务器没有进行新建或修改数据的操作。',
401: '用户没有权限(令牌、用户名、密码错误)。',
403: '用户得到授权,但是访问是被禁止的。',
404: '发出的请求针对的是不存在的记录,服务器没有进行操作。',
406: '请求的格式不可得。',
410: '请求的资源被永久删除,且不会再得到的。',
422: '当创建一个对象时,发生一个验证错误。',
500: '服务器发生错误,请检查服务器。',
502: '网关错误。',
503: '服务不可用,服务器暂时过载或维护。',
504: '网关超时。'
};
function isValidKey(key: number | string, obj: {}): key is keyof typeof obj {
return key in obj;
}
function checkStatus(response: Response) {
if (response.status >= 200 && response.status < 300) {
return response;
}
let errortext;
if (isValidKey(response.status, codeMessage)) {
errortext = codeMessage[response.status] || response.statusText;
}
notification.error({
message: `请求错误 ${response.status}: ${response.url}`,
description: errortext
});
const error = new Error(errortext);
error.name = String(response.status);
throw error;
}
export default function request<T>(url: string, options?: object) {
const defaultOptions = {
credentials: 'include',
headers: {},
};
const newOptions: any = { ...defaultOptions, ...options };
const { method = 'get' } = newOptions;
if (
method.toUpperCase() === 'POST' ||
method.toUpperCase() === 'PUT' ||
method.toUpperCase() === 'DELETE'
) {
if (!(newOptions.body instanceof FormData)) {
newOptions.headers = {
Accept: 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
...newOptions.headers
};
// 判断
for (let key in newOptions.headers) {
if (newOptions.headers.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
if (
key === 'Content-Type' &&
newOptions.headers[key] === 'application/json; charset=utf-8'
) {
newOptions.body = JSON.stringify(newOptions.body);
break;
}
}
}
} else {
newOptions.headers = {
Accept: 'application/json',
...newOptions.headers
};
}
}
if (newOptions.params !== undefined) {
url = url + '?' + queryString.stringify({ ...newOptions.params });
}
return new Promise((res: (value: T) => void, rej: (value?: any) => void) => {
fetch(/^https|http/.test(url) ? url : baseUrl + url, newOptions)
.then(checkStatus)
.then(response => {
if (newOptions.method === 'DELETE' || response.status === 204) {
return response.text();
}
return response.json();
})
.then((response) => {
if (response.code === 10003 || response.status === 10008) {
window.location.href = baseUrl;
} else if (response.code !== 10000) {
notification.error({
message: response.msg,
});
rej(response);
}
res(response);
})
.catch(e => {
rej(e);
});
});
}
Redux 与类型
进行中…
工程篇
命名空间
*在一个模块化的系统中,是可以不需要使用命名空间的。
namespace 命名空间(之前又叫内部空间),目标是解决重名问题。
举例子,你项目中需要验证表单里的用户输入,这时你想要写一套验证器,一般的做法会在 utils 文件中新建一个 validation 文件,将所有的验证方法集中编写并导出。随着验证器的不断增多,可能你会开始担心与其它对象产生命名冲突,为了避免全局污染,TS 希望我们把所有验证器包裹到一个命名空间内,而不是放在全局命名空间下。
// validation.ts
namespace Validation {
const lettersRegexp = /^[A-Za-z]+$/
const numberRegexp = /^[0-9]+$/
// 定义一个字符串验证器
export interface StringValidator {
isAcceptable(s: string): boolean
}
// 定义一个使用字符串验证器实现的文本验证器类
export class LettersOnlyValidator implements StringValidator {
isAcceptable (s: string) {
return lettersRegexp.test(s)
}
}
// 定义一个使用字符串验证器实现的ZipCode验证器类
export class ZipCodeValidator implements StringValidator {
isAcceptable (s: string) {
return s.length === 5 && numberRegexp.test(s)
}
}
}
使用时我们可以将 validation.ts 编译成 validation.js,然后在 index.html 中引入使用。
tsc valition.ts
<script type="text/javascript" src="./validation.js"><script>
利用别名来简化命名空间操作:
// 接上面 valuation.ts
import lettersOnlyValidator = Validation.LettersOnlyValidator
let lov = new lettersOnlyValidator()
声明合并
*申明合并更重要的是为了兼容老的项目,我们建议将申明放在一起
如果定义了多个相同名字的函数、接口申明,那么编译器会将相同名字的申明合并为一个申明。好处是可以将程序中散落各处的重名申明合并在一起,这样在使用时候对这个多处的定义同时具有感知能力,避免对接口成员的遗漏。
函数合并
function reverse(x: number): number
function reverse(x: string): string
function reverse(x: number | string): number | string {
if (typeof x === 'number') {
return Number(x.toString().split('').reverse().join(''))
} else if (typeof x === 'string') {
return x.split('').reverse().join('')
}
return ''
}
console.log(reverse(123))
接口合并**
interface People {
name: string
}
interface People {
age: number
}
let people: People = {
name: 'allen',
age: 26
}
console.log(people) // { name: 'allen', age: 26 }
相当于:
interface People {
name: string
age: number
}
let people: People = {
name: 'allen',
age: 26
}
console.log(people) // { name: 'allen', age: 26 }
注意,合并的属性的类型必须都是一致的:
interface People {
name: string
height: number
}
interface People {
age: number,
height: number // 重复的属性,但拥有相同的类型,不会报错
}
interface People {
name: string
height: number
}
interface People {
age: number,
height: string // Subsequent property declarations must have the same type. Property 'height' must be of type 'number', but here has type 'string'.
}
接口中方法合并,同上函数合并具有函数重载:
interface People {
name: string
say(lang: string): string // 顺序2
}
interface People {
age: number,
say(lang: string[]): string[] // 顺序1
}
相当于:
interface People {
name: string
age: number,
say(lang: string[]): string[]
say(lang: string): string,
}
命名空间的合并**
// *命名空间必须放在后面
// 函数与命名空间
function Lib () {}
namespace Lib {
export let version = '1.0'
}
console.log(Lib.version) // 1.0
// 类与命名空间
class Lib {}
namespace Lib {
export let state = 1
}
console.log(Lib.state) // 1
// 枚举与命名空间
enum Color {
Red,
Yellow,
Blue
}
namespace Color {
export function mixin () {}
}
console.log(Color)
/**
{ '0': 'Red',
'1': 'Yellow',
'2': 'Blue',
Red: 0,
Yellow: 1,
Blue: 2,
mixin: [Function: mixin] }
*/
如何编写申明文件
在使用 Typescript 时,有时候我们需要用到第三方库,比如说 jquery。如果我们按照非 Typescript 项目的方式使用 jquery 会是这样的:
import $ from 'jquery'
// 抛错
/**
Could not find a declaration file for module 'jquery'. '/Users/didi/selfspace/react-ts-practices/node_modules/jquery/dist/jquery.js' implicitly has an 'any' type.
Try `npm install @types/jquery` if it exists or add a new declaration (.d.ts) file containing `declare module 'jquery';`ts(7016)
*/
意思是没有找到 jquery 的申明文件,需要安装 @types/jquery。很幸运,一般的库官方都已经提供了申明文件。我们只需要同时安装:
npm install @types/jquery
你使用的第三方库是否有官方提供的申明文件,可以通过 http://microsoft.github.io/TypeSearch/ 网站查。
那如果没有申明文件的时候,你就需要自己写了,这也是给社区贡献代码的好时候。
全局类库global-lib.js
function globalLib(options) {
console.log(options)
}
globalLib.version = '1.0.0'
globalLib.doSomething = function () {
console.log('globalLib do something')
}
同级编写一个申明文件 global-lib.d.ts
declare function globalLib(options: globalLib.Options): void
declare namespace globalLib {
const version: string
function doSomething(): void
interface Options {
[key: string]: any
}
}
模块库**
module-lib.js
const version = '1.0.0'
function doSomething() {
console.log('moduleLib do something')
}
function moduleLib(options) {
console.log(options)
}
moduleLib.version = version
moduleLib.doSomething = doSomething
module.exports = moduleLib
同级编写一个申明文件 module-lib.d.ts
declare function moduleLib(options: Options): void
declare namespace moduleLib {
const version: string
function doSomething(): void
interface Options {
[key: string]: any
}
}
export = moduleLib
UMD库**umd-lib.js
(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
define(factory)
} else if (typeof module === 'object' && module.exports) {
module.exports = factory()
} else {
root.umdLib = factory()
}
}(this, function () {
return {
version: '1.0.0',
doSomething() {
console.log('umdLib do something')
}
}
}))
同级编写一个申明文件 umd-lib.d.ts
declare namespace umdLib {
const version: string
function doSomething(): void
}
export as namespace umdLib
export = umdLib
tsconfig.json 配置
{
"compilerOptions": {
/** 输出代码 ES 版本,可以是 ["es3", "es5", "es2015", "es2016", "es2017", "esnext"] */
"target": "es5",
/** 引入库定义文件 */
"lib": [
"dom",
"dom.iterable",
"esnext"
],
/** 允许编译时有 js 文件 */
"allowJs": true,
/** 对库定义文件跳过类型检查 */
"skipLibCheck": true,
/** 支持从 CommonJS/AMD/UMD 默认导入,并且可以正常工作。 */
"esModuleInterop": true,
/** 允许引入没有默认导出的模块 */
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
/** 同时开启 alwaysStrict, noImplicitAny, noImplicitThis 和 strictNullChecks */
"strict": true,
/** 不允许不同变量来代表同一文件 */
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
/** 指定模块生成方式 */
"module": "esnext",
/** 指定模块解析方式 */
"moduleResolution": "node",
/** 是否允许把 json 文件当做模块进行解析 */
"resolveJsonModule": true,
/** 每个文件需要是一个模块 */
"isolatedModules": true,
/** 不生成编译文件,即不生成 js */
"noEmit": true,
/** jsx 的编译方式 */
"jsx": "react"
},
/** 只编译 src 目录下文件 */
"include": [
"src"
]
}
目录模板
.
├── README.md
├── config
├── mock
├── package.json
├── scripts
├── src
│ ├── app.ts
│ ├── assets
│ ├── components
│ ├── constants
│ ├── global.less
│ ├── global.ts
│ ├── helper
│ ├── layouts
│ ├── models
│ ├── pages
│ ├── routes
│ ├── apis
│ ├── styles
│ ├── type
│ └── utils
├── tsconfig.json
├── typings.d.ts
└── yarn.lock
编译工具
进行中…
代码检测工具
关于代码检测工具,Typescript 官方从 TSLint 转向 ESLint,原因是 TSLint 执行规则的方式存在一些架构问题,从而影响了性能,修复这些问题会破坏现有的规则。并且 ESLint 的性能更好,社区用户拥有 ESLint 的规则配置。
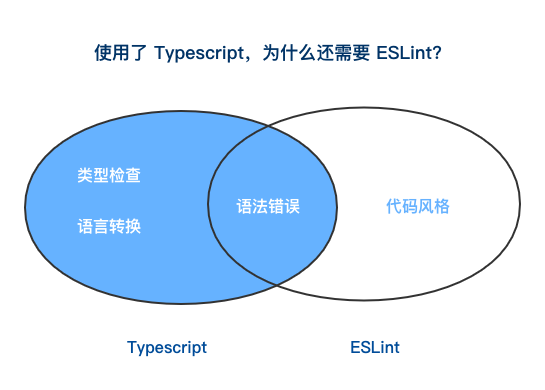
安装 eslint、@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin、@typescript-eslint/parser
配置 .eslintrc.json:
{
// 解析器
"parser": "@typescript-eslint/parser",
"parserOptions": {
"project": "./tsconfig.json"
},
// 继承的扩展
"extends": ["plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended"],
// 插件
"plugins": ["@typescript-eslint"],
// 规则
"rules": {}
}
package.json 中配置指令:
"script": {
"lint": "eslint src --ext .js,.ts,.tsx"
}
单元测试
进行中…
约定篇
- 有 jsx 代码的文件名后缀使用
.tsx,其它的使用.ts。 - 类型定义放在文件的最前面,导入内容之后。 ```typescript import React, { Component } from ‘react’
interface People { gender: number name: string age: number }
- interface 接口命名使用大驼峰法,可以与进行约束的函数等命名保持一致。
```typescript
interface People {
gender: number
name: string
age: number
}
const people: Readonly<People> = {
gender: '123', // Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'.ts(2322)
name: 'allen',
age: 26
}
- interface 声明顺序:只读参数放第一位,必须参数第二位,可选参数第三位,不确定参数放最后。 ```typescript interface People { readonly national: ‘string’ gender: number name: string age?: number
}
- interface 接口管理,可以按照功能模块统一 interface/xx.ts 下编写。
- 不要使用如下类型 `Number`,`String`,`Boolean` 或 `Object`。 这些类型指的是非原始的装盒对象。
```typescript
/** ❌错误 */
function atest(s: String): String
// 应该使用 number、string 和 boolean 非原始类型
/** ✅正确 */
function atest(s: string): string
- 回调函数返回值类型 ```typescript // 不要为返回值被忽略的回调函数设置 any 类型的返回值类型 // 为什么:使用 void 相对安全,因为它防止了你不小心使用 x 的返回值 /* ❌错误 / function fn(x: () => any) { x() }
/* ✅正确 / function fn(x: () => void) { x() }
- 回调函数里的可选参数
```typescript
// 当回调函数不在乎是否带某一个参数进行调用时,你不需要把这个参数当成可选参数来达到目的,因为总是允许提供一个接收较少参数的回调函数。
/** ❌错误 */
interface Fetcher {
getObj(done: (data: any, elapsedTime?: number) => void): void
}
/** ✅正确 */
interface Fetcher {
getObj(done: (data: any, elapsedTime: number) => void): void
}
- 函数重载顺序 ```typescript // 不要把一般的重载放在精确的重载前面 // 为什么:Typescript 会选择第一个匹配到的重载当解析函数时,如果前面的重载比后面的“普通”,那么后面的都被隐藏而不会被调用。 /* ❌错误 / declare function fn(x: any): any declare function fn(x: HTMLElement): number declare function fn(x: HTMLDivElement): string
var elem: HTMLDivElement var x = fn(elem) // x: any
/* ✅正确 / declare function fn(x: HTMLDivElement): string declare function fn(x: HTMLElement): number declare function fn(x: any): any
var elem: HTMLDivElement var x = fn(elem) // x: string
- 使用可选参数
```typescript
// 不要为仅在末尾参数不同时写不同的重载
// 应尽量使用可选参数
/** ❌错误 */
interface ITest {
diff(one: string): number
diff(one: string, two: string): number
diff(one: string, two: string, three: boolean): number
}
/** ✅正确 */
interface ITest {
diff(one: string, two?: string, three?: boolean): numbernm,-[p;lb hv
}
- 使用联合类型 ```typescript // 不要为仅在某一个位置上的参数类型不同的情况下定义重载 // 应尽量使用联合类型 /* ❌错误 / interface Moment { utcOffset(): number utcOffset(b: number): Moment utcOffset(b: string): Moment }
/* ✅正确 / interface Moment { utcOffset(): number utcOffset(b: number|string): Moment }
- JSX 语法中,只有 as 语法断言是被允许的
```typescript
// Typescript 中类型断言有两种写法
// 其一“尖括号”语法
let someVal: any = 'this is a string'
let strLen: number = (<string>someVal).length
// 另一种为 as 语法
// 当你在 Typescript 中使用 JSX 时,只有 as 语法断言是被允许的
let someVal: any = 'this is a string'
let strLen: number = (someVal as string).length
- 类型推断 ```typescript // Typescript 里,在有些没有明确指出类型的地方,类型推断会帮助提供类型 let x = 1 x = ‘be string’ // Type ‘“be string”‘ is not assignable to type ‘number’.ts(2322)
// 虽然 Typescript 会在设置默认参数值和决定函数返回值时推断类型 // 但是 我还是不建议不手动设置类型,这会让代码不那么直观 let x: number = 1 ```
参考资料
https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react-typescript-cheatsheet
https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript-React-Starter
https://github.com/piotrwitek/react-redux-typescript-guide
https://piotrwitek.github.io/react-redux-typescript-guide/


