1.1mybatis模块图
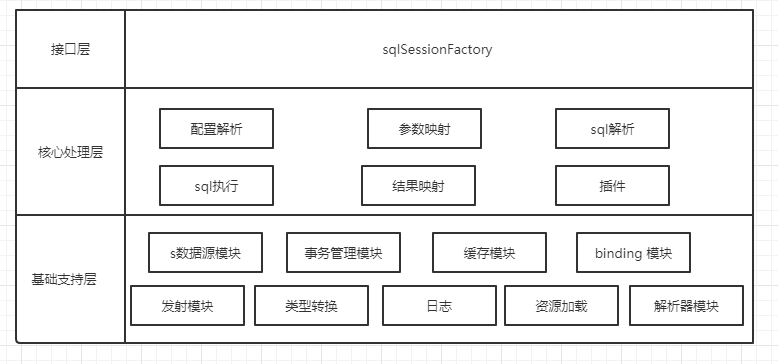
1.接口层 : 提供给外部使用的接口
2.核心处理层:负责具体的实现逻辑,解析配置,Mapper接口和xml绑定, SQL解析、执行和结果映射处理等。
3.基础支持层:xml数据解析、数据源控制、事务控制、缓存处理、反射功能,类型转换、日志控制、资源加载等功能模块。
1.2mybatis 源码分析
mybatis的官网 https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/index.html
1.2.1开始
根据官网配置
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><environments default="development"><environment id="development"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="123456"/></dataSource></environment></environments><mappers><mapper resource="mybatis/UserMapper.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
启动类
public class TestMybatis {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
//把xml配置文件转成输入流,方便下一步的xml解析器解析
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserDO userDO = userMapper.getById(15L);
System.out.println("===================" + userDO.getName());
sqlSession.commit();
}
}
当然除了这两个类还有 mapper.xml 和 mapper接口 这里不累赘了。
1.2.2执行分析
1.2.2.1解析build方法
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
执行流程图如下。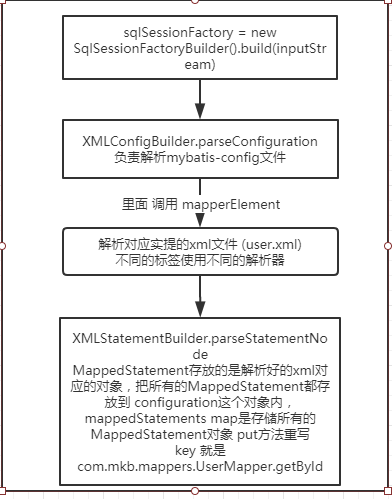
1:首先通过 XMLConfigBuilder 解析器把Stream流转成xml对象。
2:然后先解析其他标签 如: environments plugins 等等 存储在 configuration 中。
3:解析 mappers标签,再解析 resultMap sql cache 等等 存储在 configuration 中,然后统一解析 select update 开的语句
context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete")
4:然后把select 里面的数据解析成一个对象 MappedStatement 这个对象 包含 sql 语句 开头 结束等等。因为包含多个 方法 所以把集合 存储在 configuration 中。key 是 com.mkb.mappers.UserMapper.getById 就是 这个mapper的全路径加上方法名称。
1.2.2.2解析openSession
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
DefaultSqlSession var8;
try {
Environment environment = this.configuration.getEnvironment();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = this.getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception var12) {
this.closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + var12, var12);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var8;
}
1:先获取 Environment 就是配置文件的
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
2 : 初始化事务
3:初始化即将要执行的sql 的执行器,也就是下面代理生成的对象要调用的对象。
4:把生成好的上面三个对象 和之前的 configuration 全部传给 SqlSession
1.2.2.3解析getMapper
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
1 : 生成 sqlsession后通过 动态代理来生成 userMapper 的代理类。具体 handler 是 MapperProxy
这个是mybatis生成的mapper接口,整合spring过程这个这个实例化方式还不同 后面讲解
1.2.2.4解析getById
1:然后反射调用 mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args) ,然后判断sql 根据不同语法执行
MapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
Object param;
switch(this.command.getType()) {
case INSERT:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case UPDATE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case DELETE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case SELECT:
if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) {
this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (this.method.returnsMany()) {
result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsMap()) {
result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) {
result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
if (this.method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !this.method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
}
if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
} else {
return result;
}
继续调用 sqlSession.selectOne uptate 或者其他一个执行方法
过程中会调用CachingExecutor query
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return this.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
通过 getBoundSql 方法把 $ 的 值传入。
首选会去缓存中取值
List list;
try {
++this.queryStack;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List)this.localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) { //1.缓存取值
this.handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else { //数据库取值
list = this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
--this.queryStack;
}
可以看到缓存中值不为空,去数据库取值.
接着会调用SimpleExecuter的 prepareStatement ,可以看到调用的是jdbc的语法。
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = this.getConnection(statementLog);
Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection, this.transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
再会调用,PreparedStatementHandler 的 方法,
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement)statement;
ps.execute();
return this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
可以看到调用的是 PreparedStatement 的execute方法。
然后通过 resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);这个方法 采用不同的适配器去解析返回结果。
查询完成把数据放到缓存中 。
List list;
try {
list = this.doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
this.localCache.removeObject(key);
}
this.localCache.putObject(key, list);
到这整个sql的执行过程结束。

