SQL: 结构化查询语言
DDL: 数据定义语言;数据库,数据表他们的结构
create(创建) drop(删除) alter(修改)
DML: 数据操作语言:主要用来操作语言:
insert(插入) update(修改) delete(删除)
DCL ;数据控制语言:定义访问权限,取消访问权限:安全设置
grant
DQL:数据查询语言:
select(查询) from 子句 where 子句
数据库的CRUD 操作
- 连接数据库
2.创建数据库 ```sql create database 数据库名字;//返回根目录/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -u root -p
//创建数据库的时候,指定字符集 create database 数据库的名字 character set 字符集(utf8); //创建数据库的时候加入校对规则 create database 数据库的名字 character set 字符集(utf8)collate 校对规则;
3.查看数据库
```sql
show databases;
//下面这三个数据库不要动
information_schema
mysql
performance_schema
//查看数据库定义的语句
show create database 数据库名字
4.修改数据库
alter database 数据库名字 character set 字符集
5.删除数据库
drop database 数据库名字;
6.数据库的操作指令
--切换数据库(选中数据库)
use 数据库名字
--查看当前使用的数据库
select database();
表的CRUD操作
创建表
create table 表名(
列名 列的类型(长度) 约束,
列名2 列的类型(长度) 约束
)
列表类型:
java sql
int int
char char 固定长度 长度:字符的个数
String varchar 可变长度
double double
float float
date: YYYY-MM-DD
time: hh:mm:ss
datetime:YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss 默认值为空null
timestamp:YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss 默认使用当前时间
text :主要存放文本
blob: 存放二进制
列的约束:
主键约束: primary key
唯一约束: unique
非空约束: not null
创建表
1.分析实体:学生
2.学生id
3.姓名
4.性别
5.年龄
create table student(
sid int primary key,
sname varchar(),
sex int,
age int
);
2.查看表
--查看所有表
show tables;
--查看表的创建
show create table student(表名);
--查看表结构
desc 表名
3.修改表
添加列(add)
alter table 表名 add 列名 列的类型 列的约束;
修改列(modify)
alter table 表名 modify 列名 修改后的类型 修改后的约束;
修改列名(change)
alter table 表名 change 旧列名 新列名 新的类型 约束;
删除列(drop)
alter table 表名 drop 列名;
//下面两个尽量不要动
修改表名:(rename)
rename table 旧表名 to 新表名
修改表的字符集:
alter table 表名 charcter set 字符集
删除表
drop table 表名
sql 完成对表中的数据的CRUD的操作
1.插入数据
insert into 表名(列名1,列名2,列名3) values(值1,值2,值3);
--简单写法
insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,值3);
插入部分列 必须使用第一种,不能使用简单写法
--批量插入
insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,值3),(值1,值2,值3),(值1,值2,值3),(值1,值2,值3);
insert into student values(3,'王二','男',19),(4,'王二','男',19),(5,'王二','男',19),(6,'王二','男',19);
--查看表的内容
select * from 表名
2.删除操作
delete from 表名 where 条件 如果没有条件,表中数据全部删除
delete; DML 一条一条删除表数据
truncate:DDL,先删除表再重建表
数据小:delete
数据多:truncate:
3.更新表的记录
update 表名 set 列名=列的值,列名2=列的值 where 条件
不加条件 都会修改
日期和字符要加单引号
4.查询表的记录
select distinct * 或者(列名1,列名2....) from 表名 where 条件;
--商品分类 :手机数码 鞋靴箱包
1.分类的id
2.分类的名称
3.分类的描述
create table category(
-> cid int primary key auto_increment,
-> cname varchar(10),
-> cdesc varchar(31)
-> );
insert into category values(null,'手机数码','电子产品'),(null,'鞋靴箱包','江南制造'),(null,'香烟酒水','中国制造'),(null,'酸奶饼干','蒙牛制造'),(null,'馋
嘴零食','瓜子花生');
--所有商品
1.商品id
2.商品名称
3.商品价格
4.商品分类id
auto_increment,自动增加
create table product(
pid int primary key auto_increment,
pname varchar(10),
price double,
pdate timestamp not null default current_timestamp,
cno int
);
insert into product values(null,'小米',998,null,1),(null,'锤子',2888,null,1),(null,'addids',799,null,2),(null,'老村长',99,null,3),(null,'劲酒',88,null,3),(null,'蒙牛',9,null,4),(null,'辣条',1,null,5);
insert into product (pid,pname,price,cno) values(null,'锤子',2888,1),(null,'addids',799,2),(null,'老村长',99,3),(null,'劲酒',88,3),(null,'蒙牛',9,4),(null,'辣条',1,5);
--简单查询
--查询所有商品
select * from 表名
--查询部分
select 列名1,列名2...from 表名
--别名
1.表别名 : as ; select p.pname,p.price from product as p; as可以省略
2.列别名 : as: select pname as 商品名称,price 商品价格 from product;
--去掉重复的值
distinct
select distinct price from product;
--运算查询:仅仅在查询结果上做了运算 没有改变表
select *,price*0.8 (as)折后价 from product; //中间有逗号
--条件查询
指定条件,确定要操作的所有商品信息
select * from product where price > 100;
关系运算符:> = >= < <= != <>
逻辑运算: and or not
select * from product where price between 10 and 100;
select * from product where price<20 or price>600;
--模糊查询:
_ : 代表一个字符
% : 代表多个字符
select * from product where pname like '%小%';
select * from product where pname like '_酒%';
-- in 范围查询
select * from product where cno in(1,3,5);
--排序查询
asc: 升序
desc: 降序
select * from product order by price;(默认升序)
select * from product order by price desc;
select * from product order by price asc;
select * from product where cno=3 order by price;
--聚合函数
sum():求和
avg(): 平均
count():统计数量
max():最大值
min():最小值
select sum(price) from product;
select avg(price) from product;
select count(*) from product;
注意:where 后面不能直接聚合函数 需要加()
商品价格大于平均价格
select * from product where price >(select avg(price) from product);
--分组
group by
1.根据cno字段分组,分组后统计商品的个数
select cno,count(*) from product group by cno;
2.根据 cno字段分组,分组统计每组商品的平均价格,并且价格大于>60
第一句话; select cno,avg(price)
分组; from product group by cno
大于60 having avg(price) > 60;
having 关键字 可以接聚合函数 出现在分组之后
where 关键字 他不可以接聚合函数 ,出现在分组之前
商品和商品分类的关系;所属关系
SQL编写熟顺序
-- S F W G H 0
select ... from ...where ...group by .... having ...order by...
执行顺序
F . W ...G..H...S...0..
from ...where ...group by...having ...select ...order by...
多表创建和查询
多表之间的关系维护
主键约束:默认不能为空,唯一,外键都是指向另外一张表的主键,一张表只能有一个主键
唯一约束:不可以作为其他表的外键,可以有多个
建库原则:一个应用建一个库
建表原则:
- 一对多:(商品和分类)在多的一方添加一个外键指向一的那张表的主键
- 多对多:老师和学生,学生和课程:多建一个中间表:至少有两个外键分别指向原来那张表,把多对多的变成一对一,将两张表的主键建立连接,让两张表的主键相同。
- 一对一:公民身份证:和一对多处理相同,将任意一张表的添加一个外键并且这个外键要唯一,指向另外一张表。或者两张表合成一张表 或者两张表的建立连接,让两张表里面主键相同,实际用途:拆表
添加外键约束: forerign key
//上面的例子中,给product表中的cno添加一个外键foreign key 指向category表中的cid
alter table product add foreign key(cno) references category(cid);
例子:商上商城
用户表、订单表、商品表、商品分类表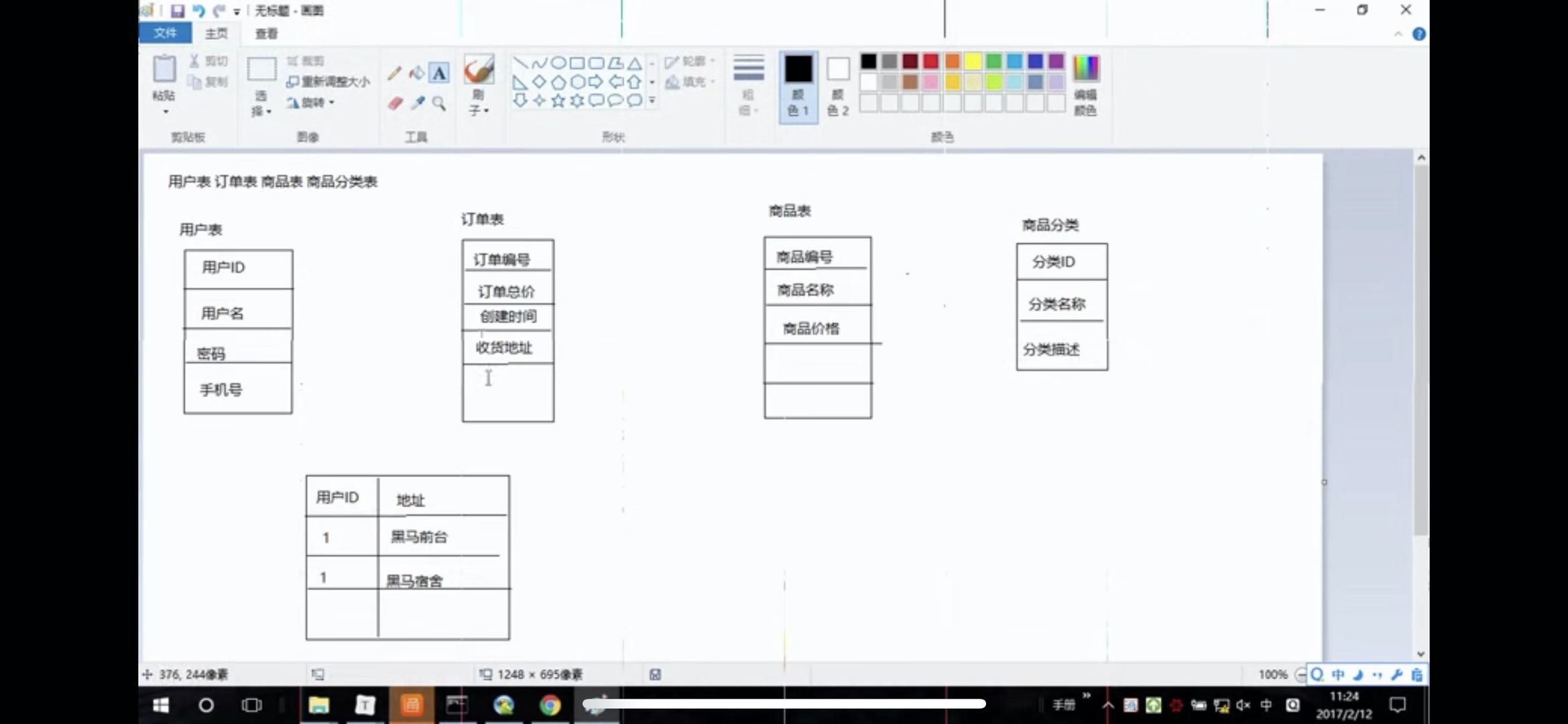
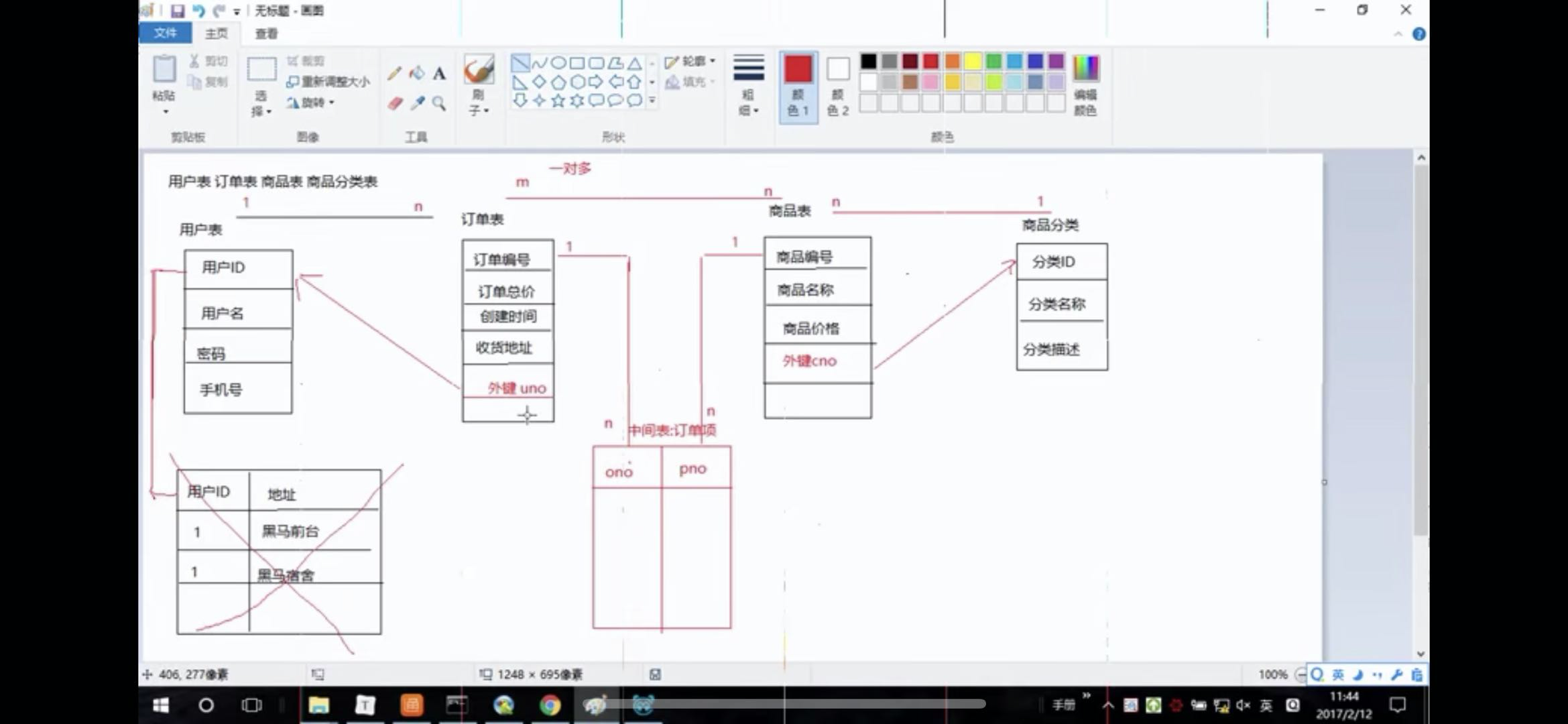
//用户表
create table user(
uid int primary key auto_increment,
username VARCHAR(31),
password varchar(31),
phone varchar(11)
);
insert into user values(null,'zs','123','13879380479');
//订单表
create table orders(
oid int primary key auto_increment,
sum int not null,
otime timestamp not null default current_timestamp,
adresss varchar(100),
uno int,
foreign key (uno)references user(uid)
);
insert into orders (oid,sum,adresss,uno) values(null,200,'复旦',1);
insert into orders (oid,sum,adresss,uno) values(null,250,'家',1);
//商品表
create table product(
pid int primary key auto_increment,
pname varchar(10),
price double,
cno int,
foreign key(cno) references category(cid)
);
//商品分类表
create table category(
cid int primary key auto_increment,
cname varchar(15),
cdesc varchar(100)
);
insert into product (pid,pname,price,cno) values(null,'锤子',2888,1),(null,'addids',799,2),(null,'老村长',99,3),(null,'劲酒',88,3),(null,'蒙牛',9,4),(null,'辣条',1,5);
insert into category values(null,'手机数码','电子产品'),(null,'鞋靴箱包','江南制造'),(null,'香烟酒水','中国制造'),(null,'酸奶饼干','蒙牛制造'),(null,'馋嘴零食','瓜子花生');
//订单项:中间表
create table orderitem(
ono int,
pno int,
foreign key(ono) references orders(oid),
foreign key(pno) references product(pid),
ocount int,
subsum double
);
//1号订单 200块
insert into orderitem values(1,5,20,180);
insert into orderitem values(1,6,20,20);
//2号订单 250
insert into orderitem values(2,5,20,180);
insert into orderitem values(2,6,70,70);
//交叉查询 笛卡尔积
select * from product,category;
+-----+-----------+-------+------+-----+--------------+--------------+
| pid | pname | price | cno | cid | cname | cdesc |
+-----+-----------+-------+------+-----+--------------+--------------+
| 1 | 锤子 | 2888 | 1 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 1 | 锤子 | 2888 | 1 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 1 | 锤子 | 2888 | 1 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 1 | 锤子 | 2888 | 1 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 1 | 锤子 | 2888 | 1 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
| 2 | addids | 799 | 2 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 2 | addids | 799 | 2 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 2 | addids | 799 | 2 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 2 | addids | 799 | 2 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 2 | addids | 799 | 2 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
| 3 | 老村长 | 99 | 3 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 3 | 老村长 | 99 | 3 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 3 | 老村长 | 99 | 3 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 3 | 老村长 | 99 | 3 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 3 | 老村长 | 99 | 3 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
| 4 | 劲酒 | 88 | 3 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 4 | 劲酒 | 88 | 3 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 4 | 劲酒 | 88 | 3 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 4 | 劲酒 | 88 | 3 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 4 | 劲酒 | 88 | 3 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
| 5 | 蒙牛 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 5 | 蒙牛 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 5 | 蒙牛 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 5 | 蒙牛 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 5 | 蒙牛 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
| 6 | 辣条 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 6 | 辣条 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 6 | 辣条 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 6 | 辣条 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 6 | 辣条 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
| 7 | 小米 | 998 | 1 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 7 | 小米 | 998 | 1 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 7 | 小米 | 998 | 1 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 7 | 小米 | 998 | 1 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 7 | 小米 | 998 | 1 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
这上面很多条没有意义 在上面的基础上加入条件过滤
---隐式内连接
select * from product,category where cno=cid;
+-----+-----------+-------+------+-----+--------------+--------------+
| pid | pname | price | cno | cid | cname | cdesc |
+-----+-----------+-------+------+-----+--------------+--------------+
| 1 | 锤子 | 2888 | 1 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 7 | 小米 | 998 | 1 | 1 | 手机数码 | 电子产品 |
| 2 | addids | 799 | 2 | 2 | 鞋靴箱包 | 江南制造 |
| 3 | 老村长 | 99 | 3 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 4 | 劲酒 | 88 | 3 | 3 | 香烟酒水 | 中国制造 |
| 5 | 蒙牛 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 酸奶饼干 | 蒙牛制造 |
| 6 | 辣条 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 馋嘴零食 | 瓜子花生 |
+-----+-----------+-------+------+-----+--------------+--------------+
内连接是两表交集
显式内连接 (inner 和 outer 可以省略)
select * from product (as)p inner join category (as)c on p.cno = c.cid;
隐式内连接:在查询的结果做过滤
显式内连接; 带着条件去查询(效率更高)
--左外连接:
select * from product p left outer join category c on p.cno = c.cid;
左外连接会将左表中的数据全查询出来,如果右表中没有对应的数据,则全是null;
--右外连接
select *from product p right outer join category c on p.cno = c.cid;
右外连接会将右表数据全部查询出来,如果左表没有对应数据,,则全是null
分页查询:
limit 第一个参数是索引(不包括这个索引点)第二个参数是显示个数i
select * from product limit 0 ,3;
select * from product limit 3,3;
子查询:查询语句中嵌套查询语句
//查询分类名是手机数码的所有商品
1.查询分类名是手机数码
select cid from category where cname ='手机数码';
2.得出结果
select * from product where cno =(select cid from category where cname ='手机数码');
//查询出商品名称,商品分类名称所有信息
1.左连接方式
select p.pname,c.cname from product p left outer join category c on p.cno = c.cid;
2.子查询方式
1.在商品表中查找和分类有关的列
select pname,cno from product;
+-----------+------+
| pname | cno |
+-----------+------+
| 锤子 | 1 |
| addids | 2 |
| 老村长 | 3 |
| 劲酒 | 3 |
| 蒙牛 | 4 |
| 辣条 | 5 |
| 小米 | 1 |
+-----------+------+
根据cno查询分类表中的商品名称
select pname,(select cname from category c where c.cid = p.cno) as 商品分类 from product p;
+-----------+--------------+
| pname | 商品分类 |
+-----------+--------------+
| 锤子 | 手机数码 |
| addids | 鞋靴箱包 |
| 老村长 | 香烟酒水 |
| 劲酒 | 香烟酒水 |
| 蒙牛 | 酸奶饼干 |
| 辣条 | 馋嘴零食 |
| 小米 | 手机数码 |
+-----------+--------------+
having 和 where 的区别
having与where的区别:
having是在分组后对数据进行过滤
where是在分组前对数据进行过滤
having后面可以使用聚合函数
where后面不可以使用聚合

