寄存器
ARM64 有34个寄存器,包括31个通用寄存器、SP、PC、CPSR。
| 寄存器 | 位数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| x0-x30 | 64bit | 通用寄存器,如果有需要可以当做32bit使用:W0-W30 |
| FP(x29) | 64bit | Frame Pointer,保存栈帧地址(栈底指针) |
| LR(x30) | 64bit | Link Register,通常称X30为程序链接寄存器,保存子程序结束后需要执行的下一条指令 |
| SP | 64bit | Stack Pointer,保存栈指针,使用 SP/WSP来进行对SP寄存器的访问。 |
| PC | 64bit | Program Counter,程序计数器,俗称PC指针,总是指向即将要执行的下一条指令,在arm64中,软件是不能改写PC寄存器的。 |
| CPSR | 64bit | Current Program Status Register,状态寄存器 |
- x0-x7: 用于子程序调用时的参数传递,x0还用于返回值传递
- x8: 间接寻址结果
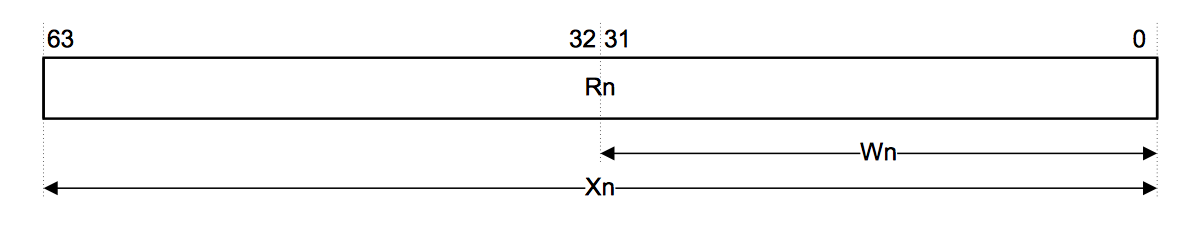
- x0 - x30 是31个通用整形寄存器。每个寄存器可以存取一个64位大小的数。 当使用 x0 - x30 访问时,它就是一个64位的数。当使用 w0 - w30 访问时,访问的是这些寄存器的低32位,如图:
- CPSR(状态寄存器)
NZCV是状态寄存器的条件标志位,分别代表运算过程中产生的状态,其中:
• N, negative condition flag,一般代表运算结果是负数
• Z, zero condition flag, 指令结果为0时Z=1,否则Z=0;
• C, carry condition flag, 无符号运算有溢出时,C=1。
• V, oVerflow condition flag 有符号运算有溢出时,V=1。
- 栈
栈就是指令执行时存放临时变量的内存空间,具有特殊的访问方式:后进先出, Last In Out Firt。
- 栈是从高地址到低地址存储数据的,栈底是高地址,栈顶是低地址。
- FP指向栈底
- SP指向栈顶
系统寄存器
CurrentEL current exception level,当前异常级别
sctlr_eln system control register,系统控制寄存器。n可为0、1、2、3,代表四种EL状态。
指令
常见指令
MOV X1,X0 ;将寄存器X0的值传送到寄存器X1ADD X0,X1,X2 ;寄存器X1和X2的值相加后传送到X0SUB X0,X1,X2 ;寄存器X1和X2的值相减后传送到X0AND X0,X0,#0xF ;X0的值与0xF相位与后的值传送到X0ORR X0,X0,#9 ;X0的值与9相位或后的值传送到X0EOR X0,X0,#0xF ;X0的值与0xF相异或后的值传送到X0LDR X5,[X6,#0x08] ;load ram X6寄存器加0x08的和的地址值内的数据传送到X5STR X0, [SP, #0x8] ;store ram:往内存中写数据(偏移值为正)X0寄存器的数据传送到SP+0x8地址值指向的存储空间STUR w0, [x29, #-0x8] ;往内存中写数据(偏移值为负)STP x29, x30, [sp, #0x10] ;store pair,存放一对数据, 入栈指令LDP x29, x30, [sp, #0x10] ;load pair 一对寄存器, 从内存读取数据到寄存器CBZ ;比较(Compare),如果结果为零(Zero)就转移(只能跳到后面的指令)CBNZ ;比较,如果结果非零(Non Zero)就转移(只能跳到后面的指令)CMP ;比较指令,相当于SUBS,影响程序状态寄存器CPSRB ;跳转指令,跳转范围128MB。可带条件跳转与cmp配合使用,如B.EQ,跳转范围1MB。BL ;带返回的跳转指令, 返回地址保存到LR(X30)BR Xn ;跳转指令,跳到寄存器Xn存储的地址BLR ;带返回的跳转指令,返回地址保存到LR(X30)RET ;子程序返回指令,返回地址默认保存在LR(X30)
数据处理指令
算数和逻辑操作
| Type | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Arithmetic | ADD, SUB, ADC, SBC, NEG |
| Logical | AND, BIC, ORR, ORN, EOR, EON |
| Comparison | CMP, CMN, TST |
| Move | MOV, MVN |
有些指令结尾还有个S,比如ADDS、SUBS、ADCS、SBCS、ANDS和BICS,这意味着这些指令会设置flag。还有些结尾不带S的指令也会设置flag,比如CMP、CMN和TST。
ADC和SBC也是加法和减法,不同的是它们也会把进位标记(carry condition flag)当作输入。
ADC{S} Rd, Rn, Rm // Rd = Rn + Rm + CSBC{S} Rd, Rn, Rm // Rd = Rn - Rm - 1 + CADD W0, W1, W2, LSL #3 // W0 = W1 + (W2 << 3)SUBS X0, X4, X3, ASR #2 // X0 = X4 - (X3 >> 2), set flagsMOV X0, X1 // Copy X1 to X0CMP W3, W4 // Set flags based on W3 - W4ADD W0, W5, #27 // W0 = W5 + 27
BIC(Bitwise bit Clear)指令将目的寄存器后面的地一个寄存器的值与第二个寄存器的值取反相与后赋值给目的寄存器,例如清除寄存器x0的bit 11:
MOV X1, #0x800BIC X0, X0, X1
ORN和EON也是分别和第二个操作符取反后进行或和异或操作。
乘除法指令
| Opcode | Description |
|---|---|
| Multiply instructions | |
| MADD | Multiply add |
| MNEG | Multiply negate |
| MSUB | Multiply subtract |
| MUL | Multiply |
| SMADDL | Signed multiply-add long |
| SMNEGL | Signed multiply-negate long |
| SMSUBL | Signed multiply-subtract long |
| SMULH | Signed multiply returning high half |
| SMULL | Signed multiply long |
| UMADDL | Unsigned multiply-add long |
| UMNEGL | Unsigned multiply-negate long |
| UMSUBL | Unsigned multiply-subtract long |
| UMULH | Unsigned multiply returning high half |
| UMULL | Unsigned multiply long |
| Divide instructions | |
| SDIV | Signed divide |
| UDIV | Unsigned divide |
例子
MUL X0, X1, X2 // X0 = X1 * X2MNEG X0, X1, X2 // X0 = -(X1 * X2)UDIV W0, W1, W2 // W0 = W1 / W2 (unsigned, 32-bit divide)SDIV X0, X1, X2 // X0 = X1 / X2 (signed, 64-bit divide)
移位指令
| Instruction | Description |
|---|---|
| Shift | |
| ASR | Arithmetic shift right |
LSL |
Logical shift left |
| LSR | Logical shift right |
ROR |
Rotate right |
| Move | |
| MOV | Move |
MVN |
Bitwise NOT |
对于逻辑左移和逻辑右移,移出的bit就丢了。而算数左移和算数右移会保留符号位。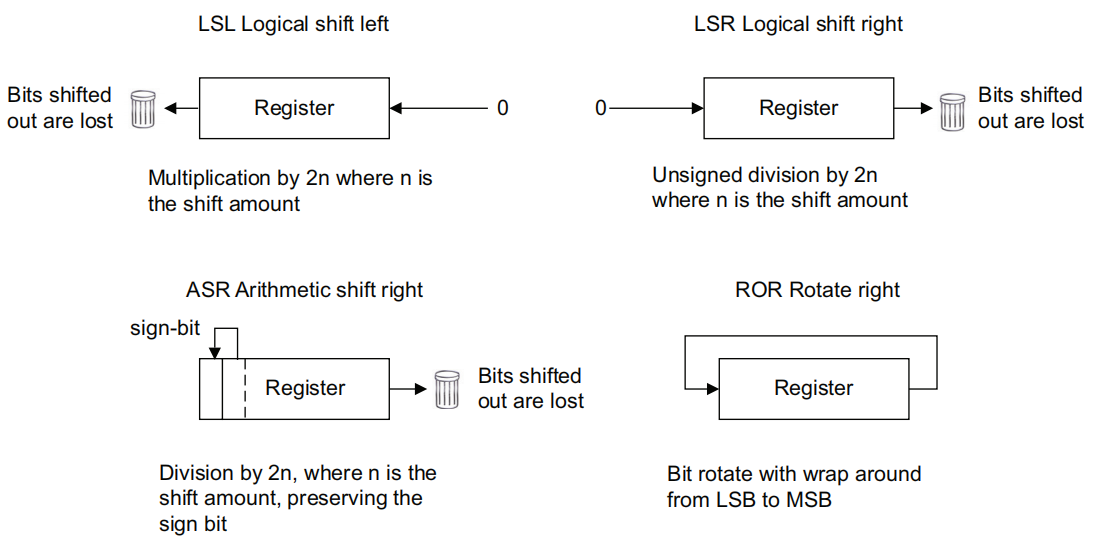
位域和字节操作指令
| Instruction | Description |
|---|---|
| SXTB | signed extend a byte |
| SXTH | signed extend a halfword |
| SXTW | signed extend a word |
| UXTB | unsigned extend a byte |
| UXTH | unsigned extend a halfword |
例子:
SXTB X0, W1 // Sign extend the least significant byte of register W1// from 8-bits to 64-bit by repeating the leftmost bit of the// byte.
条件指令
| CSEL | |
| CSINC | |
| CSINV | |
| CSNEG | |
| CSET | |
| CSETM | |
| CMP | |
| CMN | |
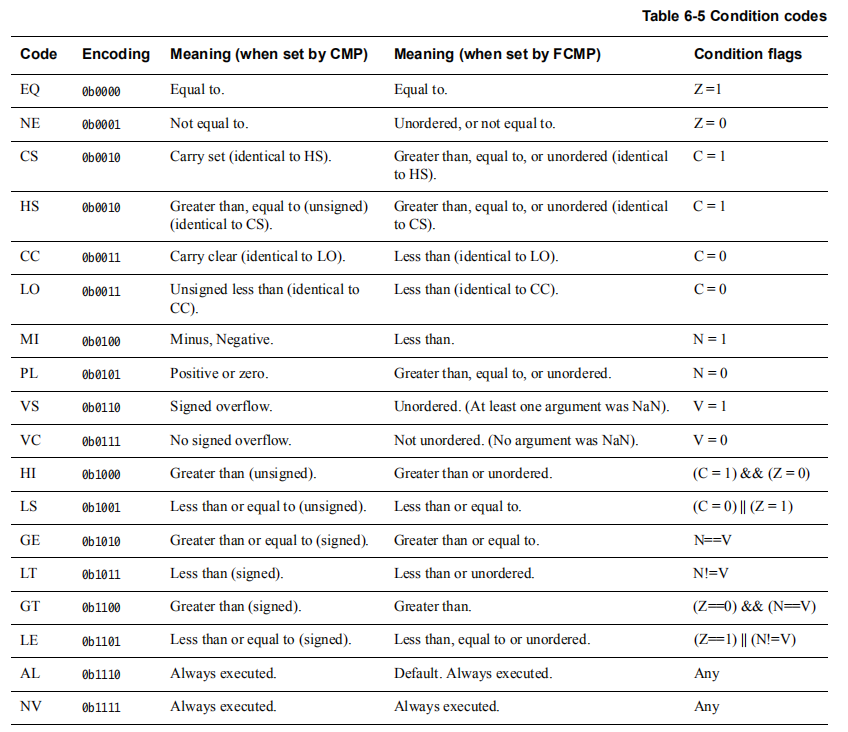
例子:
CSINC X0, X1, X0, NE // Set the return register X0 to X1 if Zero flag clear,// else increment X0CINC X0, X0, LS // If less than or same (LS) then X0 = X0 + 1CSET W0, EQ // If the previous comparison was equal (Z=1) then W0 = 1,// else W0 = 0CSETM X0, NE // If not equal then X0 = -1, else X0 = 0
这类指令能代替分支指令或条件执行指令。编译器可以执行if-then-else语句的两个分支,然后选择一个正确的结果。例如下面的C代码:
if (i == 0)r = r + 2;elser = r - 1;
转化成汇编可能是:
CMP w0, #0 // if (i == 0)SUB w2, w1, #1 // r = r - 1ADD w1, w1, #2 // r = r + 2CSEL w1, w1, w2, EQ // select between the two results
内存访问指令
加载指令格式
LDR Rt, <addr>
LDR指令加上不同的后缀,可以指定加载数据的大小。
• LDRB (8-bit, zero extended).
• LDRSB (8-bit, sign extended).
• LDRH (16-bit, zero extended).
• LDRSH (16-bit, sign extended).
• LDRSW (32-bit, sign extended)
存储指令格式
STR Rn, <addr>
例子:
//偏移量模式LDR X0, [X1] //Load from the address in X1LDR X0, [X1, #8] //Load from address X1 + 8LDR X0, [X1, X2] //Load from address X1 + X2LDR X0, [X1, X2, LSL, #3] //Load from address X1 + (X2 << 3)LDR X0, [X1, W2, SXTW] //Load from address X1 + sign_extend(W2)LDR X0, [X1, W2, SXTW, #3] //Load from address X1 + (sign_extend(W2) << 3)//索引模式LDR X0, [X1, #8]! //Pre-index: Update X1 first (to X1 + #8), then load from the new addressLDR X0, [X1], #8 //Post-index: Load from the unmodified address in X1 first, then update X1 (to X1 + #8)STP X0, X1, [SP, #-16]! //Push X0 and X1 to the stack.LDP X0, X1, [SP], #16 //Pop X0 and X1 off the stack.//PC相关模式 <label>必须是4字节对齐LDR W0, <label> //Load 4 bytes from <label> into W0LDR X0, <label> //Load 8 bytes from <label> into X0LDRSW X0, <label> //Load 4 bytes from <label> and sign-extend into X0LDR S0, <label> //Load 4 bytes from <label> into S0LDR D0, <label> //Load 8 bytes from <label> into D0LDR Q0, <label> //Load 16 bytes from <label> into Q0//Load and Store pairLDP W3, W7, [X0] //Loads word at address X0 into W3 and word at//address X0 + 4 into W7. See Figure 6-6.LDP X8, X2, [X0, #0x10]! //Loads doubleword at address X0 + 0x10 into X8//and the doubleword at address X0 + 0x10 + 8//into X2 and add 0x10 to X0. See Figure 6-7.LDPSW X3, X4, [X0] //Loads word at address X0 into X3 and word at//address X0 + 4 into X4, and sign extends both//to doubleword size.LDP D8, D2, [X11], #0x10 //Loads doubleword at address X11 into D8 and//the doubleword at address X11 + 8 into D2 and//adds 0x10 to X11.STP X9, X8, [X4] //Stores the doubleword in X9 to address X4 and//stores the doubleword in X8 to address X4 + 8.
内存屏障和栅栏指令
| Instruction | Description |
|---|---|
| DMB | Data Memory Barrier |
| DSB | Data Synchronization Barrier |
| ISB | Instruction Synchronization Barrier |
| LDAR | Load-Acquire |
| STLR | Store-Release |
流程控制
| 分支指令 | |
|---|---|
| B (offset) | Program relative branch forward or back 128MB. A conditional version, for example B.EQ, has a 1MB range. |
| BL (offset | As B but store the return address in X30, and hint to branch prediction logic that this is a function call |
| BR Xn | Absolute branch to address in Xn. |
| BLR Xn | As BR but store the return address in X30, and hint to branch prediction logic that this is a function call. |
| RET{Xn} | As BR, but hint to branch prediction logic that this is a function return. Returns to the address in X30 by default, but a different register can be specified |
| 条件分支指令 | |
| CBZ Rt, label | Compare and branch if zero. If Rt is zero, branch forward or back up to 1MB. |
| CBNZ Rt, label | Compare and branch if non-zero. If Rt is not zero, branch forward or back up to 1MB |
| TBNZ Rt, bit, label | Test and branch if zero. Branch forward or back up to 32kB. |
| TBNZ Rt, bit, label | Test and branch if non-zero. Branch forward or back up to 32kB. |
例子:
CBZ Rt, label // Compare and branch if zeroCBNZ Rt, label // Compare and branch if not zeroTBZ Rt, bit, label // Test and branch if Rt<bit> zeroTBNZ Rt, bit, label // Test and branch if Rt<bit> is not zero
系统控制和其他指令
异常处理指令
SVC #imm16 // Supervisor call, allows application program to call the kernel// (EL1).HVC #imm16 // Hypervisor call, allows OS code to call hypervisor (EL2).SMC #imm16 // Secure Monitor call, allows OS or hypervisor to call Secure// Monitor (EL3)
系统寄存器访问
MRS Xt, <system register> // This copies a system register into a general// purpose register//For exampleMRS X4, ELR_EL1 // Copies ELR_EL1 to X4MSR <system register>, Xt // This copies a general-purpose register into a// system register//For exampleMSR SPSR_EL1, X0 // Copies X0 to SPSR_EL1MSR SPSel, #imm // A value of 0 or 1 in this register is used to select// between using EL0 stack pointer or the current exception// level stack pointerMSR DAIFClr, #imm4MSR DAIFSet, #imm4
调试指令
BRK #imm16 // Enters monitor mode debug, where there is on-chip debug monitor// codeHLT #imm16 // Enters halt mode debug, where external debug hardware is connected
暗示指令
所有的暗示指令都可以看作为NOP,但它们可以有特定实现的效果。
• NOP // No operation - not guaranteed to take time to execute• YIELD // Hint that the current thread is performing a task that// can be swapped out• WFE // Wait for Event• WFI // Wait for interrupt• SEV // Send Event• SEVL // Send Event Local
地址生成
ADR Xd, label
Address:在PC值上加一个21bit的有符号偏移量,结果写到寄存器Xd中。用来计算PC ±1MiB范围内的有效地址。
ADRP Xd, label
Address of Page:有符号的21bit偏移量向左移12bit,然后和PC值相加,结果写入寄存器Xd中。用来计算4KiB对齐内存的基地址。可以用来寻址PC ±4GiB范围内的空间。

