1、System类
- System类代表系统,系统级的很多属性和控制方法都放置在该类的内部。该类位于java.lang包。
- 由于该类的构造器是private的,所以无法创建该类的对象,也就是无法实例化该类。其内部的成员变量和成员方法都是static的,所以也可以很方便的进行调用。
- 成员变量
- System类内部包含in、out和err三个成员变量,分别代表标准输入流(键盘输入),标准输出流(显示器)和标准错误输出流(显示器)。
- 成员方法
- native long currentTimeMillis():
- 该方法的作用是返回当前的计算机时间,时间的表达格式为当前计算机时间和GMT时间(格林威治时间)1970年1月1号0时0分0秒所差的毫秒数。
- void exit(int status):
- 该方法的作用是退出程序。其中status的值为0代表正常退出,非零代表异常退出。使用该方法可以在图形界面编程中实现程序的退出功能等。
- void gc():
- 该方法的作用是请求系统进行垃圾回收。至于系统是否立刻回收,则取决于系统中垃圾回收算法的实现以及系统执行时的情况。String
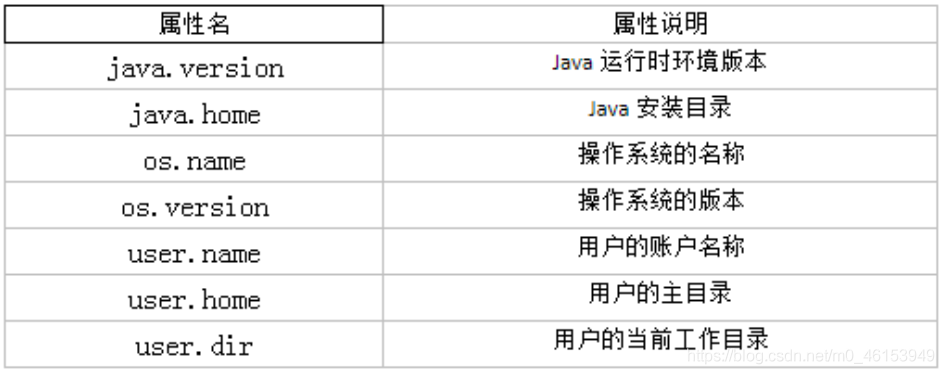
- getProperty(String key):
- 该方法的作用是获得系统中属性名为key的属性对应的值。系统中常见的属性名以及属性的作用如下表所示:
- native long currentTimeMillis():
import org.junit.Test;/*** 其他常用类的使用* 1.System* 2.Math* 3.BigInteger 和 BigDecimal*/public class OtherClassTest {@Testpublic void test1() {String javaVersion = System.getProperty("java.version");System.out.println("java的version:" + javaVersion);String javaHome = System.getProperty("java.home");System.out.println("java的home:" + javaHome);String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");System.out.println("os的name:" + osName);String osVersion = System.getProperty("os.version");System.out.println("os的version:" + osVersion);String userName = System.getProperty("user.name");System.out.println("user的name:" + userName);String userHome = System.getProperty("user.home");System.out.println("user的home:" + userHome);String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");System.out.println("user的dir:" + userDir);}}
2、Math类
java.lang.Math提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算。其方法的参数和返回值类型一般为double型。
- abs 绝对值
- acos,asin,atan,cos,sin,tan 三角函数
- sqrt 平方根
- pow(double a,doble b) a的b次幂
- log 自然对数
- exp e为底指数
- max(double a,double b)
- min(double a,double b)
- random() 返回0.0到1.0的随机数
- long round(double a) double型数据a转换为long型(四舍五入)
- toDegrees(double angrad) 弧度—>角度
toRadians(double angdeg) 角度—>弧度
3、BigInteger与BigDecimal
Integer类作为int的包装类,能存储的最大整型值为2^31 -1,Long类也是有限的,最大为2^63 -1。如果要表示再大的整数,不管是基本数据类型还是他们的包装类都无能为力,更不用说进行运算了。
- java.math包的BigInteger可以表示不可变的任意精度的整数。BigInteger提供所有Java 的基本整数操作符的对应物,并提供java.lang.Math 的所有相关方法。另外,BigInteger还提供以下运算:模算术、GCD 计算、质数测试、素数生成、位操作以及一些其他操作。
- 构造器
- BigInteger(String val):根据字符串构建BigInteger对象
- 常用方法

- 一般的Float类和Double类可以用来做科学计算或工程计算,但在商业计算中,要求数字精度比较高,故用到java.math.BigDecimal类。
- BigDecimal类支持不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制定点数。
- 构造器
- public BigDecimal(double val)
- public BigDecimal(String val)
- 常用方法
- public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend)
- public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend)
- public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand)
- public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode) ```java import org.junit.Test;
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger;
/**
- 其他常用类的使用
- 1.System
- 2.Math
3.BigInteger 和 BigDecimal */ public class OtherClassTest {
@Test public void test2() {
BigInteger bi = new BigInteger("1243324112234324324325235245346567657653");BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("12435.351");BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("11");System.out.println(bi);
// System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2));
System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, 25, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
} }
```

