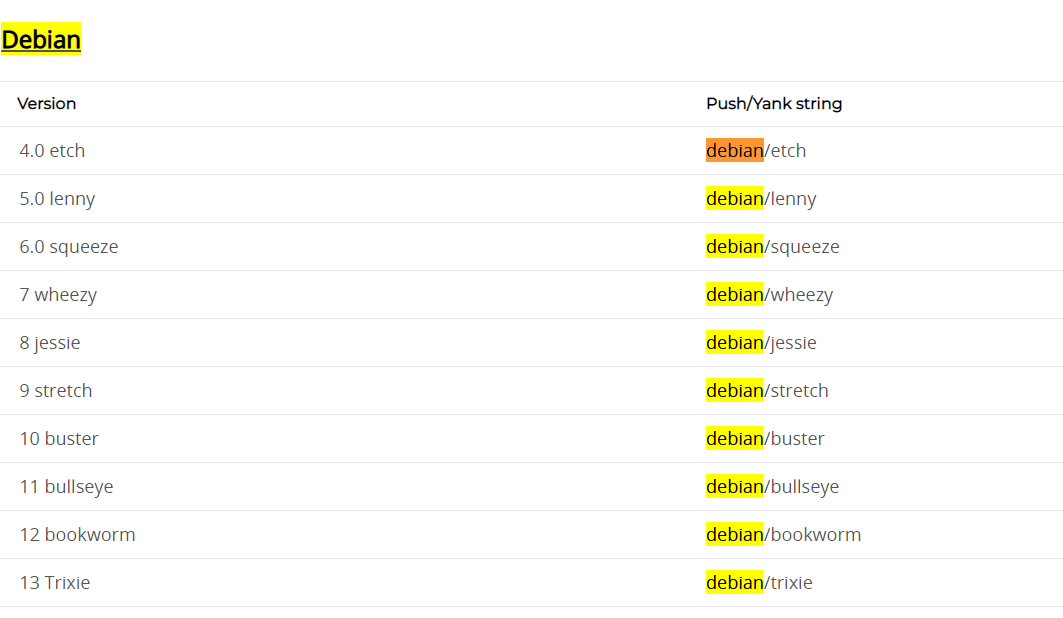
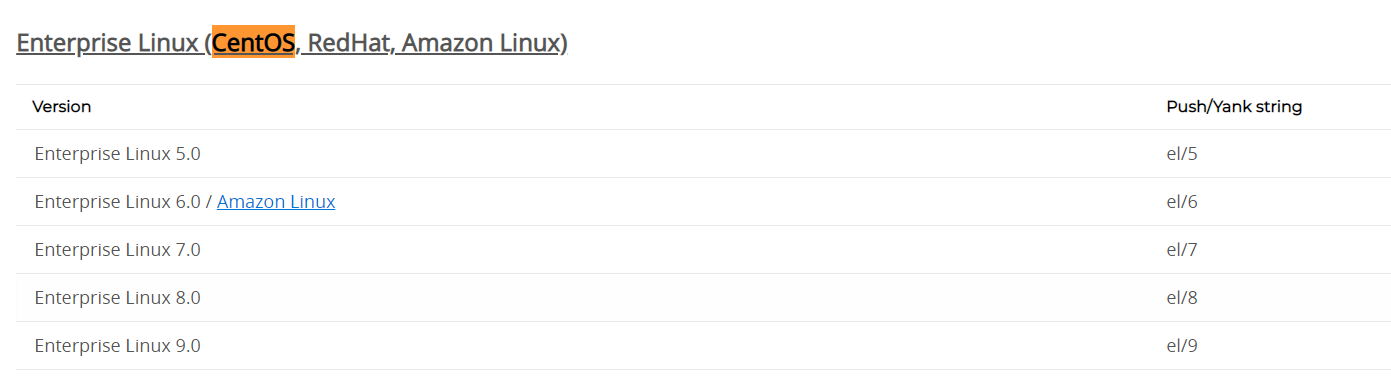
参考:https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/mirror#apt
YUM repository mirroring
These directions will walk you through using the open source tool reposync to mirror your YUM repository.
- Ensure you’ve installed this repository on your system. reposync will use the YUM configuration in /etc/yum.repos.d/ for mirroring.
- Install reposync and createrepo:sudo yum install yum-utils createrepoNOTE: reposync on CentOS 5 is buggy. We strongly encourage users to consider upgrading their reposync to a newer version.
- Create a directory for storing your repository data:mkdir -p /path/to/repository
- Run reposync specifying the the repository ID and the output directory.reposync —repoid=gitlab_gitlab-ce —download_path=/path/to/repository
- Finally, you should use createrepo to regenerate the repository metadata:createrepo -o /path/to/repository /path/to/repository
Your YUM repository mirror is ready to use.
APT repository mirroring
These directions will walk you through using the open source tool apt-mirror to mirror your APT repository.
Install apt-mirror:sudo apt-get install apt-mirrorNOTE: If you are running Debian Wheezy or earlier, you must upgrade to a recent version (0.4.9 or newer) of apt-mirror for HTTPS support.
- Create a directory for your mirror:mkdir /path/to/repo-mirror
- Determine which version of Ubuntu or Debian you’d like to mirror. You’ll need to add this to your apt-mirror config in the next step.
- Modify the apt-mirror config, using your favorite editor:sudo nano /etc/apt/mirror.listThe default /etc/apt/mirror.list configuration is split into two sections. The top section includes global configuration values. Set base_path to the directory you created above:set base_path /path/to/repo-mirror set nthreads 5 set _tilde 0The bottom section of /etc/apt/mirror.list contains a list of repositories to mirror. Use the example below, taking care to replace ubuntu and trusty with your Linux distribution and version:deb https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/**ubuntu**/ trusty main deb-src https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/**ubuntu**/ trusty main
- Import the GPG key for this repository by following the instructions on the GPG panel.
公钥:https://packages.gitlab.com/app/gitlab/gitlab-ce/gpg#gpg-apt
APT GPG keys
NOTE: If you installed gitlab/gitlab-ce with our Bash script, Chef cookbook, or Puppet module the GPG key is automatically installed. There is nothing additional you need to do.
GPG signature info
gitlab/gitlab-ce has its APT metadata signed with the default GPG key.
Import GPG key for gitlab/gitlab-ce
1. Ensure you have curl installed:sudo apt-get install curl
1. Ensure you have GPG installed:sudo apt-get install gnupg
1. Add the GPG key:
For versions equivalent to or later than Debian/Raspbian Stretch, Ubuntu Xenial, Linux Mint Sarah, Elementary OS Loki:
curl -fsSL https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/gpgkey | gpg —dearmor > /usr/share/keyrings/gitlab_gitlab-ce-archive-keyring.gpg
For versions equivalent to or older than Debian/Raspbian Jessie, Ubuntu Wily, Linux Mint Rosa, Elementary OS Freya:
curl -fsSL https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/gpgkey | gpg —dearmor > /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.gpg
4. For versions equivalent to or later than Debian/Raspbian Stretch, Ubuntu Xenial, Linux Mint Sarah, Elementary OS Loki - specify the GPG key in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d entry, as below. All older versions do not require the signed-by option. deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/gitlab_gitlab-ce-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/
Remove GPG key for gitlab/gitlab-ce
For GPG keys stored in /usr/share/keyrings:
1. Remove the GPG key:sudo rm /usr/share/keyrings/gitlab_gitlab-ce-archive-keyring.gpg
For GPG keys stored in /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d:
1. Remove the GPG key:sudo apt-key remove 3F01618A51312F3F
1. You will see the output “OK” when complete. You can verify the key has been removed by running:sudo apt-key list
List all GPG keys known to APT
1. List all GPG keys known to APT:apt-key list
|
| —- |
- Run apt-mirror to generate the mirror.sudo apt-mirror
- Your APT repository mirror is ready to use.