Human Reporting Bias
The frequency with which people write about actions, outcomes, or properties is not a reflection of real-word frequenies or the degree to which a property is characteristic of a class of individuals
Human Biases in Data
| Selection bias | Selection does not reflect a random sample | | —- | —- | | Out-group homogeneity bias | Tendency to see outgroup members as more alike than ingroup member | | Biased Data Representation | some groups are represented less positively than others | | Biased Labels | annotations in dataset reflects the worldviews of your annotators |
Human Biases in Interpretation
| Confirmation bias | The tendency to search for, interpret, favor, recall information in a way that confirms preexisting beliefs | | —- | —- | | Overgeneralization | Coming to conclusion based on information that is too general and/or not specific enough | | Correlation fallacy | Confusing correlation with causation | | Automation bias | Propensity for humans to favor suggestions from automated decision-making systems over contradictory information without automation |
Bias network effect
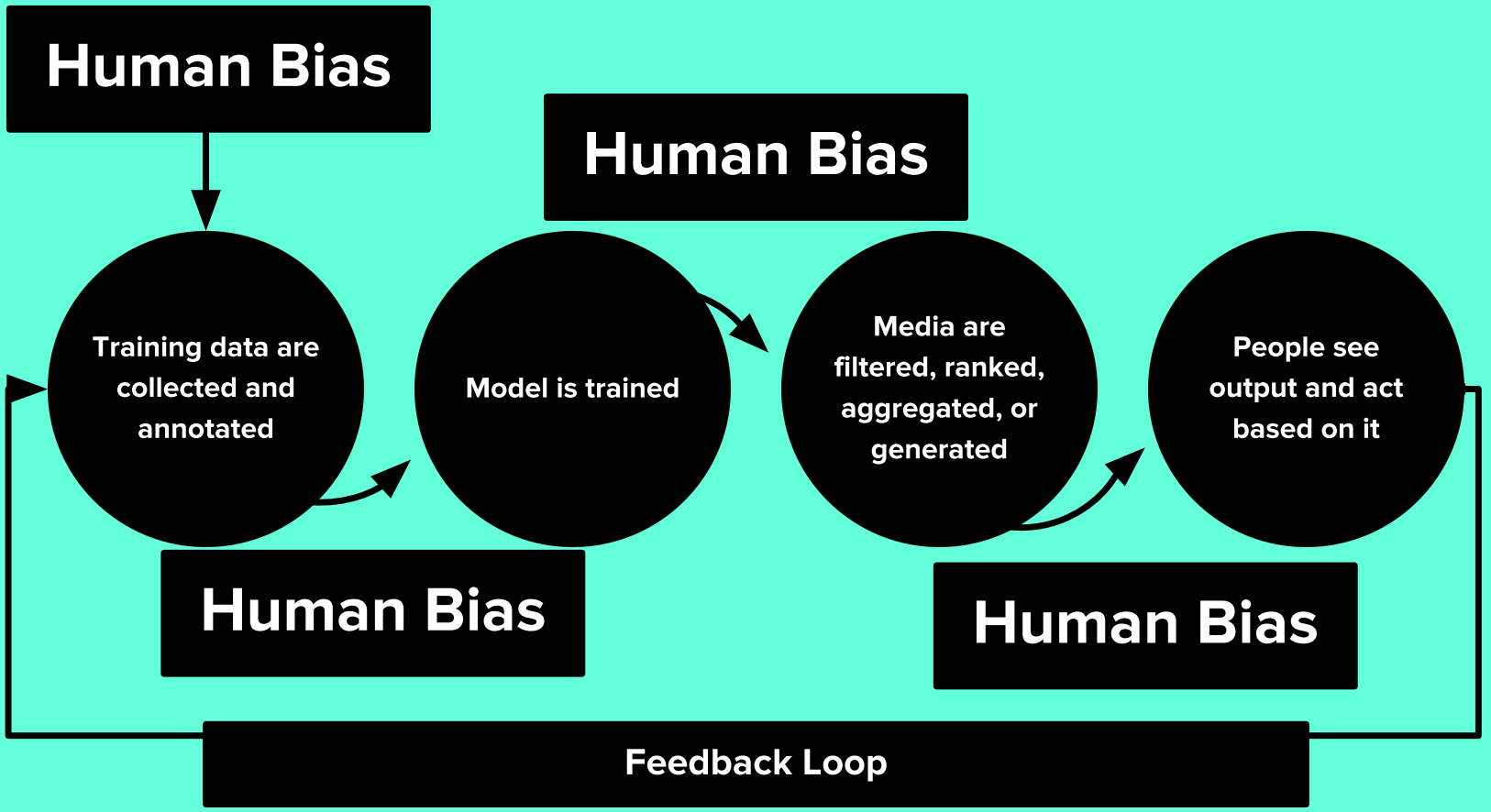
- Human data perpetuates human biases
- as ML learns from human data,
the result is a bias network effect
Bias can be Good, Bad, Neutral
| Bias in statistics and ML | bias of an estimtor, bias term | | —- | —- | | Congnitive biases | confimation bias, recency bias, optimism bias | | algorithmic bias | characteristics historically associated with discrimination and marginalization, when and where they manifest in algorithmic systems or algorithmcally aided decsion-making |
Measuring Algorithmic Bias: evaluate for fairness & inclusion
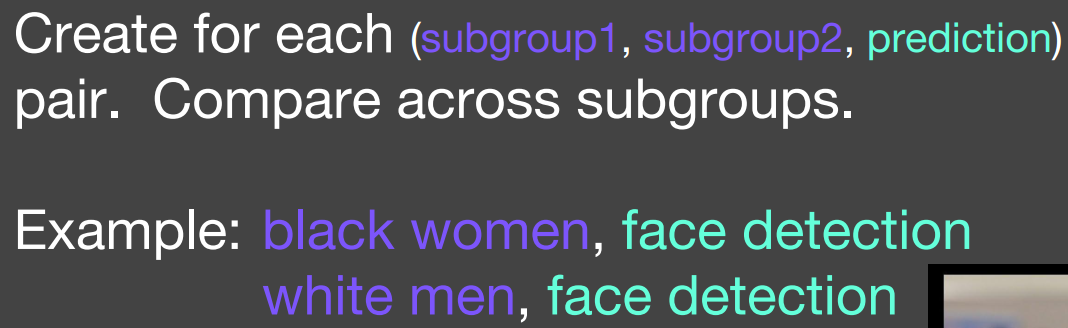
Disaggregated Evaluation
Intersectional Evaluation
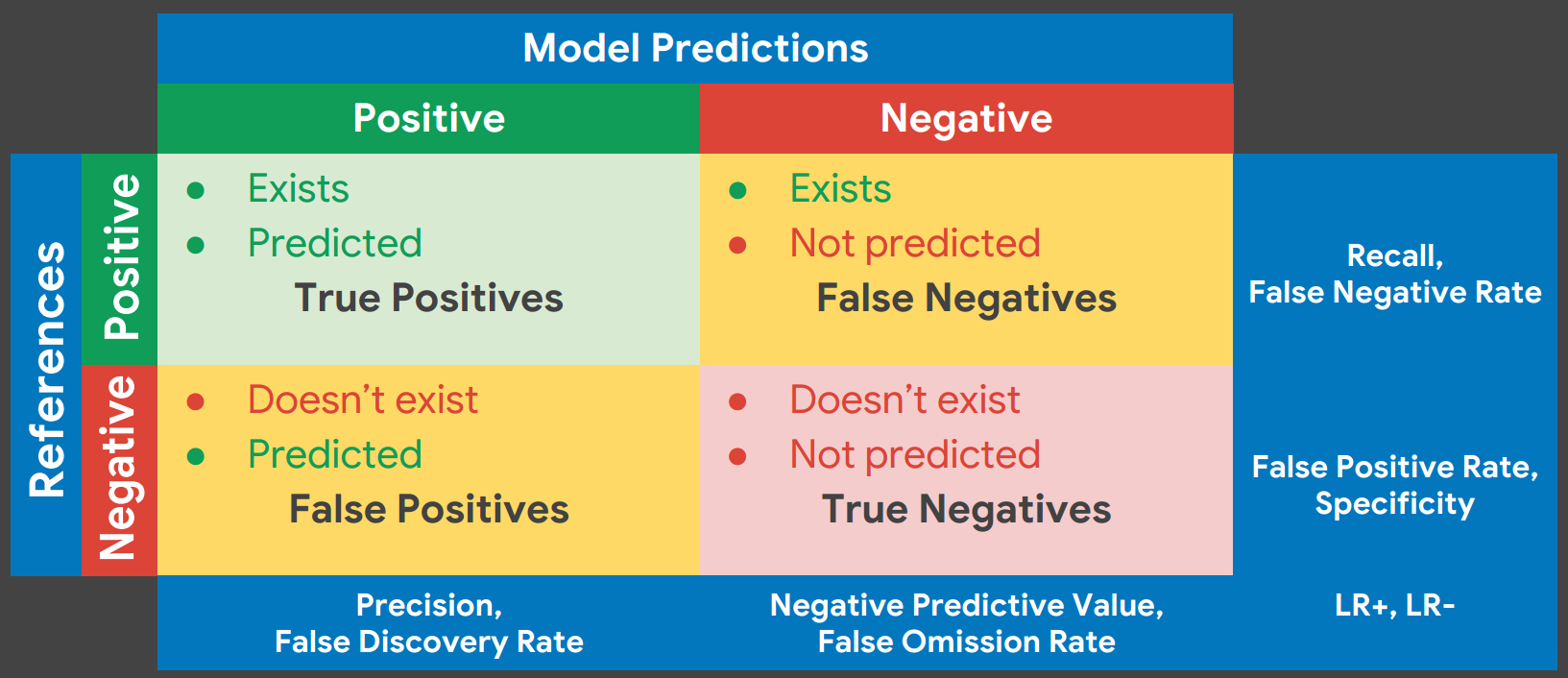
Confusion Matirx