单文件编译
先上 hello world 代码,保存为 helloworld.go
package mainimport "fmt"func main() {fmt.Println("Hello World!")}
$go build helloworld.go
生成 helloworld.exe, 文件名和源码文件名一直。 也可以加上 -o 参数, 指定要生成的可执行文件名。比如:
$go build -o hello helloworld.goJesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog (master)$ lshello* helloworld.exe* helloworld.goJesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog (master)$ ./helloHello World!Jesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog (master)$
如果想看更多 go build 的参数的话, 可以直接在命令行输入 go help build
$ go help buildusage: go build [-o output] [-i] [build flags] [packages]Build compiles the packages named by the import paths,along with their dependencies, but it does not install the results.If the arguments to build are a list of .go files from a single directory,build treats them as a list of source files specifying a single package.When compiling packages, build ignores files that end in '_test.go'.When compiling a single main package, build writesthe resulting executable to an output file named afterthe first source file ('go build ed.go rx.go' writes 'ed' or 'ed.exe')or the source code directory ('go build unix/sam' writes 'sam' or 'sam.exe').The '.exe' suffix is added when writing a Windows executable.When compiling multiple packages or a single non-main package,build compiles the packages but discards the resulting object,serving only as a check that the packages can be built.The -o flag forces build to write the resulting executable or objectto the named output file or directory, instead of the default behavior describedin the last two paragraphs. If the named output is a directory that exists,then any resulting executables will be written to that directory.The -i flag installs the packages that are dependencies of the target.The build flags are shared by the build, clean, get, install, list, run,and test commands:-aforce rebuilding of packages that are already up-to-date.-nprint the commands but do not run them.-p nthe number of programs, such as build commands ortest binaries, that can be run in parallel.The default is the number of CPUs available.-raceenable data race detection.Supported only on linux/amd64, freebsd/amd64, darwin/amd64, windows/amd64,linux/ppc64le and linux/arm64 (only for 48-bit VMA).-msanenable interoperation with memory sanitizer.Supported only on linux/amd64, linux/arm64and only with Clang/LLVM as the host C compiler.On linux/arm64, pie build mode will be used.-vprint the names of packages as they are compiled.-workprint the name of the temporary work directory anddo not delete it when exiting.-xprint the commands.-asmflags '[pattern=]arg list'arguments to pass on each go tool asm invocation.-buildmode modebuild mode to use. See 'go help buildmode' for more.-compiler namename of compiler to use, as in runtime.Compiler (gccgo or gc).-gccgoflags '[pattern=]arg list'arguments to pass on each gccgo compiler/linker invocation.-gcflags '[pattern=]arg list'arguments to pass on each go tool compile invocation.-installsuffix suffixa suffix to use in the name of the package installation directory,in order to keep output separate from default builds.If using the -race flag, the install suffix is automatically set to raceor, if set explicitly, has _race appended to it. Likewise for the -msanflag. Using a -buildmode option that requires non-default compile flagshas a similar effect.-ldflags '[pattern=]arg list'arguments to pass on each go tool link invocation.-linksharedbuild code that will be linked against shared libraries previouslycreated with -buildmode=shared.-mod modemodule download mode to use: readonly, vendor, or mod.See 'go help modules' for more.-modcacherwleave newly-created directories in the module cache read-writeinstead of making them read-only.-modfile filein module aware mode, read (and possibly write) an alternate go.modfile instead of the one in the module root directory. A file named"go.mod" must still be present in order to determine the module rootdirectory, but it is not accessed. When -modfile is specified, analternate go.sum file is also used: its path is derived from the-modfile flag by trimming the ".mod" extension and appending ".sum".-pkgdir dirinstall and load all packages from dir instead of the usual locations.For example, when building with a non-standard configuration,use -pkgdir to keep generated packages in a separate location.-tags tag,lista comma-separated list of build tags to consider satisfied during thebuild. For more information about build tags, see the description ofbuild constraints in the documentation for the go/build package.(Earlier versions of Go used a space-separated list, and that formis deprecated but still recognized.)-trimpathremove all file system paths from the resulting executable.Instead of absolute file system paths, the recorded file nameswill begin with either "go" (for the standard library),or a module path@version (when using modules),or a plain import path (when using GOPATH).-toolexec 'cmd args'a program to use to invoke toolchain programs like vet and asm.For example, instead of running asm, the go command will run'cmd args /path/to/asm <arguments for asm>'.The -asmflags, -gccgoflags, -gcflags, and -ldflags flags accept aspace-separated list of arguments to pass to an underlying toolduring the build. To embed spaces in an element in the list, surroundit with either single or double quotes. The argument list may bepreceded by a package pattern and an equal sign, which restrictsthe use of that argument list to the building of packages matchingthat pattern (see 'go help packages' for a description of packagepatterns). Without a pattern, the argument list applies only to thepackages named on the command line. The flags may be repeatedwith different patterns in order to specify different arguments fordifferent sets of packages. If a package matches patterns given inmultiple flags, the latest match on the command line wins.For example, 'go build -gcflags=-S fmt' prints the disassemblyonly for package fmt, while 'go build -gcflags=all=-S fmt'prints the disassembly for fmt and all its dependencies.For more about specifying packages, see 'go help packages'.For more about where packages and binaries are installed,run 'go help gopath'.For more about calling between Go and C/C++, run 'go help c'.Note: Build adheres to certain conventions such as those describedby 'go help gopath'. Not all projects can follow these conventions,however. Installations that have their own conventions or that usea separate software build system may choose to use lower-levelinvocations such as 'go tool compile' and 'go tool link' to avoidsome of the overheads and design decisions of the build tool.See also: go install, go get, go clean.
后面用到再分享其他参数。
新增一个文件 calc.go 文件,增加一个求和的函数,同时 main.go 中增加这个函数的调用。
// calc.gopackage mainfunc sum(a int, b int) int {return a + b}//helloworld.gopackage mainimport "fmt"func main() {fmt.Println("Hello World!")fmt.Println(sum(10, 20))}
编译方式如下 go build helloworld.go calc.go
$ go build helloworld.go calc.goJesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog (master)$ ./helloworld.exeHello World!30
上面这种情况,适合学习的时候写点简短的代码, 并不适合构建大型项目。
多文件多模块编译
实际工作中,往往只有一个 main.go ,然后其他函数和功能都放在包里面,那么这种情况下,该如何进行编译?这里以一个计算包,一个main.go 为例。
文件目录结构如下:main.go 和 calc 文件夹在同一目录。
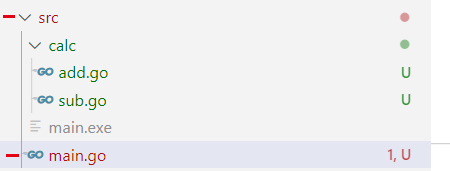
// add.gopackage calcfunc Add(a int, b int) int {return a + b}
// sub.gopackage calcfunc Sub(a int, b int) int {return a - b}
package mainimport "fmt"import "calc"func main() {fmt.Println("Hello!")fmt.Println(calc.Add(10, 20), calc.Sub(20, 10))fmt.Println("Bye bye!")}
Jesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog/src (master)$ go build main.goJesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog/src (master)$ ./main.exeHello!30 10Bye bye!
如果报错,可以 export GO111MODULE=off 关闭 go module
export GOPATH= /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog/ 指定工程目录
如果增加新的模块, 只需要建个新文件,和calc 同级目录,到此,基本的工程项目目录构建的差不多了。
go module
go1.11 之后引入了 go module。 通过 go env 命令,可以看到有个变量 GO111MODULE 变量。
在上面代码结构基础上,先用 go mod init 初始化一个mod 文件。
$ go mod init bloggo: creating new go.mod: module blogJesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog/src (master)$ go buildJesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog/src (master)$ lsblog.exe* calc/ go.mod main.go xxx.exe*Jesson@LAPTOP-QJ5P400E MINGW64 /e/mygitee/go-learn/blog/src (master)$
这样 main.go 中的引用 calc 包的路径,要做点改动, 改为 import”blog/calc”

