在使用 SQL 进行数据分析的过程中,关联查询是经常要使用到的操作。在传统的 OLTP 和 OLAP 领域中,关联查询的数据集都是有界的,因此可以依赖于缓存有界的数据集进行查询。但是在 Streaming SQL 中,针对 Stream Join Stream 的情况,由于关联查询的两侧都是连续无界的数据流,传统数据表中 Join 操作的实现和优化方式可能并不完全适用。在这篇文章中,我们将介绍双流 Join 面临的挑战,并对 Flink SQL 中双流 Join 的具体实现机制进行分析。
双流 Join 的挑战
在传统的数据库或批处理场景中 ,关联查询的数据集都是有限的,因此可以依赖于缓存有界的数据集,使用诸如 Nested-Loop Join,Sort-Merged Join 或者 Hash Join 等方法进行匹配查询。但是在 Streaming SQL 中,两个数据流的关联查询主要面临如下两个问题:一方面,数据流是无限的,缓存数据对 long-running 的任务而言会带来较高的存储和查询压力;另一方面,两侧数据流中消息到达的时间存在不一致的情况,可能造成关联结果的缺失。
对于上述的第一个问题,为了保证关联结果的正确性,需要将数据流中所有历史数据缓存下来。随着两个数据流中数据源源不断到来,缓存历史数据带来的开销越来越大,且每一条新到达的消息都会激发对另一侧历史数据的查询。为了解决该问题,一种方法是通过时间窗口将关联的数据范围限制在特定的时间范围内,即 Window Join(关于时间窗口可以参考之前的文章);另一种方法是,在存储开销和关联准确度方面做一下权衡,在缓存的历史数据上增加生存时间的限制,这样可以避免缓存的数据无限增长,但相应地可能会造成准确度的降低。
上述第二个问题,主要针对的是外连接的情况。由于两侧数据到达时间的不确定性,对于特定消息,可能出现 t1 时刻不存在匹配记录,而 t2 (t2 > t1) 时刻存在匹配记录的情况。对于外连接,要求在不存在关联结果的情况下返回 NULL 值。因此为了保证关联结果的正确性,一种方式是通过时间窗口限制关联的数据范围,但这样就要求在窗口结束时才输出结果,会导致输出延迟;另一种方式是采取“撤销-更正”的方式,先输出 NULL 值,在后续关联记录到达时再撤销已输出的记录,修正为关联的正确结果,其缺点是会造成输出记录数的放大。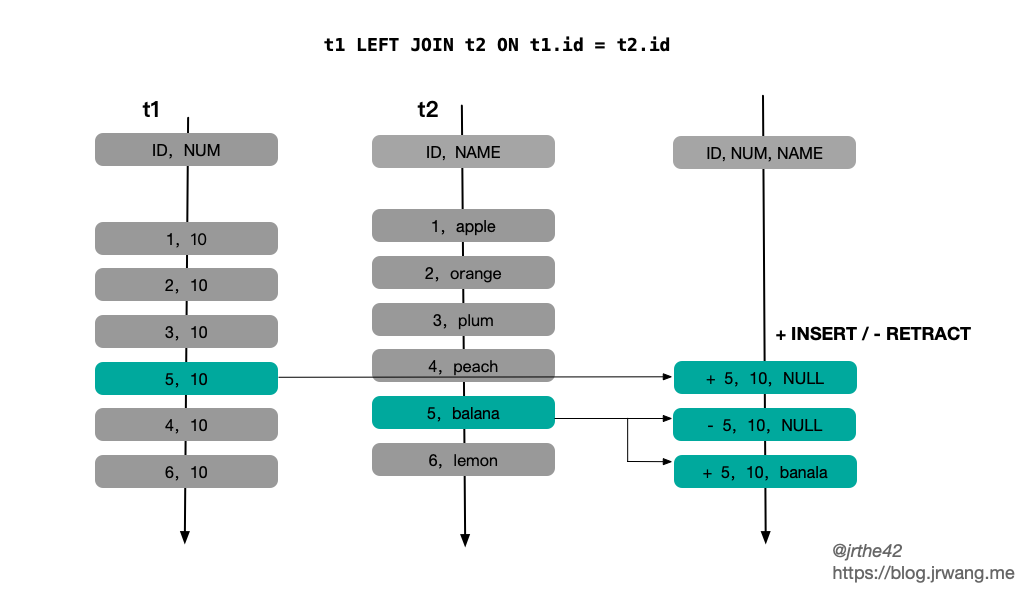
从上述的分析可以看出,时间窗口在关联查询中通过限制关联数据的范围,可以部分程度上解决 Streaming Join 面临的问题,其基本思路是将无限的数据流切分为有限的时间窗口。但时间窗口关联并不适合所有的情况,很多时候两个数据流的关联查询并不能限定在特定的时间窗口内;此外,时间窗口关联还存在输出延迟的情况。
本文的后续部分将对 Flink SQL 中普通双流 Join 的实现机制加以介绍,Window Join 的实现机制将在后续的文章中进行分析。
双流 Join 的实现机制
一条 Join 语句的转换
首先,我们以一条简单的 Join 语句为例,跟踪一条 Join 语句的变换过程。
| ``` — table A(‘a1, ‘a2, ‘a3) — table B(‘b1, ‘b2, ‘b3) SELECT a1, b1 FROM A JOIN B ON a1 = b1 and a2 > b2
|| --- |上述的 SQL 语句在经过解析后,被转换为如下的逻辑计划:| LogicalProject(a1=[$0], b1=[$3])+- LogicalJoin(condition=[AND(=($0, $3), >($1, $4))], joinType=[inner]):- LogicalTableScan(table=[[A, source: [TestTableSource(a1, a2, a3)]]])+- LogicalTableScan(table=[[B, source: [TestTableSource(b1, b2, b3)]]]) || --- |这份逻辑计划首先被转换为 Flink SQL 内部的 RelNode,即:| FlinkLogicalCalc(select=[a1, b1])+- FlinkLogicalJoin(condition=[AND(=($0, $2), >($1, $3))], joinType=[inner]):- FlinkLogicalCalc(select=[a1, a2]): +- FlinkLogicalTableSourceScan(table=[[A, source: [TestTableSource(a1, a2, a3)]]], fields=[a1, a2, a3])+- FlinkLogicalCalc(select=[b1, b2])+- FlinkLogicalTableSourceScan(table=[[B, source: [TestTableSource(b1, b2, b3)]]], fields=[b1, b2, b3]) || --- |此后,经过一系列优化规则被优化为最终的执行计划,如下:| Calc(select=[a1, b1])+- Join(joinType=[InnerJoin], where=[AND(=(a1, b1), >(a2, b2))], select=[a1, a2, b1, b2], leftInputSpec=[NoUniqueKey], rightInputSpec=[NoUniqueKey]):- Exchange(distribution=[hash[a1]]): +- Calc(select=[a1, a2]): +- TableSourceScan(table=[[A, source: [TestTableSource(a1, a2, a3)]]], fields=[a1, a2, a3])+- Exchange(distribution=[hash[b1]])+- Calc(select=[b1, b2])+- TableSourceScan(table=[[B, source: [TestTableSource(b1, b2, b3)]]], fields=[b1, b2, b3]) || --- |至此,逻辑计划的优化阶段结束,进入物理计划生成的阶段。<br />Flink SQL 会为 `StreamExecJoin` 操作生成一个 `TwoInputTransformation` 变换,内部算子为 `StreamingJoinOperator`,用于在两个数据流中匹配关联记录;为 `StreamExecExchange` 操作生成一个 `PartitionTransformation` 变换,用来确定上游算子输出的记录转发到下游算子的分区。<a name="e33737e6"></a>### [](https://blog.jrwang.me/2020/2020-01-05-flink-sourcecode-sql-stream-join/#%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E9%87%8D%E8%A6%81%E7%9A%84%E5%8F%98%E6%8D%A2%E8%A7%84%E5%88%99)两个重要的变换规则在逻辑计划优化的过程中,有两个重要的规则需要关注,分别是 `StreamExecJoinRule` 和 `FlinkExpandConversionRule`。<br />顾名思义,`StreamExecJoinRule` 主要用于将 `FlinkLogicalJoin` 转换为 `StreamExecJoin`。但是这个变换是有条件限制的,即 `FlinkLogicalJoin` 的关联条件中不包含时间窗口。首先来看一下这个规则的匹配条件:|
class StreamExecJoinRule extends RelOptRule( operand(classOf[FlinkLogicalJoin], operand(classOf[FlinkLogicalRel], any()), operand(classOf[FlinkLogicalRel], any())), “StreamExecJoinRule”) { override def matches(call: RelOptRuleCall): Boolean = { val join: FlinkLogicalJoin = call.rel(0) //关联结果是否需要从右表投射数据,SEMI JOIN 和 ANTI JOIN 不需要选择右表的数据 if (!join.getJoinType.projectsRight) { // SEMI/ANTI JOIN 总是被转换为 StreamExecJoin return true } val left: FlinkLogicalRel = call.rel(1).asInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalRel] val right: FlinkLogicalRel = call.rel(2).asInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalRel] val tableConfig = call.getPlanner.getContext.unwrap(classOf[FlinkContext]).getTableConfig val joinRowType = join.getRowType //左表不支持 Temporal Table if (left.isInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalSnapshot]) { throw new TableException( “Temporal table join only support apply FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF on the right table.”) } //不支持 Temporal Table JOIN if (right.isInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalSnapshot] || TemporalJoinUtil.containsTemporalJoinCondition(join.getCondition)) { return false } //从关联条件中提取 1)时间窗口边界 2)其它条件 val (windowBounds, remainingPreds) = WindowJoinUtil.extractWindowBoundsFromPredicate( join.getCondition, join.getLeft.getRowType.getFieldCount, joinRowType, join.getCluster.getRexBuilder, tableConfig) //存在窗口,则不适用于该规则 if (windowBounds.isDefined) { return false } //普通关联条件不能访问时间属性 // remaining predicate must not access time attributes val remainingPredsAccessTime = remainingPreds.isDefined && WindowJoinUtil.accessesTimeAttribute(remainingPreds.get, joinRowType) //RowTime 属性不能出现在普通 join 的关联条件中 //@see https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57181771/flink-rowtime-attributes-must-not-be-in-the-input-rows-of-a-regular-join val rowTimeAttrInOutput = joinRowType.getFieldList .exists(f => FlinkTypeFactory.isRowtimeIndicatorType(f.getType)) if (rowTimeAttrInOutput) { throw new TableException( “Rowtime attributes must not be in the input rows of a regular join. “ + “As a workaround you can cast the time attributes of input tables to TIMESTAMP before.”) } // joins require an equality condition // or a conjunctive predicate with at least one equality condition // and disable outer joins with non-equality predicates(see FLINK-5520) // And do not accept a FlinkLogicalTemporalTableSourceScan as right input !remainingPredsAccessTime } }
|| --- |其基本逻辑就是,在普通的双流 Join 中不支持 Temporal Table,不支持时间窗口,不支持访问时间属性。这里需要注意的一点是,在普通的双流 Join 中,Flink 没法保证关联结果按照时间先后顺序提交,会破坏时间属性的顺序,因此在[普通的双流 Join 中关联条件不支持时间属性](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57181771/flink-rowtime-attributes-must-not-be-in-the-input-rows-of-a-regular-join)。<br />`StreamExecJoinRule` 会将 `FlinkLogicalJoin` 转换为 `StreamexecJoin`,但相应地,需要先对 `FlinkLogicalJoin` 的两个输入进行变换。在这里,会将 `FlinkRelDistribution` 这个 trait 下推到输入算子中。`FlinkRelDistribution` 用于确定上游算子结果转发到下游算子的分区信息。例如,如果关联条件中存在等值关联条件,那么就会按照对应的关联键进行哈希分区,确保相同键的记录被转发到相同的 Task 中,即 `FlinkRelDistribution.hash`;而如果关联条件中不存在等值条件,那么所有的记录只能被转发到同一个 Task 中,即 `FlinkRelDistribution.SINGLETON`。|
class StreamExecJoinRule{ override def onMatch(call: RelOptRuleCall): Unit = { val join: FlinkLogicalJoin = call.rel(0) val left = join.getLeft val right = join.getRight //根据是否存在等值关联条件确定 FlinkRelDistribution def toHashTraitByColumns( columns: util.Collection[_ <: Number], inputTraitSets: RelTraitSet): RelTraitSet = { val distribution = if (columns.isEmpty) { FlinkRelDistribution.SINGLETON } else { FlinkRelDistribution.hash(columns) } inputTraitSets .replace(FlinkConventions.STREAM_PHYSICAL) .replace(distribution) } val joinInfo = join.analyzeCondition() val (leftRequiredTrait, rightRequiredTrait) = ( toHashTraitByColumns(joinInfo.leftKeys, left.getTraitSet), toHashTraitByColumns(joinInfo.rightKeys, right.getTraitSet)) val providedTraitSet = join.getTraitSet.replace(FlinkConventions.STREAM_PHYSICAL) //变换输入 val newLeft: RelNode = RelOptRule.convert(left, leftRequiredTrait) val newRight: RelNode = RelOptRule.convert(right, rightRequiredTrait) //生成 StreamExecJoin val newJoin = new StreamExecJoin( join.getCluster, providedTraitSet, newLeft, newRight, join.getCondition, join.getJoinType) call.transformTo(newJoin) } }
|| --- |对 `FlinkRelDistribution` 的匹配变换规则在 `FlinkExpandConversionRule` 中。`FlinkExpandConversionRule` 的作用是处理 `RelDistribution` 和 `RelCollation` 这两种 trait,其中 `RelDistribution` 描述数据的物理分布情况,`RelCollation` 描述排序情况(通常在 Batch 模式下应用在 ORDER BY 语句中)。<br />在 `FlinkExpandConversionRule` 中会为目标 trait 包含 `FlinkRelDistribution` 的变换生成一个 `StreamExecExchange`:|
class FlinkExpandConversionRule(flinkConvention: Convention) extends RelOptRule( operand(classOf[AbstractConverter], operand(classOf[RelNode], any)), “FlinkExpandConversionRule”) { override def matches(call: RelOptRuleCall): Boolean = { // from trait 和 to trait 不一致 val toTraitSet = call.rel(0).asInstanceOf[AbstractConverter].getTraitSet val fromTraitSet = call.rel(1).asInstanceOf[RelNode].getTraitSet toTraitSet.contains(flinkConvention) && fromTraitSet.contains(flinkConvention) && !fromTraitSet.satisfies(toTraitSet) } override def onMatch(call: RelOptRuleCall): Unit = { val converter: AbstractConverter = call.rel(0) val child: RelNode = call.rel(1) val toTraitSet = converter.getTraitSet // try to satisfy required trait by itself. satisfyTraitsBySelf(child, toTraitSet, call) // try to push down required traits to children. satisfyTraitsByInput(child, toTraitSet, call) } private def satisfyTraitsBySelf( node: RelNode, requiredTraits: RelTraitSet, call: RelOptRuleCall): Unit = { var transformedNode = node val definedTraitDefs = call.getPlanner.getRelTraitDefs // 处理 FlinkRelDistribution if (definedTraitDefs.contains(FlinkRelDistributionTraitDef.INSTANCE)) { val toDistribution = requiredTraits.getTrait(FlinkRelDistributionTraitDef.INSTANCE) transformedNode = satisfyDistribution(flinkConvention, transformedNode, toDistribution) } if (definedTraitDefs.contains(RelCollationTraitDef.INSTANCE)) { val toCollation = requiredTraits.getTrait(RelCollationTraitDef.INSTANCE) transformedNode = satisfyCollation(flinkConvention, transformedNode, toCollation) } checkSatisfyRequiredTrait(transformedNode, requiredTraits) call.transformTo(transformedNode) } } object FlinkExpandConversionRule { def satisfyDistribution( flinkConvention: Convention, node: RelNode, requiredDistribution: FlinkRelDistribution): RelNode = { val fromTraitSet = node.getTraitSet val fromDistribution = fromTraitSet.getTrait(FlinkRelDistributionTraitDef.INSTANCE) if (!fromDistribution.satisfies(requiredDistribution)) { requiredDistribution.getType match { case SINGLETON | HASHDISTRIBUTED | RANGE_DISTRIBUTED | BROADCAST_DISTRIBUTED | RANDOM_DISTRIBUTED => flinkConvention match { case FlinkConventions.BATCH_PHYSICAL => // replace collation with empty since distribution destroy collation …… new BatchExecExchange(node.getCluster, traitSet, node, requiredDistribution) case FlinkConventions.STREAM_PHYSICAL => val updateAsRetraction = fromTraitSet.getTrait(UpdateAsRetractionTraitDef.INSTANCE) val accMode = fromTraitSet.getTrait(AccModeTraitDef.INSTANCE) // replace collation with empty since distribution destroy collation val traitSet = fromTraitSet .replace(requiredDistribution) .replace(flinkConvention) .replace(RelCollations.EMPTY) .replace(updateAsRetraction) .replace(accMode) // 生成 StreamExecExchange new StreamExecExchange(node.getCluster, traitSet, node, requiredDistribution) case => throw new TableException(s”Unsupported convention: $flinkConvention”) } case _ => throw new TableException(s”Unsupported type: ${requiredDistribution.getType}”) } } else { node } } }
|| --- |<a name="516fb8ac"></a>### [](https://blog.jrwang.me/2020/2020-01-05-flink-sourcecode-sql-stream-join/#%E7%89%A9%E7%90%86%E6%89%A7%E8%A1%8C%E8%AE%A1%E5%88%92)物理执行计划在得到最终的逻辑执行计划后,需要将其转换为物理执行计划,即生成 Flink 内部的 `Transformation` 算子。<br />首先,`StreamExecJoin` 的输入是两个 `StreamExecExchange` 节点,`StreamExecExchange` 会生成 `PartitionTransformation` 算子,用来决定上游数据到下游的分布情况。根据 `RelDistribution.Type` 的不同,`PartitionTransformation` 的 `StreamPartitioner` 会选择使用 `GlobalPartitioner`(对应 `RelDistribution.Type.SINGLETON`) 或是 `KeyGroupStreamPartitioner`(对应 `RelDistribution.Type.HASH_DISTRIBUTED`)。|
class StreamExecExchange { //生成物理执行计划 override protected def translateToPlanInternal( planner: StreamPlanner): Transformation[BaseRow] = { val inputTransform = getInputNodes.get(0).translateToPlan(planner) .asInstanceOf[Transformation[BaseRow]] val inputTypeInfo = inputTransform.getOutputType.asInstanceOf[BaseRowTypeInfo] val outputTypeInfo = BaseRowTypeInfo.of( FlinkTypeFactory.toLogicalRowType(getRowType)) relDistribution.getType match { // 如果分布是 SINGLETON(不存在等值关联条件),所有记录被转发至同一个分区 case RelDistribution.Type.SINGLETON => val partitioner = new GlobalPartitioner[BaseRow] val transformation = new PartitionTransformation( inputTransform, partitioner.asInstanceOf[StreamPartitioner[BaseRow]]) transformation.setOutputType(outputTypeInfo) transformation.setParallelism(1) transformation case RelDistribution.Type.HASHDISTRIBUTED => val selector = KeySelectorUtil.getBaseRowSelector( relDistribution.getKeys.map(.toInt).toArray, inputTypeInfo) // 如果分布是 HASH(存在等值关联条件),按 HASH 分区 val partitioner = new KeyGroupStreamPartitioner(selector, DEFAULTLOWER_BOUND_MAX_PARALLELISM) val transformation = new PartitionTransformation( inputTransform, partitioner.asInstanceOf[StreamPartitioner[BaseRow]]) transformation.setOutputType(outputTypeInfo) transformation.setParallelism(ExecutionConfig.PARALLELISM_DEFAULT) transformation case => throw new UnsupportedOperationException( s”not support RelDistribution: ${relDistribution.getType} now!”) } } }
|| --- |对于 `StreamExecJoin`,则会为其生成一个 `TwoInputTransformation`,其内部的转换代码如下:|
class StreamExecJoin { override protected def translateToPlanInternal( planner: StreamPlanner): Transformation[BaseRow] = { val tableConfig = planner.getTableConfig val returnType = BaseRowTypeInfo.of(FlinkTypeFactory.toLogicalRowType(getRowType)) // 对上游输入做变换 val leftTransform = getInputNodes.get(0).translateToPlan(planner) .asInstanceOf[Transformation[BaseRow]] val rightTransform = getInputNodes.get(1).translateToPlan(planner) .asInstanceOf[Transformation[BaseRow]] val leftType = leftTransform.getOutputType.asInstanceOf[BaseRowTypeInfo] val rightType = rightTransform.getOutputType.asInstanceOf[BaseRowTypeInfo] // 获取 Join Key,即 等值关联条件 val (leftJoinKey, rightJoinKey) = JoinUtil.checkAndGetJoinKeys(keyPairs, getLeft, getRight, allowEmptyKey = true) // 生成 KeySelector 的代码,用于提取 Join Key // 如果不存在等值关联条件,返回的是 NullBinaryRowKeySelector,Join Key 为空 val leftSelect = KeySelectorUtil.getBaseRowSelector(leftJoinKey, leftType) val rightSelect = KeySelectorUtil.getBaseRowSelector(rightJoinKey, rightType) // 分析 Join 的输入侧,是否存在 UniqueKey, JoinKey 是否包含 UniqueKey // 会根据 UniqueKey 优化状态的存储和查找方式 val leftInputSpec = analyzeJoinInput(left) val rightInputSpec = analyzeJoinInput(right) // 生成比较关联条件的代码,这里只处理非等值关联条件况,等值关联的条件是通过状态隐式完成的 val generatedCondition = JoinUtil.generateConditionFunction( tableConfig, cluster.getRexBuilder, getJoinInfo, leftType.toRowType, rightType.toRowType) //状态保存时间 val minRetentionTime = tableConfig.getMinIdleStateRetentionTime //内部算子 val operator = if (joinType == JoinRelType.ANTI || joinType == JoinRelType.SEMI) { new StreamingSemiAntiJoinOperator( joinType == JoinRelType.ANTI, leftType, rightType, generatedCondition, leftInputSpec, rightInputSpec, filterNulls, minRetentionTime) } else { val leftIsOuter = joinType == JoinRelType.LEFT || joinType == JoinRelType.FULL val rightIsOuter = joinType == JoinRelType.RIGHT || joinType == JoinRelType.FULL new StreamingJoinOperator( leftType, rightType, generatedCondition, leftInputSpec, rightInputSpec, leftIsOuter, rightIsOuter, filterNulls, minRetentionTime) } //变换 val ret = new TwoInputTransformationBaseRow, BaseRow, BaseRow // 输入存在 RelDistribution.Type.SINGLETON(没有等值关联条件),则 Join 算子的并行度设为 1 if (inputsContainSingleton()) { ret.setParallelism(1) ret.setMaxParallelism(1) } // set KeyType and Selector for state // 设置状态的 KeySelector,状态是 KeyedState ret.setStateKeySelectors(leftSelect, rightSelect) ret.setStateKeyType(leftSelect.getProducedType) ret } }
|| --- |`StreamExecJoin` 转换为 `TwoInputTransformation` 的过程中,首先会分析上游两个输入的特征,包括是否存在关联键(Join Key,对应等值关联条件),是否存在唯一键(Unique Key,唯一键可以用来保证上游的输出是唯一的,参考[Flink 源码阅读笔记(18)- Flink SQL 中的流和动态表](https://blog.jrwang.me/2019/2019-10-16-flink-sourcecode-stream-and-dynamic-table/#%E5%88%A4%E6%96%AD%E5%94%AF%E4%B8%80%E9%94%AE)),关联键中是否包含唯一键等。根据 Join 类型的不同, `TwoInputTransformation` 内部的算子是 `StreamingJoinOperator` 或者 `StreamingSemiAntiJoinOperator`(用于 SEMI/ANTI Join)。`StreamingJoinOperator` 内部使用 KeyedState,因此会将状态的 KeySelector 设置为关联键。<a name="2ccd49a1"></a>### [](https://blog.jrwang.me/2020/2020-01-05-flink-sourcecode-sql-stream-join/#%E7%8A%B6%E6%80%81%E5%AD%98%E5%82%A8%E7%9A%84%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96)状态存储的优化双流 Join 的情况下,为了保证关联结果的正确性,需要将历史记录保存在状态中。随着数据流中的数据源源不断到来,缓存历史数据带来的开销越来越大。为此,Flink SQL 一方面支持通过配置状态 TTL 来限制状态的保存时间,另一方面针对状态存储的结构进行了优化。<br />根据 `JoinInputSideSpec` 中输入侧的特点(是否包含唯一键、关联键是否包含唯一键),Flink SQL 设计了几种不同的状态存储结构,即 `JoinKeyContainsUniqueKey`, `InputSideHasUniqueKey` 和 `InputSideHasNoUniqueKey`,分别如下:<br />[](https://blog.jrwang.me/img/flink-sql-join/flink-stream-join-state.png)<br />上述几种不同的状态存储都实现了 `JoinRecordStateView` 接口,提供的三个方法如下,分别对应向状态中添加一条记录、撤回一条记录、查询关联记录这三种情况:|
public interface JoinRecordStateView { /**
* Add a new record to the state view.*/void addRecord(BaseRow record) throws Exception;/*** Retract the record from the state view.*/void retractRecord(BaseRow record) throws Exception;/*** Gets all the records under the current context (i.e. join key).*/Iterable<BaseRow> getRecords() throws Exception;
}
|| --- |`StreamingJoinOperator` 中的状态使用的是 KeyedState,key 就是当前记录的 Join Key。在不同情况下,不同状态存储的结构和访问开销如下:| | State Structure | Update Row | Query by JK | Note || --- | --- | --- | --- | --- || `JoinKeyContainsUniqueKey` | `<JK,ValueState<Record>>` | O(1) | O(1) | || `InputSideHasUniqueKey` | `<JK,MapState<UK,Record>>` | O(2) | O(N) | N = size of MapState || `InputSideHasNoUniqueKey` | `<JK,MapState<Record, appear-times>>` | O(2) | O(N) | N = size of MapState |上述表格中的内容其实不难理解,根据 Join Key 和 Unique Key 的特性,状态的结构分为三种情况:- 如果 Join Key 包含了 Unique Key,那么一个 Join Key 只会对应一条记录,因此状态存储选择的是 `ValueState`- 如果输入存在 Unique Key,但 Join Key 不包含 Unique Key,一个 Join Key 可能会对应多条记录,但这些记录的 Unique Key 一定不同,因此选择使用 `MapState`,key 为 Unique Key, value 为对应的记录- 如果输入不存在 Unique Key,那么状态状态只能是 `ListState` 或者 `MapState`,从 update 和 retract 的效率考虑,选择使用 `MapState`,直接使用记录本身作为 Key,value 为记录出现的次数还有一种特殊的情况,即不存在 Join Key(笛卡尔积),这种情况其实是 `InputSideHasNoUniqueKey` 的一种特例,所有记录的 Join Key 都是 `BinaryRowUtil.EMPTY_ROW`。<br />从最终的性能上来看,`JoinkKeyContainsUniqueKey` > `InputSideHasUniqueKey` > `InputSideHasNoUniqueKey`。<br />如果是外连接,那么作为外连接的一侧,其状态需要实现的是 `OuterJoinRecordStateView` 接口,它的具体实现也分为三种情况,如下:<br />[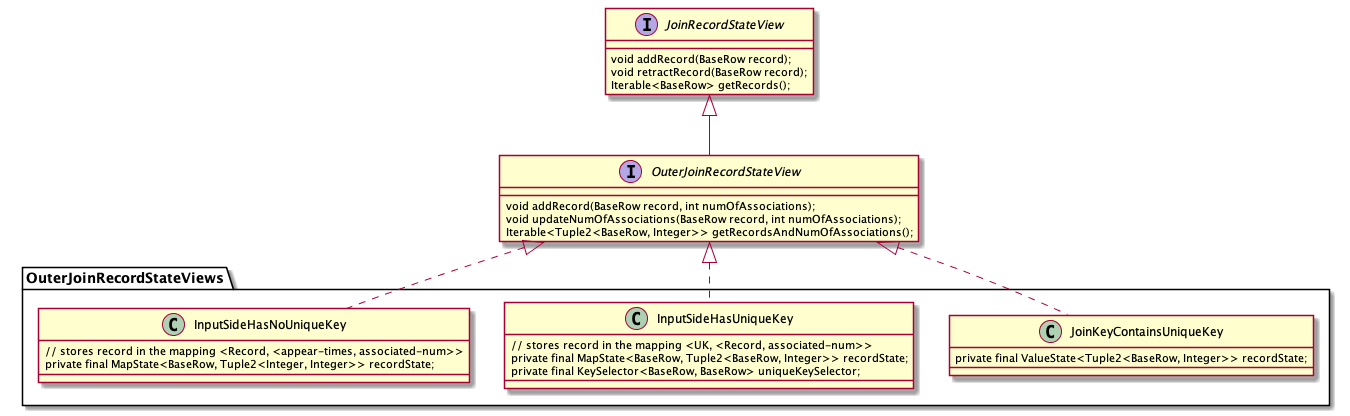](https://blog.jrwang.me/img/flink-sql-join/flink-stream-join-state-outer.png)<br />`OuterJoinRecordStateView` 是对 `JoinRecordStateView` 的扩展,除了会将记录本身存储在状态里,还会将该条记录在另一侧关联到的记录数存储下来。之所以要将关联记录数存储在状态中,主要是为了方便 Outer Join 中处理和撤回用 NULL 值填充的结果。在下文介绍关联的具体逻辑时会进一步介绍。除此以外,`OuterJoinRecordStateView` 和 `JoinRecordStateView` 的存储结构是一致的。<a name="6edd703c"></a>### [](https://blog.jrwang.me/2020/2020-01-05-flink-sourcecode-sql-stream-join/#%E5%85%B3%E8%81%94%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86%E9%80%BB%E8%BE%91)关联处理逻辑`StreamingJoinOperator` 中的主要逻辑其实就是两步:- 在数据到达时更新本侧的状态- 在数据到达时根据 Join Key 去查询另一侧的状态在 Streaming SQL 中存在 ACCUMULATE 和 RETRACT 这两种类型的消息,在 Join 中需要分别考虑。如果达到的消息是 ACCUMULATE 类型的记录,那么相应的处理逻辑的伪代码如下:| //record is ACCif input side is outer //本侧是outer joinif no matched row on the other side //另一侧没有匹配记录send +[record + null]state.add(record, 0) // 0 表示另一侧没有关联的记录else // other.size > 0if other side is outerif (associated rows in matched rows == 0)//另一侧之前在本侧没有匹配的记录,所以需要撤回之前的 [null + other]send -[null + other]elseskipendifotherState.update(other, old + 1) //另一侧关联的记录 + 1endifsend +[record, other]s //另一侧有多少匹配的记录就发送多少条state.add(record, other.size) //更新状态endifelse //本侧不是 outer joinstate.add(record)if no matched row on the other side //另一侧没有匹配记录skip //无需输出else // other.size > 0if other size is outerif (associated rows in matched rows == 0)send -[null + other]elseskipendifotherState.update(other, old + 1) //另一侧关联的记录 + 1endifsend +[record + other]s //另一侧有多少匹配的记录就发送多少条endifendif || --- |Inner Join 的情况比较简单,这里需要注意的是对 Outer Join 的处理。Outer Join 要求在没有匹配记录时输出用 NULL 值填充的结果,但是后续另一侧有匹配记录到达时,就需要撤回已发送的 NULL 值填充记录,更正为正常的关联的结果。因此,在 `OuterJoinRecordStateView` 中会保存关联记录数,如果关联记录数为 0,则表明之前已经发送了 NULL 值填充的记录,那么就需要进行撤回操作,从而避免了每次重新计算已关联的记录数。<br />如果接收到的记录是一条 RETRACT 消息,那么相应处理逻辑的伪代码如下:| //record is RETRACTstate.retract(record)if no matched rows on the other side //另一侧没有关联记录if input side is outersend -[record + null]endifelse //另一侧存在关联记录send -[record, other]s //要撤回已发送的关联记录if other side is outerif the matched num in the matched rows == 0, this should never happen!if the matched num in the matched rows == 1, send +[null + other]if the matched num in the matched rows > 1, skipotherState.update(other, old - 1) //另一侧关联的记录数 - 1endifendif || --- |下图简单给出了一个 inner join 的例子,两侧的状态都是 `InputSideHasNoUniqueKey`,上下两部分分别对应 ACCMULATE 和 RETRACT 的情形: [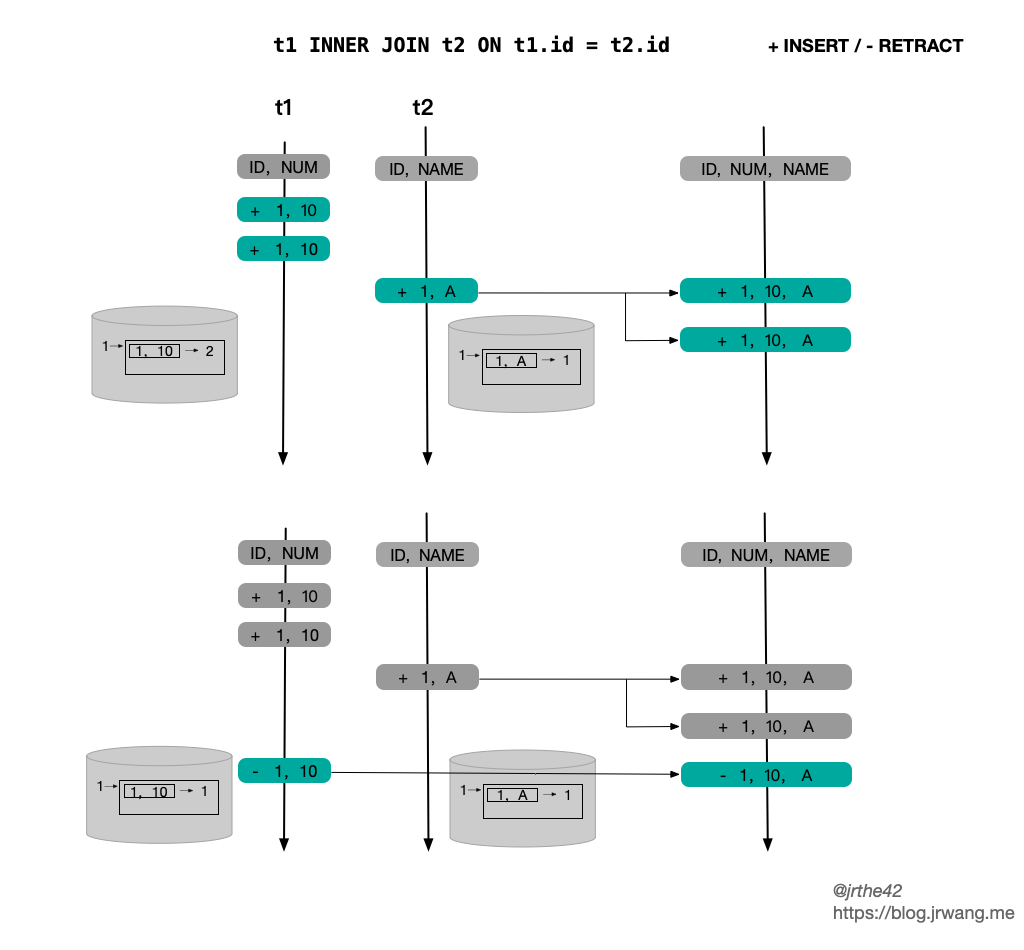](https://blog.jrwang.me/img/flink-sql-join/flink-sql-inner-join-example.png)<br />下图则是 Full outer join 的情况: [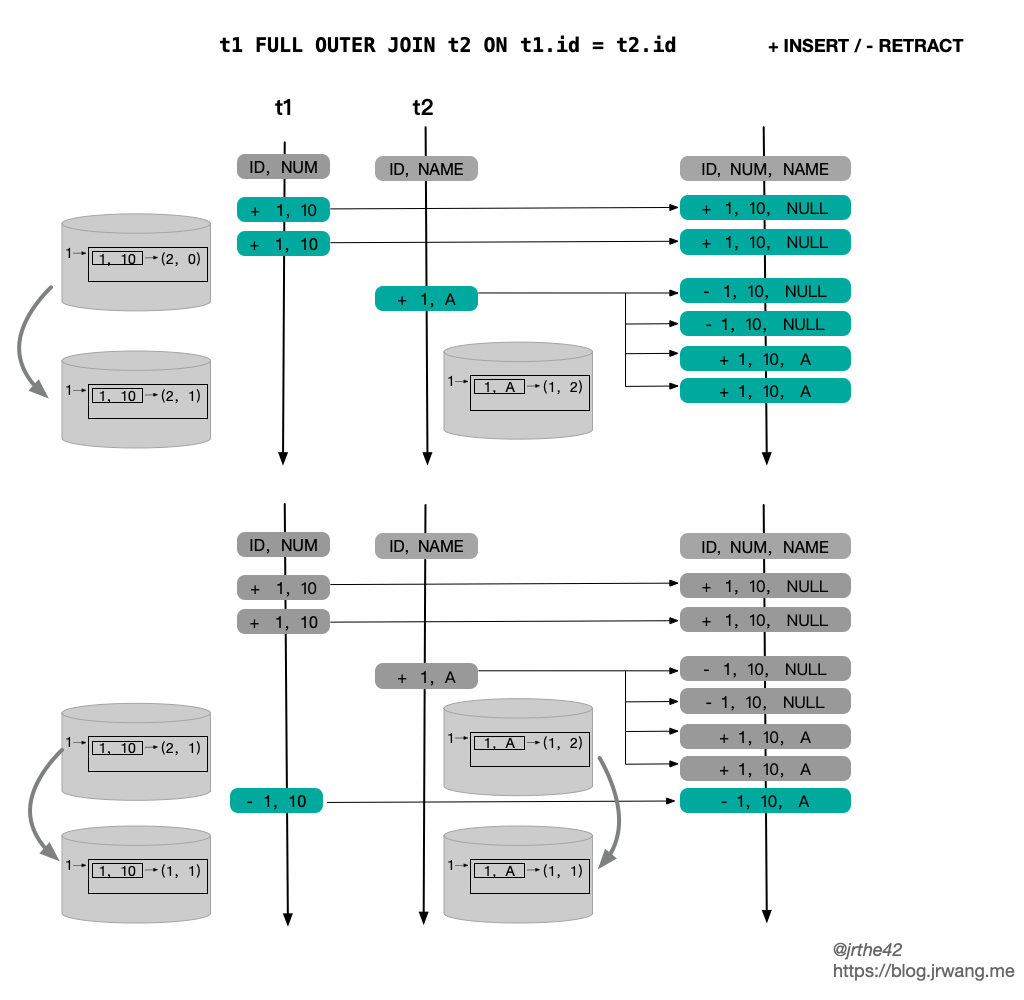](https://blog.jrwang.me/img/flink-sql-join/flink-sql-outer-join-example.png)<a name="semi-anti-join"></a>### [](https://blog.jrwang.me/2020/2020-01-05-flink-sourcecode-sql-stream-join/#semi-anti-join)SEMI/ANTI JOINFlink SQL 除了支持普通的 Join 以外,还支持 SEMI JOIN(半连接) 和 ANTI JOIN(反连接)。SEMI/ANTI Join 和普通 Join 的区别在于不需要从右表获取数据,简单的例子如下:|
— SEMI JON SELECT FROM l WHERE a IN (SELECT d FROM r) — ANTI JOIN SELECT FROM l WHERE a NOT IN (SELECT d FROM r) ``` | | —- |
SEMI/ANTI Join 最终被变换为 StreamingSemiAntiJoinOperator 算子,左右两侧的状态存储分别使用 OuterJoinRecordStateView 和 JoinRecordStateView。StreamingSemiAntiJoinOperator 和 StreamingJoinOperator 的逻辑非常接近,但由于不需要拼接右表的数据,因此更为简单,这里就不作进一步介绍了。
小结
本文分析了 Streaming SQL 中双流 Join 面临的挑战,并对 Flink SQL 中双流 Join 的具体实现机制进行了介绍。Flink SQL 基于状态生存时间来限制无限数据流下状态的无限增长,并充分利用唯一键特性优化状态的存储形式;另外,Flink 基于 ACC/RETRACT 机制确保了关联结果的正确性。
参考
-EOF-

