简介及用法
CompletableFuture是什么?
- 可以明确完成的future,可以set value和status。
- 实现了
CompletionStage接口支持任务依赖。可以用于java异步编程。
基本用法:https://www.callicoder.com/java-8-completablefuture-tutorial/
CompletableFuture源码分析
CompletableFuture成员变量:
//通过result为不为null判断future是否完成,AltResult用来封装null结果和捕获异常volatile Object result; // Either the result or boxed AltResult//无锁并发栈,使用cas实现,用来实现任务依赖volatile Completion stack; // Top of Treiber stack of dependent actionsfinal boolean internalComplete(Object r) { // CAS from null to rreturn RESULT.compareAndSet(this, null, r);}/** Returns true if successfully pushed c onto stack. */final boolean tryPushStack(Completion c) {Completion h = stack;//把当前栈顶设为c的next,NEXT是Completion next字段的VarHandlerNEXT.set(c, h); // CAS piggyback//cas栈顶return STACK.compareAndSet(this, h, c);}
stack节点类Completion及其子类: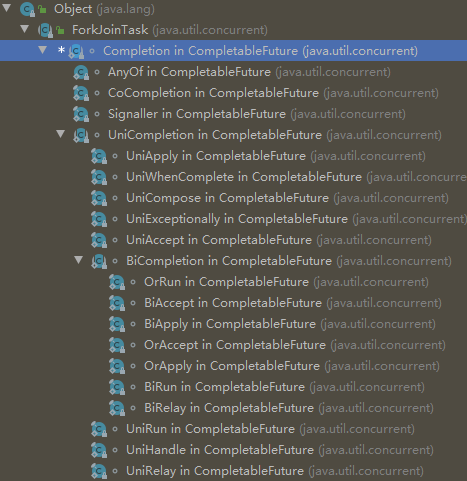
CompletableFuture默认使用ForkJoinPool._commonPool_()。CompletableFuture内部任务依赖用Completion表示,Completion继承自ForkJoinTask,实现了异步处理。并且对应不同的场景有很多子类实现。
Completion分类:
- single-input (UniCompletion),
- two-input (BiCompletion),
- projected (BiCompletions using exactly one of two inputs),
- shared (CoCompletion, used by the second of two sources),
- zero-input source actions,
- Signallers that unblock waiters.
具体逻辑jdk源码注释写比较清楚。
下面我们结合一段demo代码,简单过一下源码。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new IllegalStateException(e);}System.out.println("Some Result");return "Some Result";}).thenApplyAsync(result -> {System.out.println("Processed Result" + result);return "Processed Result" + result;});
从任务定义的角度分析:
supplyAsync->asyncSupplyStage,主要是生成一个AsyncSupply丢到线程池里执行。
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {return asyncSupplyStage(ASYNC_POOL, supplier);}static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e,Supplier<U> f) {if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();//直接生成AsyncSupply执行e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));return d;}static final class AsyncSupply<T> extends ForkJoinTask<Void>implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {CompletableFuture<T> dep; Supplier<? extends T> fn;AsyncSupply(CompletableFuture<T> dep, Supplier<? extends T> fn) {this.dep = dep; this.fn = fn;}public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}public final boolean exec() { run(); return false; }public void run() {CompletableFuture<T> d; Supplier<? extends T> f;if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {dep = null; fn = null;if (d.result == null) {//set valuetry {d.completeValue(f.get());} catch (Throwable ex) {d.completeThrowable(ex);}}//触发依赖任务d.postComplete();}}}
thenApplyAsync-》uniApplyStage,生成一个
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);}private <V> CompletableFuture<V> uniApplyStage(Executor e, Function<? super T,? extends V> f) {if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();Object r;if ((r = result) != null)return uniApplyNow(r, e, f);//生成一个新的CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<V> d = newIncompleteFuture();//封装UniApply类型的completion,push到栈unipush(new UniApply<T,V>(e, d, this, f));return d;}
从任务执行的角度分析:
AsyncSupply task执行逻辑简单,如上面所示。这里主要看一下postComplete,主要作用是递归触发依赖任务。
代码注释1、2、3、4、5为主流程
final void postComplete() {/** On each step, variable f holds current dependents to pop* and run. It is extended along only one path at a time,* pushing others to avoid unbounded recursion.*/CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;while ((h = f.stack) != null ||//1.h当前future栈头(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) { //5.如果this.stack!=null,跳出循环。CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;if (STACK.compareAndSet(f, h, t = h.next)) {//2.cas栈到next节点if (t != null) {if (f != this) { //把嵌套依赖任务放入当前stackpushStack(h);continue;}NEXT.compareAndSet(h, t, null); // try to detach 3.cas 栈头h的next为null}f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;//4.触发栈头h,放入线程池带执行}}}
Completion.tryFire()方法:
usages: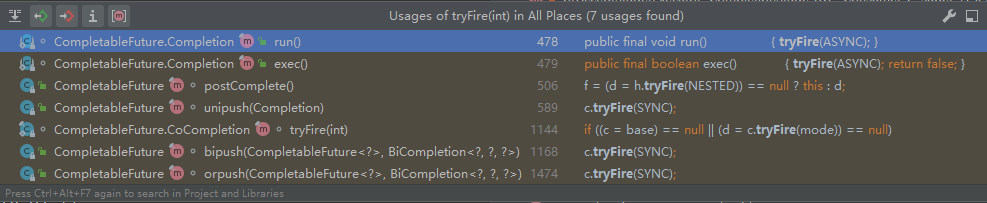
参数mode
static final int SYNC = 0; //当定义任务时,如果前置任务已经完成,则立即触发
static final int ASYNC = 1;//只在Completion run和exec中调用,也就是任务执行时使用
static final int NESTED = -1;//只在postComplete方法中调用,用于任务触发
tryFire会调用两次:
1任务的触发,最终会调用UniCompletion.claim()方法
2任务的执行。
abstract static class Completion extends ForkJoinTask<Void>implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {volatile Completion next; // Treiber stack link/*** Performs completion action if triggered, returning a* dependent that may need propagation, if one exists.** @param mode SYNC, ASYNC, or NESTED*/abstract CompletableFuture<?> tryFire(int mode);/** Returns true if possibly still triggerable. Used by cleanStack. */abstract boolean isLive();public final void run() { tryFire(ASYNC); }public final boolean exec() { tryFire(ASYNC); return false; }public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}}abstract static class UniCompletion<T,V> extends Completion {Executor executor; // executor to use (null if none)CompletableFuture<V> dep; // the dependent to completeCompletableFuture<T> src; // source for actionUniCompletion(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,CompletableFuture<T> src) {this.executor = executor; this.dep = dep; this.src = src;}/*** Returns true if action can be run. Call only when known to* be triggerable. Uses FJ tag bit to ensure that only one* thread claims ownership. If async, starts as task -- a* later call to tryFire will run action.*/final boolean claim() {Executor e = executor;if (compareAndSetForkJoinTaskTag((short)0, (short)1)) {if (e == null)return true;executor = null; // disablee.execute(this);}return false;}final boolean isLive() { return dep != null; }}

