GitHub连接:https://github.com/qdwds/data-structure
单向链表是什么 ?
链表数据结构最前面会有一个head头,它的引用||指针会指向第一个元素,以此类推直到最后一个元素的引用为 指向null为止。其实就好比火车,车头后面是车箱,车箱后面连接下一个车箱,直到后面没有车箱为止~
链表相对数组的优势
- 链表的内存控制不必是连续的,可以充分的利用电脑的内存,灵活的运用
内存动态管理 - 创建链表的时候不必确认大小,可以无限的延续下去
链表在
插入删除数据时,时间复杂度可以达到o(1),处理速度对比数组结构效率高很多链表相对数组的劣势
链表访问一个位置的数组,每次都需要
从头开始找(无法跳过前面元素访问任何一个元素)给定一个下标值,无法通过下标直接访问,需要从头一个一个访问找到对应的下标
使用场景对比
链表:频繁的插入删除一些数据。
- 数组:频繁的根据下表操作数据。‘
公共模块
```javascript // 判断两个值是否对等 const defaultEquals = (a, b) => { return a === b }
/**
- 单向链表节点
*/
const Node = class {
constructor(element) {
} }this.element = element;this.next = null;
/**
双向链表节点 */ class DoublyNode extends Node{ constructor(element,next,prev){
super(element,next); this.prev = prev || null;单向链表实现
```javascript const LinkedList = class { constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
this.count = 0; // 储存链表数量 this.head = null; // 第一个元素的引用头 this.equalsFn = equalsFn;}
// 向链表尾部添加一个新元素 push(element) {
const node = new Node(element); // 创建新的传入的节点 let current; // 过渡this.head // 第一次进来 if (this.head === null) { this.head = node; } else { current = this.head; // 可以看成递归判断整个列表里面的next,需要从头开始逐个遍历,只有最后一个进来的是null while (current.next !== null) { current = current.next; } // 只有这里才真正赋值,连接最后一个节点 current.next = node; } this.count += 1;}
// 从指定位置移除一个元素 removeAt(index) {
let current = this.head; if (index === 0) { this.head = current.next; // 直接返回第二个 } else { const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1); // 跨过要删除的项,重新连接 current = previous.next; previous.next = current.next; } this.count -= 1;} getElementAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) { let node = this.head; for (let i = 0; i < index && node !== null; i++) { node = node.next; } return node; // 返回找到的这个元素 } // 不是有效数据返回空值 return undefined;}
// 在任意位置插入
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element);
if(index === 0){
// 新节点直接给到头上
const current = this.head;
node.next = current;
this.head = node
}else{
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
// 连接新节点
const current = previous.next;
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 返回元素的位置
indexOf(element){
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.count && current !== null; i++) {
// 如果当前元素和 链表里面某一个一样 就返回下标
if(this.equalsFn(element,current.element)){
return i
}
// 如果上没有找到就重新迭代寻找
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
// 移除
remove(element){
const index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.getElementAt(index);
}
size(){
return this.count;
}
isEmpty(){
return this.size() === 0;
}
getHead(){
return this.head;
}
toString(){
if(this.head === null) return '';
let objString = `${this.head.element}`; // 自己的元素
let current = this.head.next; // 下一个节点
for (let i = 0; i < this.size() && current !== null; i++) {
objString = `${objString}, ${current.element}`;
current =current.next;
}
return objString
}
}
/**
- @链表数据结构
- Node{
- element:”a”,
- next:@Node {
- element:”b”,
- next:@Node {
- element:”c”,
- next:null
- }
- }
- } */
const linkedList = new LinkedList(); linkedList.push(‘a’); linkedList.push(‘b’); linkedList.push(‘c’); linkedList.push(‘d’); linkedList.push(‘e’); linkedList.push(‘f’); console.log(linkedList.head); // 链表数据结构 仔细看数据结构 console.log(linkedList.removeAt(2)); console.log(linkedList.head); // 链表数据结构 仔细看数据结构 console.log(linkedList.toString());
<a name="OKvhA"></a>
# 双向链表
双向链表提供两种迭代的方法: `从头到尾或从尾到头` ,可以随意访问一个节点的前一个节点或下一个节点。所以我们定义类的时候除了原有的 `next`还需要定义 `prev` 下一个节点的属性。
- 既可以从头遍历到尾,也能从尾遍历到头
- 一个节点既有向前连接的引用,也有向后连接的引用
<a name="vIYkt"></a>
## 双向链表的缺点
- 每次插入或者删除某个节点的时候,需要处理四个节点的引用,而不是两个。实现起来比较困难。
- 相对于单向列表,占内存空间更大。
<a name="6Mtx1"></a>
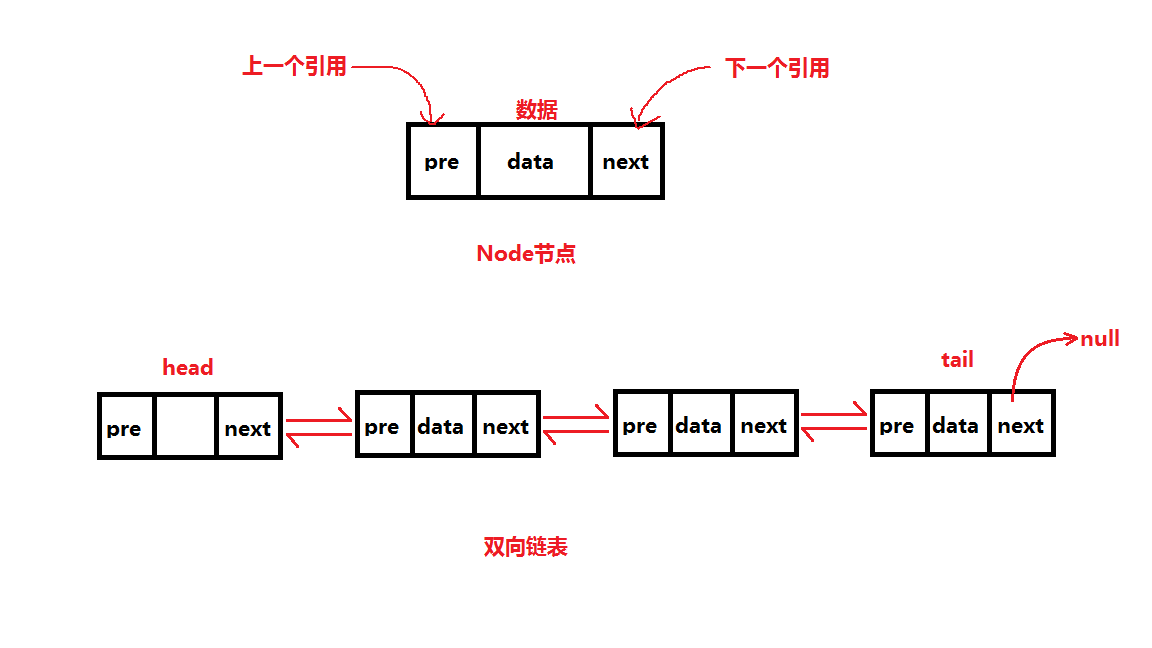
## 图解双向链表
- 可以使用一个head和一个tail分别指向头部和尾部的节点
- 每个节点都由三部分组成:前一个节点指针(pre)、保存的元素(item)、后一个节点指针(next)
- 双向链表第一个节点的pre是null
- 双向链表最后一个节点的next是null
<a name="8q2tp"></a>
## 双向链表实现
```javascript
// 双向链表就 两个指针 一个指向前面 一个指向后面
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(quealsFn = defaultEquals) {
super(quealsFn);
this.tail = null; // 链表最后一个元素的引用
}
// 插入MO数据
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
// 第一项的时候
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node; // 第一个节点
this.tail = node; // 每次插入都要设置最后一个节点
} else {
// 在设置第一个值的时候,并且第一个值存在
node.next = this.head;
current.prev = node; // 上一个
this.tail = node; // 每次插入都要设置最后一个节点
}
} else if (index === this.count) {
// 最后一项的时候
current = this.tail; // 保存变量
current.next = node; // 下一个节点
node.prev = current; // 上一个节点
this.tail = node; // 每次插入都要设置最后一个节点
} else {
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous
}
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 任意位置移除
// 需要处理三个场景 从头部 从中间 从尾部
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
// 直接移除第一项就ok
this.head = current.next;
if (this.count === 1) {
// 只有一个元素最后一个引用置空
this.tail = null;
} else {
// 置空下一个引用
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) { // 最后一项
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
current = this.getElementAt(index)
const previous = current.prev;
// 跳过中间一项 和下一项连接
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
this.count -= 1;
return current.element;
}
return null;
}
}
// 链表里面的数据打印出来就像死循环~
循环链表
循环链表 可以像链表一样至于单向引用,夜可以像双向量表一样有双向引用。循环链表和链表之间唯一的区别在于,最后一个指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用null,而是指向第一个元素(head)
双向循环链表
双向循环链表有指向head元素的tail.next和指向tail元素的head.prev
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList{
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals){
super(equalsFn)
}
// 在任意位置插入新元素
insert(element,index){
if(index >= 0 && index <= this.count){
const node = new Node(element,index);
let current = this.head; // 过渡节点
// 循环列表为空
if(index === 0){
if(this.head === null){
this.head = node;
// 设置下一个节点还是这个节点 - 循环
node.next = this.head;
}else{
// 链表中有值,并且设置的是第一个
node.next = current;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
// 更新最后一个元素
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
}else{
// 这种场景没有变化
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
// 设置下一个节点
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 移除任意节点
removeAt(index){
if(index >= 0 && index < this.count){
debugger
let current = this.head;
if(index === 0){
// 没有内容的情况下
if(this.size() === 0){
this.head = null;
}else{
const removed = this.head;
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
this.head = this.head.next; // 下一个直接赋值给原来
current.next = this.head; // 连接
current = removed;
}
}else{
// 不需要修改循环链表 最后一个元素
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next; // 连接循环量表
}
this.count -= 1;
return current.element;
}
return null;
}
}
有序链表
有序链表是指保持元素有序的链表结构。除了使用排序算法之外,还可以将元素 插入到正确的位置来保证链表的有序性 。
链表创建栈
// 其实都是通过调用双向链表上面的方法; 继承的作用;
class StackLinekdList{
constructor(){
this.items = new DoublyLinkedList();
}
post(element){
this.items.puss(element)
}
pop(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return this.items.removeAt(this.size() - 1); // 从链表尾部移除一个元素
}
peek(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return this.items.getElementAt(this.size() - 1).element;
}
isEmpty(){
return this.items.isEmpty();
}
size(){
return this.items.size();
}
clear(){
return this.items.clear();
}
toString(){
return this.items.toString();
}
}


