原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/justry_deng/article/details/81042379
HTTP 协议可能是现在 Internet 上使用得最多、最重要的协议了,越来越多的 Java 应用程序需要直接通过 HTTP 协议来访问网络资源。虽然在 JDK 的 java net包中已经提供了访问 HTTP 协议的基本功能,但是对于大部分应用程序来说,JDK 库本身提供的功能还不够丰富和灵活。HttpClient 是 Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持 HTTP 协议最新的版本和建议。
HTTP和浏览器有点像,但却不是浏览器。很多人觉得既然HttpClient是一个HTTP客户端编程工具,很多人把他当做浏览器来理解,但是其实HttpClient不是浏览器,它是一个HTTP通信库,因此它只提供一个通用浏览器应用程序所期望的功能子集,最根本的区别是HttpClient中没有用户界面,浏览器需要一个渲染引擎来显示页面,并解释用户输入,例如鼠标点击显示页面上的某处,有一个布局引擎,计算如何显示HTML页面,包括级联样式表和图像。javascript解释器运行嵌入HTML页面或从HTML页面引用的javascript代码。来自用户界面的事件被传递到javascript解释器进行处理。除此之外,还有用于插件的接口,可以处理Applet,嵌入式媒体对象(如pdf文件,Quicktime电影和Flash动画)或ActiveX控件(可以执行任何操作)。HttpClient只能以编程的方式通过其API用于传输和接受HTTP消息。
HttpClient的主要功能:
- 实现了所有 HTTP 的方法(GET、POST、PUT、HEAD、DELETE、HEAD、OPTIONS 等)
- 支持 HTTPS 协议
- 支持代理服务器(Nginx等)等
- 支持自动(跳转)转向
- ……
进入正题
准备环节
第一步:在pom.xml中引入HttpClient的依赖
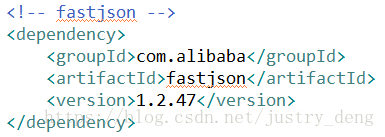
第二步:引入fastjson依赖
注:本人引入此依赖的目的是,在后续示例中,会用到“将对象转化为json字符串的功能”,也可以引其他有此功能的依赖。
注:SpringBoot的基本依赖配置,这里就不再多说了。
详细使用示例
声明:此示例中,以JAVA发送HttpClient(在test里面单元测试发送的);也是以JAVA接收的(在controller里面接收的)。
声明:下面的代码,本人亲测有效。
GET无参:
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**2. * GET---无参测试3. *4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:505. */6. @Test7. public void doGetTestOne() {8. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)9. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();10. // 创建Get请求11. HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:12345/doGetControllerOne");12.13. // 响应模型14. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;15. try {16. // 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求17. response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);18. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体19. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();20. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());21. if (responseEntity != null) {22. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());23. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));24. }25. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {26. e.printStackTrace();27. } catch (ParseException e) {28. e.printStackTrace();29. } catch (IOException e) {30. e.printStackTrace();31. } finally {32. try {33. // 释放资源34. if (httpClient != null) {35. httpClient.close();36. }37. if (response != null) {38. response.close();39. }40. } catch (IOException e) {41. e.printStackTrace();42. }43. }44. }
GET有参(方式一:直接拼接URL):
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**
2. * GET---有参测试 (方式一:手动在url后面加上参数)
3. *
4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:19:23
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void doGetTestWayOne() {
8. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
9. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
10.
11. // 参数
12. StringBuffer params = new StringBuffer();
13. try {
14. // 字符数据最好encoding以下;这样一来,某些特殊字符才能传过去(如:某人的名字就是“&”,不encoding的话,传不过去)
15. params.append("name=" + URLEncoder.encode("&", "utf-8"));
16. params.append("&");
17. params.append("age=24");
18. } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
19. e1.printStackTrace();
20. }
21.
22. // 创建Get请求
23. HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:12345/doGetControllerTwo" + "?" + params);
24. // 响应模型
25. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
26. try {
27. // 配置信息
28. RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
29. // 设置连接超时时间(单位毫秒)
30. .setConnectTimeout(5000)
31. // 设置请求超时时间(单位毫秒)
32. .setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
33. // socket读写超时时间(单位毫秒)
34. .setSocketTimeout(5000)
35. // 设置是否允许重定向(默认为true)
36. .setRedirectsEnabled(true).build();
37.
38. // 将上面的配置信息 运用到这个Get请求里
39. httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig);
40.
41. // 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求
42. response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
43.
44. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体
45. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
46. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
47. if (responseEntity != null) {
48. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
49. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
50. }
51. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
52. e.printStackTrace();
53. } catch (ParseException e) {
54. e.printStackTrace();
55. } catch (IOException e) {
56. e.printStackTrace();
57. } finally {
58. try {
59. // 释放资源
60. if (httpClient != null) {
61. httpClient.close();
62. }
63. if (response != null) {
64. response.close();
65. }
66. } catch (IOException e) {
67. e.printStackTrace();
68. }
69. }
70. }
GET有参(方式二:使用URI获得HttpGet):
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**
2. * GET---有参测试 (方式二:将参数放入键值对类中,再放入URI中,从而通过URI得到HttpGet实例)
3. *
4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:19:23
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void doGetTestWayTwo() {
8. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
9. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
10.
11. // 参数
12. URI uri = null;
13. try {
14. // 将参数放入键值对类NameValuePair中,再放入集合中
15. List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<>();
16. params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("name", "&"));
17. params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("age", "18"));
18. // 设置uri信息,并将参数集合放入uri;
19. // 注:这里也支持一个键值对一个键值对地往里面放setParameter(String key, String value)
20. uri = new URIBuilder().setScheme("http").setHost("localhost")
21. .setPort(12345).setPath("/doGetControllerTwo")
22. .setParameters(params).build();
23. } catch (URISyntaxException e1) {
24. e1.printStackTrace();
25. }
26. // 创建Get请求
27. HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
28.
29. // 响应模型
30. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
31. try {
32. // 配置信息
33. RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
34. // 设置连接超时时间(单位毫秒)
35. .setConnectTimeout(5000)
36. // 设置请求超时时间(单位毫秒)
37. .setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
38. // socket读写超时时间(单位毫秒)
39. .setSocketTimeout(5000)
40. // 设置是否允许重定向(默认为true)
41. .setRedirectsEnabled(true).build();
42.
43. // 将上面的配置信息 运用到这个Get请求里
44. httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig);
45.
46. // 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求
47. response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
48.
49. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体
50. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
51. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
52. if (responseEntity != null) {
53. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
54. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
55. }
56. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
57. e.printStackTrace();
58. } catch (ParseException e) {
59. e.printStackTrace();
60. } catch (IOException e) {
61. e.printStackTrace();
62. } finally {
63. try {
64. // 释放资源
65. if (httpClient != null) {
66. httpClient.close();
67. }
68. if (response != null) {
69. response.close();
70. }
71. } catch (IOException e) {
72. e.printStackTrace();
73. }
74. }
75. }
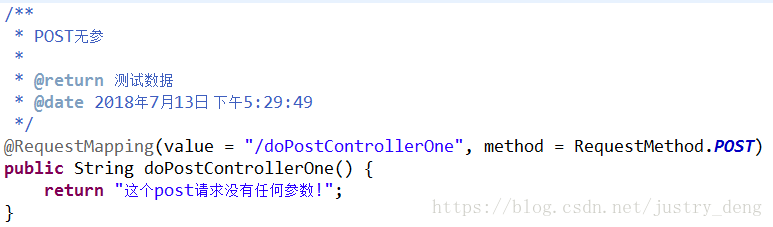
POST无参:
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**
2. * POST---无参测试
3. *
4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void doPostTestOne() {
8.
9. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
10. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
11.
12. // 创建Post请求
13. HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerOne");
14. // 响应模型
15. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
16. try {
17. // 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
18. response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
19. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体
20. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
21.
22. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
23. if (responseEntity != null) {
24. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
25. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
26. }
27. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
28. e.printStackTrace();
29. } catch (ParseException e) {
30. e.printStackTrace();
31. } catch (IOException e) {
32. e.printStackTrace();
33. } finally {
34. try {
35. // 释放资源
36. if (httpClient != null) {
37. httpClient.close();
38. }
39. if (response != null) {
40. response.close();
41. }
42. } catch (IOException e) {
43. e.printStackTrace();
44. }
45. }
46. }
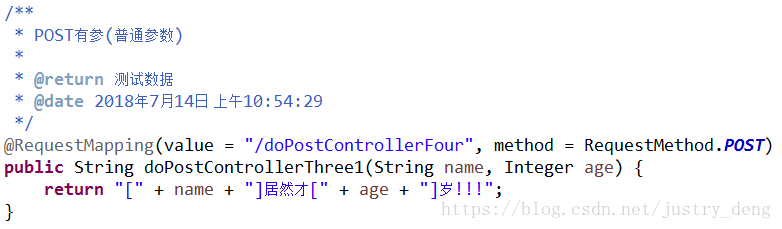
POST有参(普通参数):
注:POST传递普通参数时,方式与GET一样即可,这里以直接在url后缀上参数的方式示例。
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**
2. * POST---有参测试(普通参数)
3. *
4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void doPostTestFour() {
8.
9. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
10. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
11.
12. // 参数
13. StringBuffer params = new StringBuffer();
14. try {
15. // 字符数据最好encoding以下;这样一来,某些特殊字符才能传过去(如:某人的名字就是“&”,不encoding的话,传不过去)
16. params.append("name=" + URLEncoder.encode("&", "utf-8"));
17. params.append("&");
18. params.append("age=24");
19. } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
20. e1.printStackTrace();
21. }
22.
23. // 创建Post请求
24. HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerFour" + "?" + params);
25.
26. // 设置ContentType(注:如果只是传普通参数的话,ContentType不一定非要用application/json)
27. httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
28.
29. // 响应模型
30. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
31. try {
32. // 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
33. response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
34. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体
35. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
36.
37. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
38. if (responseEntity != null) {
39. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
40. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
41. }
42. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
43. e.printStackTrace();
44. } catch (ParseException e) {
45. e.printStackTrace();
46. } catch (IOException e) {
47. e.printStackTrace();
48. } finally {
49. try {
50. // 释放资源
51. if (httpClient != null) {
52. httpClient.close();
53. }
54. if (response != null) {
55. response.close();
56. }
57. } catch (IOException e) {
58. e.printStackTrace();
59. }
60. }
61. }
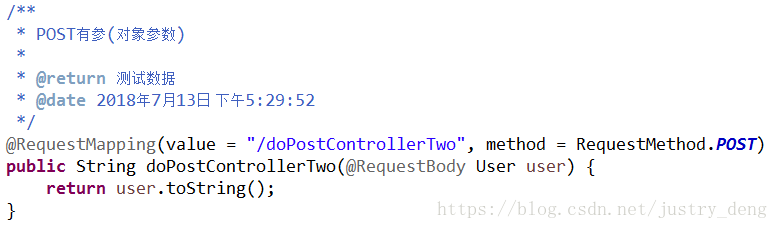
POST有参(对象参数):
先给出User类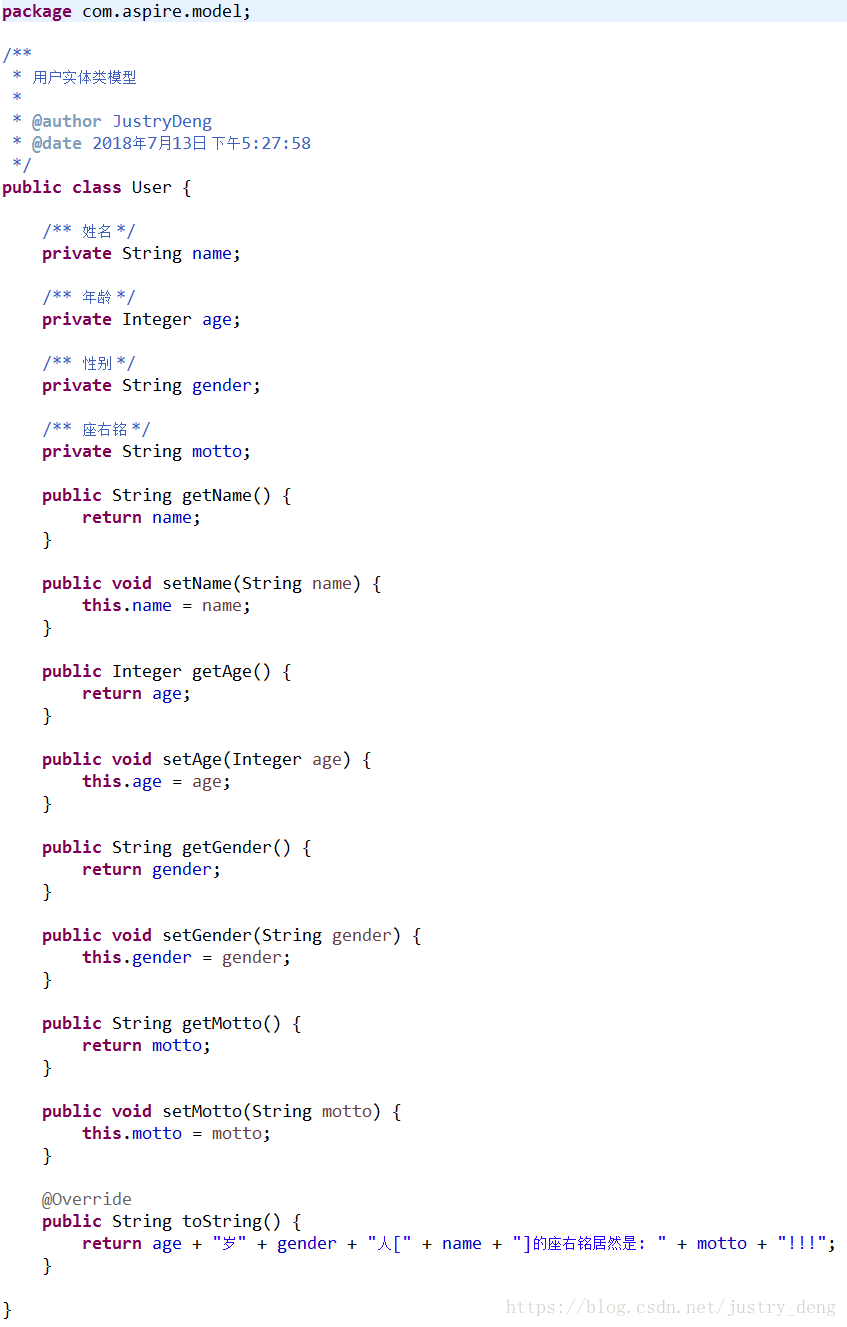
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**
2. * POST---有参测试(对象参数)
3. *
4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void doPostTestTwo() {
8.
9. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
10. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
11.
12. // 创建Post请求
13. HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerTwo");
14. User user = new User();
15. user.setName("潘晓婷");
16. user.setAge(18);
17. user.setGender("女");
18. user.setMotto("姿势要优雅~");
19. // 我这里利用阿里的fastjson,将Object转换为json字符串;
20. // (需要导入com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON包)
21. String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);
22.
23. StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(jsonString, "UTF-8");
24.
25. // post请求是将参数放在请求体里面传过去的;这里将entity放入post请求体中
26. httpPost.setEntity(entity);
27.
28. httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
29.
30. // 响应模型
31. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
32. try {
33. // 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
34. response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
35. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体
36. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
37.
38. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
39. if (responseEntity != null) {
40. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
41. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
42. }
43. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
44. e.printStackTrace();
45. } catch (ParseException e) {
46. e.printStackTrace();
47. } catch (IOException e) {
48. e.printStackTrace();
49. } finally {
50. try {
51. // 释放资源
52. if (httpClient != null) {
53. httpClient.close();
54. }
55. if (response != null) {
56. response.close();
57. }
58. } catch (IOException e) {
59. e.printStackTrace();
60. }
61. }
62. }
POST有参(普通参数 + 对象参数):
注:POST传递普通参数时,方式与GET一样即可,这里以通过URI获得HttpPost的方式为例。
先给出User类: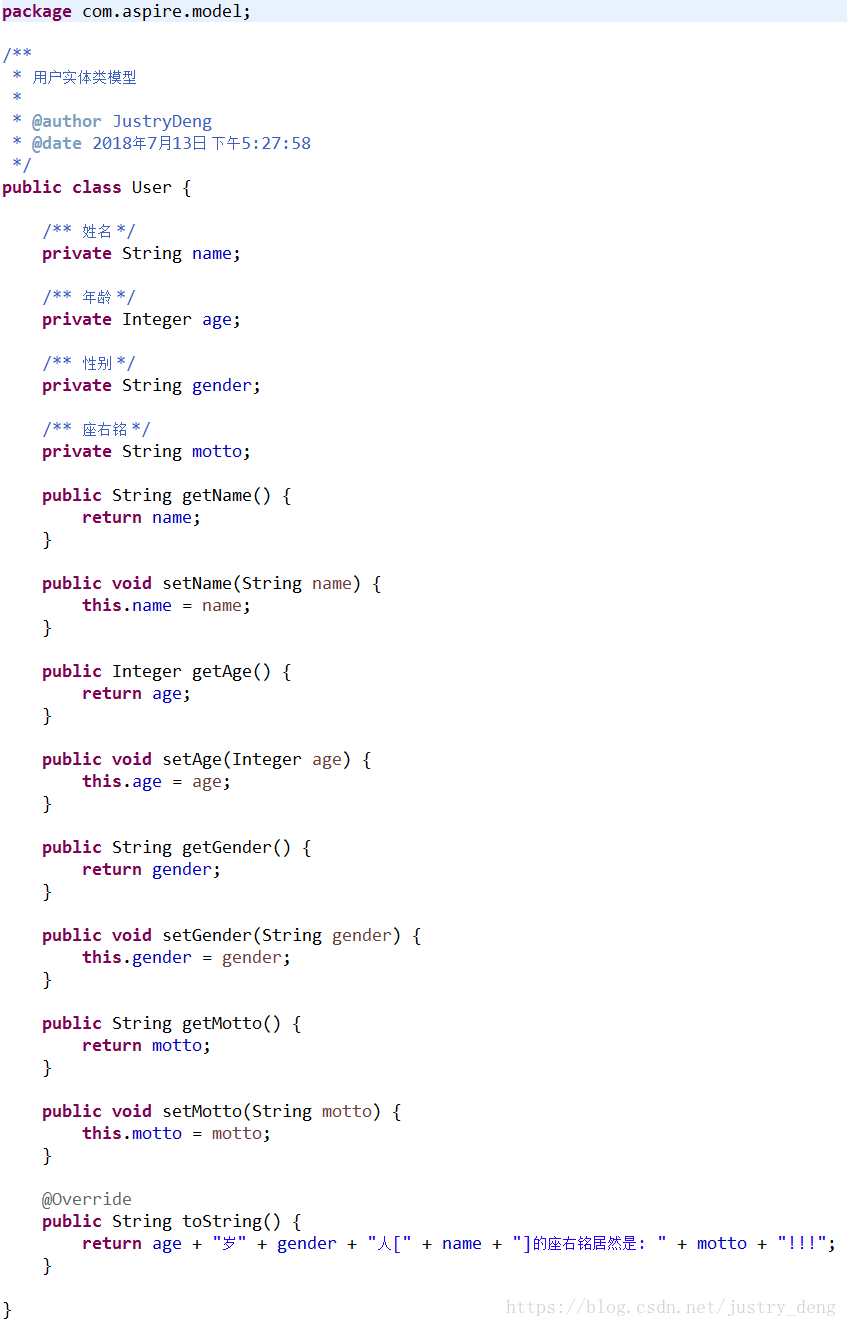
HttpClient发送示例:
1. /**
2. * POST---有参测试(普通参数 + 对象参数)
3. *
4. * @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void doPostTestThree() {
8.
9. // 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
10. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
11.
12. // 创建Post请求
13. // 参数
14. URI uri = null;
15. try {
16. // 将参数放入键值对类NameValuePair中,再放入集合中
17. List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<>();
18. params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("flag", "4"));
19. params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("meaning", "这是什么鬼?"));
20. // 设置uri信息,并将参数集合放入uri;
21. // 注:这里也支持一个键值对一个键值对地往里面放setParameter(String key, String value)
22. uri = new URIBuilder().setScheme("http").setHost("localhost").setPort(12345)
23. .setPath("/doPostControllerThree").setParameters(params).build();
24. } catch (URISyntaxException e1) {
25. e1.printStackTrace();
26. }
27.
28. HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(uri);
29. // HttpPost httpPost = new
30. // HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerThree1");
31.
32. // 创建user参数
33. User user = new User();
34. user.setName("潘晓婷");
35. user.setAge(18);
36. user.setGender("女");
37. user.setMotto("姿势要优雅~");
38.
39. // 将user对象转换为json字符串,并放入entity中
40. StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(JSON.toJSONString(user), "UTF-8");
41.
42. // post请求是将参数放在请求体里面传过去的;这里将entity放入post请求体中
43. httpPost.setEntity(entity);
44.
45. httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
46.
47. // 响应模型
48. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
49. try {
50. // 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
51. response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
52. // 从响应模型中获取响应实体
53. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
54.
55. System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
56. if (responseEntity != null) {
57. System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
58. System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
59. }
60. } catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
61. e.printStackTrace();
62. } catch (ParseException e) {
63. e.printStackTrace();
64. } catch (IOException e) {
65. e.printStackTrace();
66. } finally {
67. try {
68. // 释放资源
69. if (httpClient != null) {
70. httpClient.close();
71. }
72. if (response != null) {
73. response.close();
74. }
75. } catch (IOException e) {
76. e.printStackTrace();
77. }
78. }
79. }
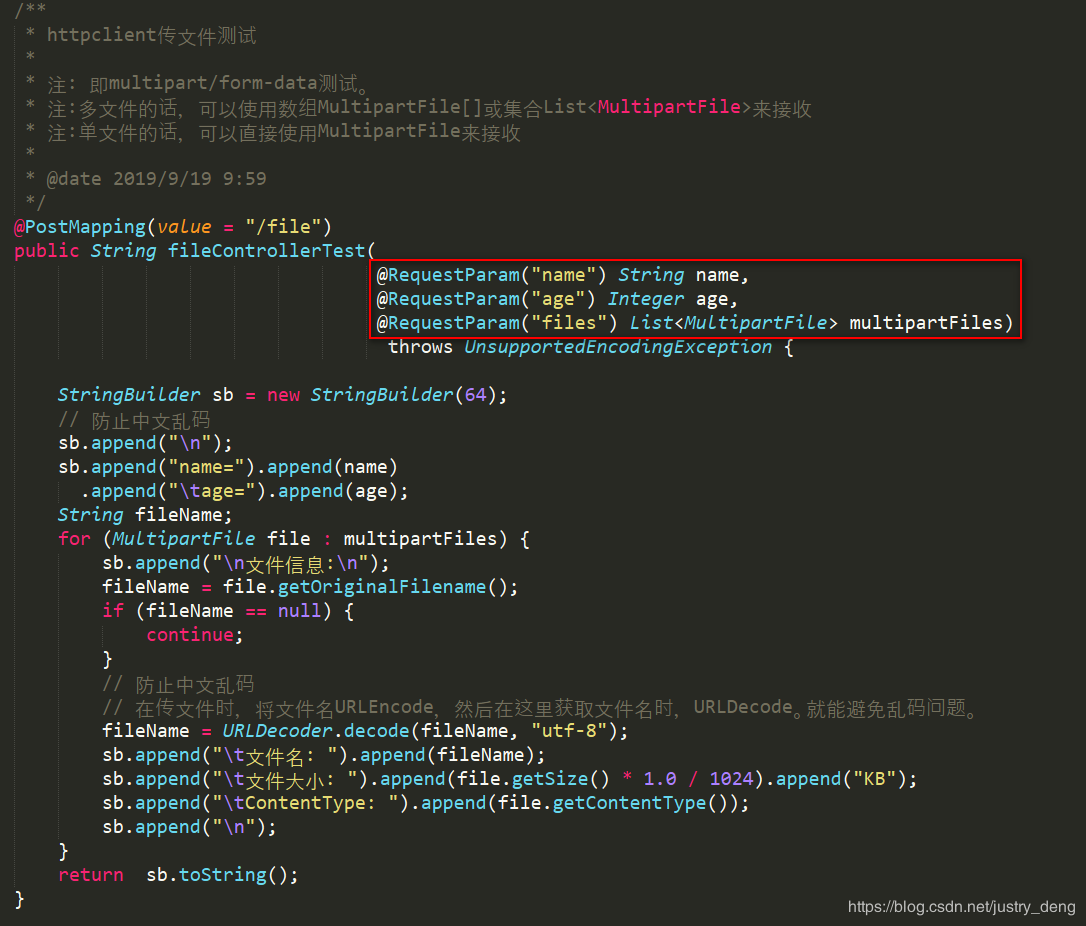
对应接收示例:
对评论区关注度较高的问题进行相关补充:
提示:如果想要知道完整的具体的代码及测试细节,可去下面给的项目代码托管链接,将项目clone下来
进行观察。如果需要运行测试,可以先启动该SpringBoot项目,然后再运行相关test方法,进行
测试。
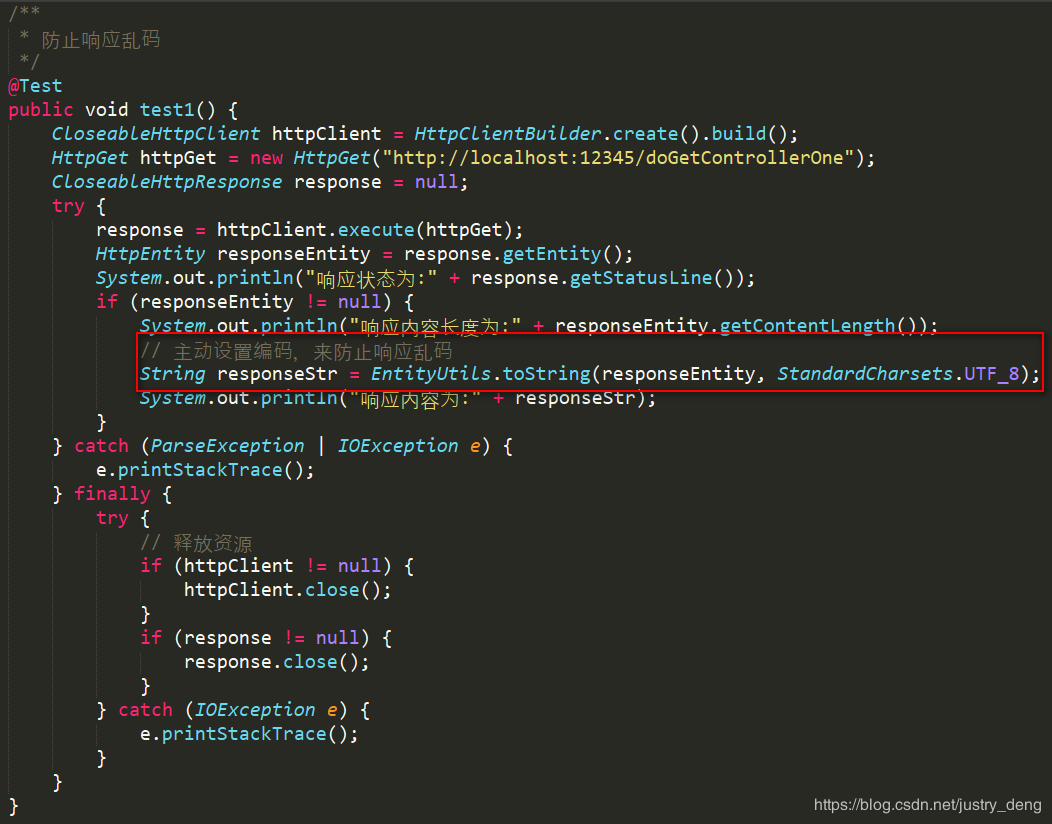
解决响应乱码问题(示例):
进行HTTPS请求并进行(或不进行)证书校验(示例):
使用示例: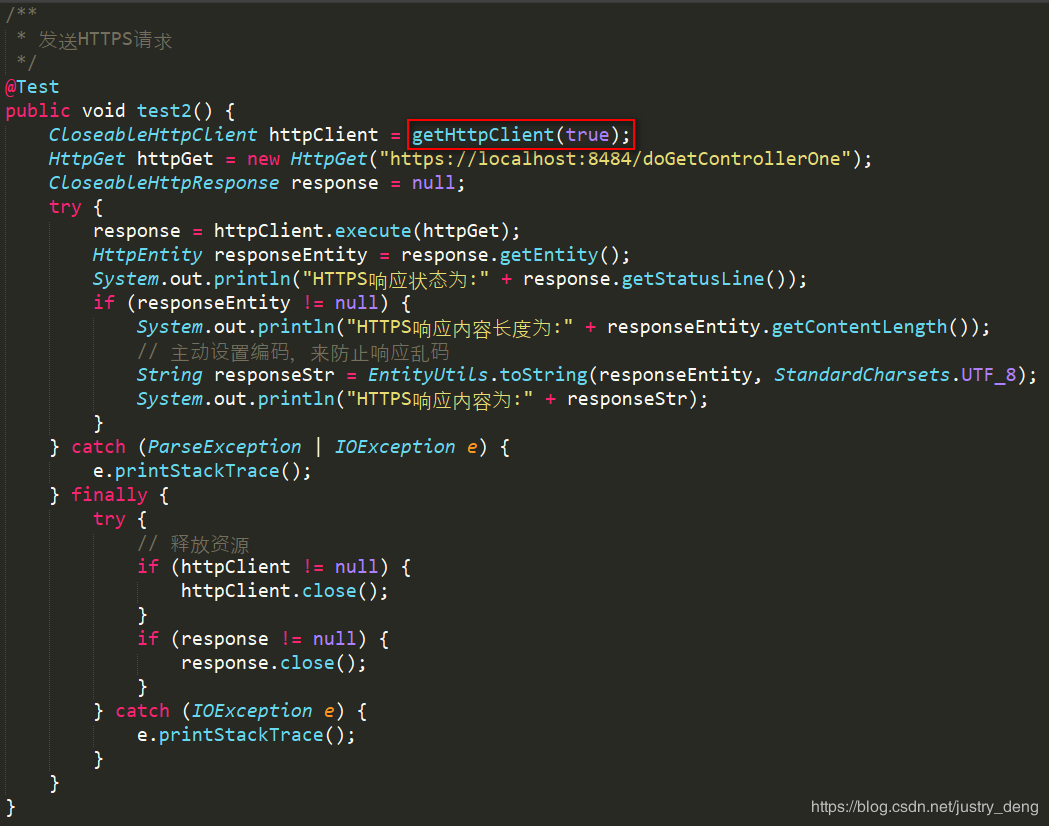
相关方法详情(非完美封装):
1. /**
2. * 根据是否是https请求,获取HttpClient客户端
3. *
4. * TODO 本人这里没有进行完美封装。对于 校不校验校验证书的选择,本人这里是写死
5. * 在代码里面的,你们在使用时,可以灵活二次封装。
6. *
7. * 提示: 此工具类的封装、相关客户端、服务端证书的生成,可参考我的这篇博客:
8. * <linked>https://blog.csdn.net/justry_deng/article/details/91569132</linked>
9. *
10. *
11. * @param isHttps 是否是HTTPS请求
12. *
13. * @return HttpClient实例
14. * @date 2019/9/18 17:57
15. */
16. private CloseableHttpClient getHttpClient(boolean isHttps) {
17. CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
18. if (isHttps) {
19. SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslSocketFactory;
20. try {
21. /// 如果不作证书校验的话
22. sslSocketFactory = getSocketFactory(false, null, null);
23.
24. /// 如果需要证书检验的话
25. // 证书
26. //InputStream ca = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("client/ds.crt");
27. // 证书的别名,即:key。 注:cAalias只需要保证唯一即可,不过推荐使用生成keystore时使用的别名。
28. // String cAalias = System.currentTimeMillis() + "" + new SecureRandom().nextInt(1000);
29. //sslSocketFactory = getSocketFactory(true, ca, cAalias);
30. } catch (Exception e) {
31. throw new RuntimeException(e);
32. }
33. httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().setSSLSocketFactory(sslSocketFactory).build();
34. return httpClient;
35. }
36. httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
37. return httpClient;
38. }
39.
40. /**
41. * HTTPS辅助方法, 为HTTPS请求 创建SSLSocketFactory实例、TrustManager实例
42. *
43. * @param needVerifyCa
44. * 是否需要检验CA证书(即:是否需要检验服务器的身份)
45. * @param caInputStream
46. * CA证书。(若不需要检验证书,那么此处传null即可)
47. * @param cAalias
48. * 别名。(若不需要检验证书,那么此处传null即可)
49. * 注意:别名应该是唯一的, 别名不要和其他的别名一样,否者会覆盖之前的相同别名的证书信息。别名即key-value中的key。
50. *
51. * @return SSLConnectionSocketFactory实例
52. * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
53. * 异常信息
54. * @throws CertificateException
55. * 异常信息
56. * @throws KeyStoreException
57. * 异常信息
58. * @throws IOException
59. * 异常信息
60. * @throws KeyManagementException
61. * 异常信息
62. * @date 2019/6/11 19:52
63. */
64. private static SSLConnectionSocketFactory getSocketFactory(boolean needVerifyCa, InputStream caInputStream, String cAalias)
65. throws CertificateException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyStoreException,
66. IOException, KeyManagementException {
67. X509TrustManager x509TrustManager;
68. // https请求,需要校验证书
69. if (needVerifyCa) {
70. KeyStore keyStore = getKeyStore(caInputStream, cAalias);
71. TrustManagerFactory trustManagerFactory = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
72. trustManagerFactory.init(keyStore);
73. TrustManager[] trustManagers = trustManagerFactory.getTrustManagers();
74. if (trustManagers.length != 1 || !(trustManagers[0] instanceof X509TrustManager)) {
75. throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected default trust managers:" + Arrays.toString(trustManagers));
76. }
77. x509TrustManager = (X509TrustManager) trustManagers[0];
78. // 这里传TLS或SSL其实都可以的
79. SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
80. sslContext.init(null, new TrustManager[]{x509TrustManager}, new SecureRandom());
81. return new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext);
82. }
83. // https请求,不作证书校验
84. x509TrustManager = new X509TrustManager() {
85. @Override
86. public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] arg0, String arg1) {
87. }
88.
89. @Override
90. public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] arg0, String arg1) {
91. // 不验证
92. }
93.
94. @Override
95. public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
96. return new X509Certificate[0];
97. }
98. };
99. SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
100. sslContext.init(null, new TrustManager[]{x509TrustManager}, new SecureRandom());
101. return new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslContext);
102. }
103.
104. /**
105. * 获取(密钥及证书)仓库
106. * 注:该仓库用于存放 密钥以及证书
107. *
108. * @param caInputStream
109. * CA证书(此证书应由要访问的服务端提供)
110. * @param cAalias
111. * 别名
112. * 注意:别名应该是唯一的, 别名不要和其他的别名一样,否者会覆盖之前的相同别名的证书信息。别名即key-value中的key。
113. * @return 密钥、证书 仓库
114. * @throws KeyStoreException 异常信息
115. * @throws CertificateException 异常信息
116. * @throws IOException 异常信息
117. * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException 异常信息
118. * @date 2019/6/11 18:48
119. */
120. private static KeyStore getKeyStore(InputStream caInputStream, String cAalias)
121. throws KeyStoreException, CertificateException, IOException, NoSuchAlgorithmException {
122. // 证书工厂
123. CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
124. // 秘钥仓库
125. KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType());
126. keyStore.load(null);
127. keyStore.setCertificateEntry(cAalias, certificateFactory.generateCertificate(caInputStream));
128. return keyStore;
129. }
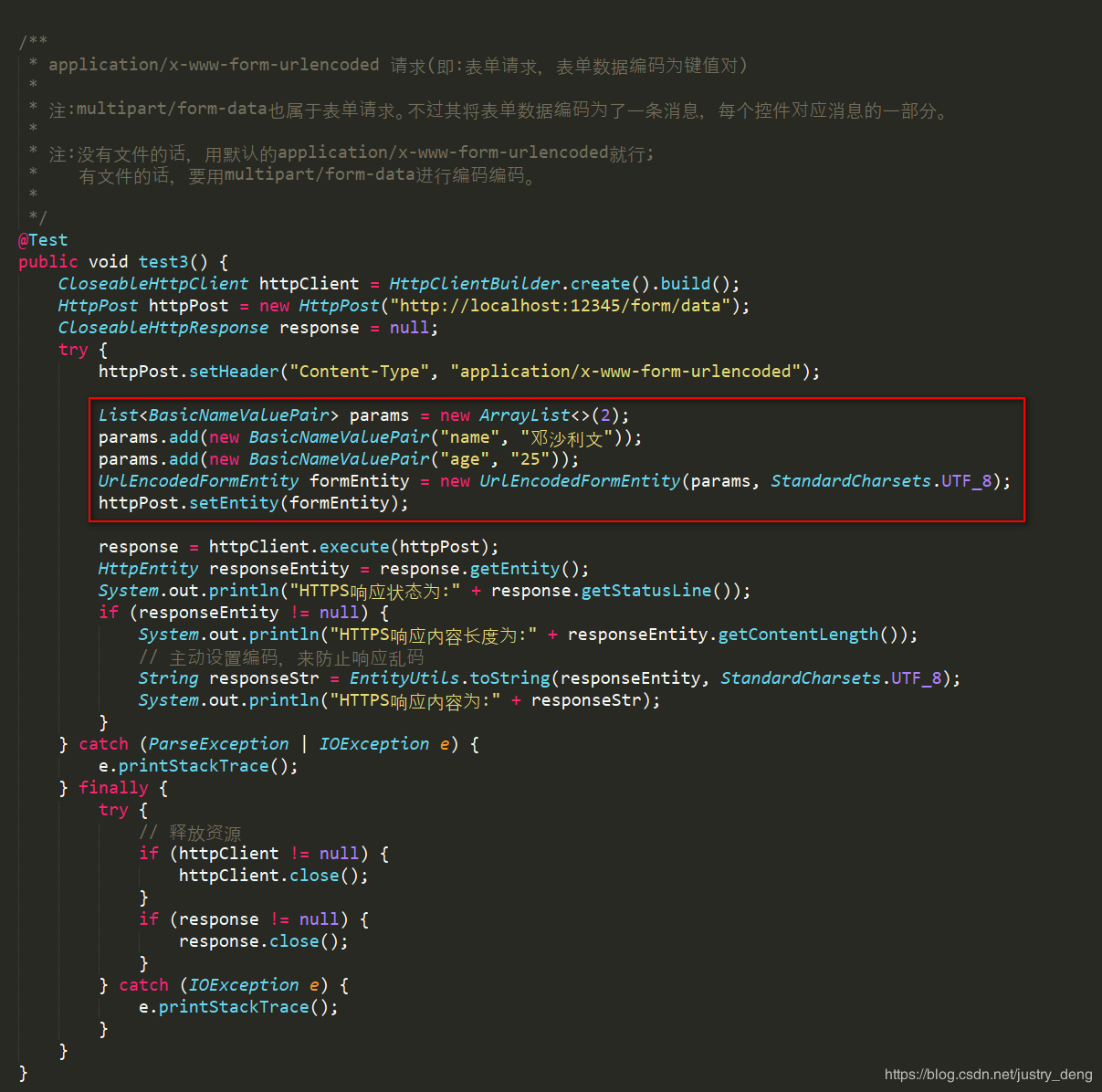
application/x-www-form-urlencoded表单请求(示例):
发送文件(示例):
准备工作:
如果想要灵活方便的传输文件的话,除了引入org.apache.httpcomponents基本的httpclient依赖外再额外引入org.apache.httpcomponents的httpmime依赖。
P.S.:即便不引入httpmime依赖,也是能传输文件的,不过功能不够强大。
在pom.xml中额外引入:
1. <!--
2. 如果需要灵活的传输文件,引入此依赖后会更加方便
3. -->
4. <dependency>
5. <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
6. <artifactId>httpmime</artifactId>
7. <version>4.5.5</version>
8. </dependency>
发送端是这样的:
1. /**
2. *
3. * 发送文件
4. *
5. * multipart/form-data传递文件(及相关信息)
6. *
7. * 注:如果想要灵活方便的传输文件的话,
8. * 除了引入org.apache.httpcomponents基本的httpclient依赖外
9. * 再额外引入org.apache.httpcomponents的httpmime依赖。
10. * 追注:即便不引入httpmime依赖,也是能传输文件的,不过功能不够强大。
11. *
12. */
13. @Test
14. public void test4() {
15. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
16. HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/file");
17. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
18. try {
19. MultipartEntityBuilder multipartEntityBuilder = MultipartEntityBuilder.create();
20. // 第一个文件
21. String filesKey = "files";
22. File file1 = new File("C:\\Users\\JustryDeng\\Desktop\\back.jpg");
23. multipartEntityBuilder.addBinaryBody(filesKey, file1);
24. // 第二个文件(多个文件的话,使用同一个key就行,后端用数组或集合进行接收即可)
25. File file2 = new File("C:\\Users\\JustryDeng\\Desktop\\头像.jpg");
26. // 防止服务端收到的文件名乱码。 我们这里可以先将文件名URLEncode,然后服务端拿到文件名时在URLDecode。就能避免乱码问题。
27. // 文件名其实是放在请求头的Content-Disposition里面进行传输的,如其值为form-data; name="files"; filename="头像.jpg"
28. multipartEntityBuilder.addBinaryBody(filesKey, file2, ContentType.DEFAULT_BINARY, URLEncoder.encode(file2.getName(), "utf-8"));
29. // 其它参数(注:自定义contentType,设置UTF-8是为了防止服务端拿到的参数出现乱码)
30. ContentType contentType = ContentType.create("text/plain", Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
31. multipartEntityBuilder.addTextBody("name", "邓沙利文", contentType);
32. multipartEntityBuilder.addTextBody("age", "25", contentType);
33.
34. HttpEntity httpEntity = multipartEntityBuilder.build();
35. httpPost.setEntity(httpEntity);
36.
37. response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
38. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
39. System.out.println("HTTPS响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
40. if (responseEntity != null) {
41. System.out.println("HTTPS响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
42. // 主动设置编码,来防止响应乱码
43. String responseStr = EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
44. System.out.println("HTTPS响应内容为:" + responseStr);
45. }
46. } catch (ParseException | IOException e) {
47. e.printStackTrace();
48. } finally {
49. try {
50. // 释放资源
51. if (httpClient != null) {
52. httpClient.close();
53. }
54. if (response != null) {
55. response.close();
56. }
57. } catch (IOException e) {
58. e.printStackTrace();
59. }
60. }
61. }
发送流(示例):
发送端是这样的:
1. /**
2. *
3. * 发送流
4. *
5. */
6. @Test
7. public void test5() {
8. CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
9. HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/is?name=邓沙利文");
10. CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
11. try {
12. InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream("流啊流~".getBytes());
13. InputStreamEntity ise = new InputStreamEntity(is);
14. httpPost.setEntity(ise);
15.
16. response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
17. HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
18. System.out.println("HTTPS响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
19. if (responseEntity != null) {
20. System.out.println("HTTPS响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
21. // 主动设置编码,来防止响应乱码
22. String responseStr = EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
23. System.out.println("HTTPS响应内容为:" + responseStr);
24. }
25. } catch (ParseException | IOException e) {
26. e.printStackTrace();
27. } finally {
28. try {
29. // 释放资源
30. if (httpClient != null) {
31. httpClient.close();
32. }
33. if (response != null) {
34. response.close();
35. }
36. } catch (IOException e) {
37. e.printStackTrace();
38. }
39. }
40. }
接收端是这样的: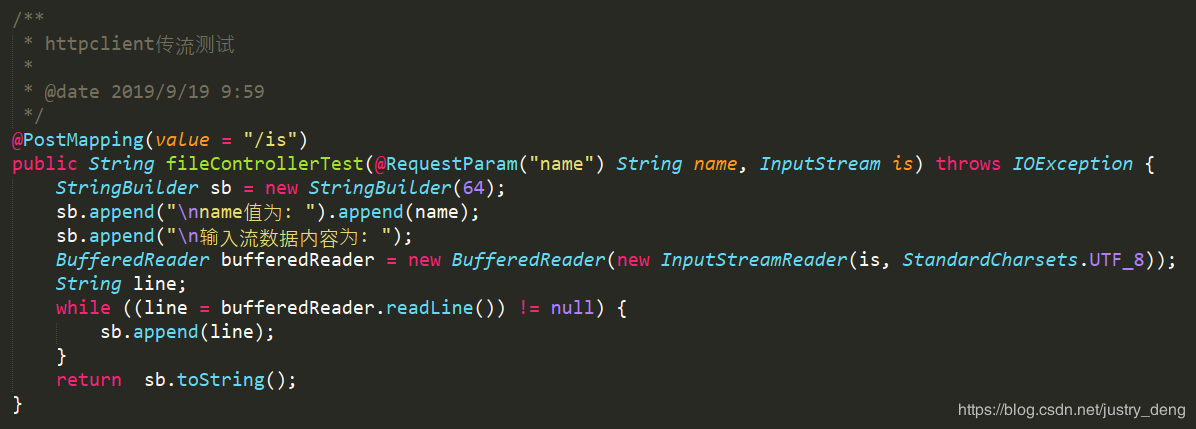
再次提示:如果想要自己进行测试,可去下面给的项目代码托管链接,将项目clone下来,然后先启动该
SpringBoot项目,然后再运行相关test方法,进行测试。
工具类提示:使用HttpClient时,可以视情况将其写为工具类。如:Github上Star非常多的一个HttpClient
的工具类是httpclientutil。本人在这里也推荐使用该工具类,因为该工具类的编写者封装了
很多功能在里面,如果不是有什么特殊的需求的话,完全可以不用造轮子,可以直接使用
该工具类。使用方式很简单,可详见[https://github.com/Arronlong/httpclientutil**](https://github.com/Arronlong/httpclientutil)**。