前提 MySQL : 5.6
MVCC简介
Multi-Version Concurrency Control 多版本并发控制,是一种并发控制方法,用于数据库管理系统中的数据并发访问,以及编程语言中的事务型内存的实现。
通俗地讲,多版本并发控制(MVCC)是一种用来解决读-写冲突的无锁并发控制方案,通过为事务分配单向增长的时间戳,为每个修改保存一个版本,版本与事务时间戳关联,读操作只读该事务开始前的数据库的快照。这样在读操作不用阻塞写操作,写操作不用阻塞读操作,从而大大提高数据库系统的并发性能,降低系统开销。
数据库处理并发的技术演变过程
- 基于表的读写锁
- 基于索引的读写锁
- MVCC
MVCC的优缺点
- 优点
- 高并发
- 读写不互相阻塞(读可见版本)
- 低加锁开销
- 读不加锁
- 缺点
- 为了实现多版本,需对行记录增加隐藏字段
- 每个行记录的变更都会生成版本快照
- 检索行时需要进行版本的比较,降低了查询效率
- 需要定期清理不再需要的行版本,回收空间
MVCC的实现原理
了解InnoDB行结构、事务链表、ReadView结构、可见性判断,对于理解MVCC的实现原理有很重要的意义。
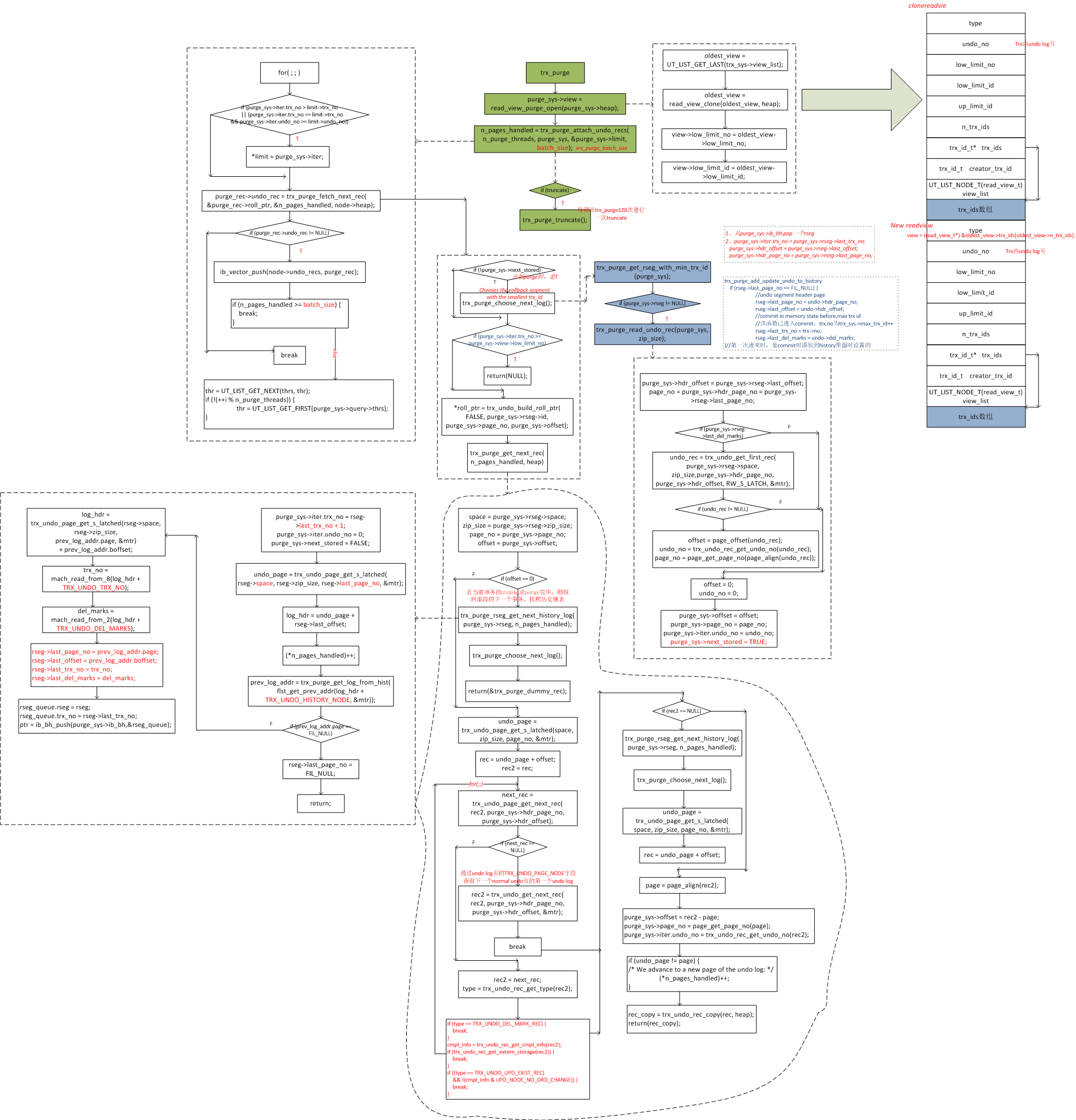
InnoDB行结构
InnoDB行结构中除了用户自定义的列之外,还会默认添加三个隐藏的系统列,参见storage/innobase/include/data0type.h
/* Precise data types for system columns and the length of those columns;NOTE: the values must run from 0 up in the order given! All codes mustbe less than 256 */#define DATA_ROW_ID 0 /* row id: a 48-bit integer */#define DATA_ROW_ID_LEN 6 /* stored length for row id */#define DATA_TRX_ID 1 /* transaction id: 6 bytes */#define DATA_TRX_ID_LEN 6#define DATA_ROLL_PTR 2 /* rollback data pointer: 7 bytes */#define DATA_ROLL_PTR_LEN 7
| 列名 | 长度(字节) | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| DATA_ROW_ID | 6 | 行标识(隐藏单调自增id) |
| DATA_TRX_ID | 6 | 修改该行数据的事务的ID |
| DATA_ROLL_PTR | 7 | undo log的指针,用于记录之前历史数据在undo log中的位置 |
InnoDB行结构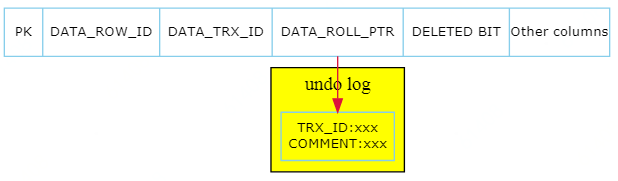
事务链表
事务在begin时会初始化一个trx_t结构体,同时保存到全局唯一的trx_sys的事务链表中。
事务链表中保存的都是还未提交的事务,事务一旦被提交,则会从事务链表中摘除。
trx_sys事务链表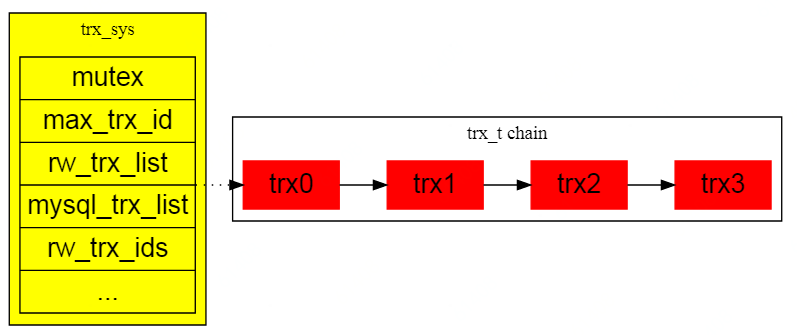
trx_t结构体
参见storage/innobase/include/trx0trx.h
从trx结构体可以看出,每个事务trx里都持有一个read_view。下文可以看到,ReadView结构体存在的意义是什么。
ReadView
InnDB为了判断某个行记录是否对当前事务可见,需要对行记录进行可见性判断,ReadView结构体(ReadView是某一个时间点,事务执行状态的一个快照)就是用来辅助判断事务的可见性。
ReadView结构体
参见storage/innobase/include/read0read.h
struct read_view_t{ulint type; /*!< VIEW_NORMAL, VIEW_HIGH_GRANULARITY */undo_no_t undo_no;/*!< 0 or if type isVIEW_HIGH_GRANULARITYtransaction undo_no when this high-granularityconsistent read view was created */trx_id_t low_limit_no;/*!< The view does not need to see the undologs for transactions whose transaction numberis strictly smaller (<) than this value: theycan be removed in purge if not needed by otherviews */trx_id_t low_limit_id;/*!< The read should not see any transactionwith trx id >= this value. In other words,this is the "high water mark". */trx_id_t up_limit_id;/*!< The read should see all trx ids whichare strictly smaller (<) than this value.In other words,this is the "low water mark". */ulint n_trx_ids;/*!< Number of cells in the trx_ids array */trx_id_t* trx_ids;/*!< Additional trx ids which the read shouldnot see: typically, these are the read-writeactive transactions at the time when the readis serialized, except the reading transactionitself; the trx ids in this array are in adescending order. These trx_ids should bebetween the "low" and "high" water marks,that is, up_limit_id and low_limit_id. */trx_id_t creator_trx_id;/*!< trx id of creating transaction, or0 used in purge */UT_LIST_NODE_T(read_view_t) view_list;/*!< List of read views in trx_sys */};
| 属性名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| creator_trx_id | 创建这个ReadView的事务ID |
| low_limit_id | 事务ID >= low_limit_id的记录,对于当前ReadView都是不可见的 |
| up_limit_id | 事务ID < up_limit_id ,对于当前ReadView都是可见的 |
| trx_ids | 事务开始时,活跃事务链表里的事务ID集合 |
通过ReadView,当前事务可以根据查询到的所有行记录中的事务ID进行匹配,以确定哪些行记录对当前事务是可见的,从而实现数据库的事务隔离。
大致处理逻辑如下:
- InnoDB行结构中有隐藏列记录了当前数据最近被哪个事务ID修改过
- 一个新事务开启时会构造trx_t结构体放入事务链表trx_sys,同时trx_t持有ReadView
- 当前事务根据ReadView中的数据去跟检索到的每一条数据去校验,看看当前事务是不是能看到这条数据
可见性判断
上文已经介绍了ReadView,现在来看下InnoDB是如何判断某个行记录对当前事务是否可见的,参见storage/innobase/lock/lock0lock.cc
bool lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees(const rec_t *rec, /*!< in: user record which should be read orpassed over by a read cursor */dict_index_t *index, /*!< in: clustered index */const ulint *offsets, /*!< in: rec_get_offsets(rec, index) */ReadView *view) /*!< in: consistent read view */{ut_ad(index->is_clustered());ut_ad(page_rec_is_user_rec(rec));ut_ad(rec_offs_validate(rec, index, offsets));/* Temp-tables are not shared across connections and multipletransactions from different connections cannot simultaneouslyoperate on same temp-table and so read of temp-table isalways consistent read. *///只读事务或者临时表是不需要一致性读的判断if (srv_read_only_mode || index->table->is_temporary()) {ut_ad(view == 0 || index->table->is_temporary());return (true);}/* NOTE that we call this function while holding the searchsystem latch. *///获取记录上的TRX_ID这里需要解释下,我们一个查询可能满足的记录数有多个。//那我们每读取一条记录的时候就要根据这条记录上的TRX_ID判断这条记录是否可见trx_id_t trx_id = row_get_rec_trx_id(rec, index, offsets);//判断记录可见性return (view->changes_visible(trx_id, index->table->name));}
真正实现了判断记录的看见性逻辑的是changes_visible函数,参见 storage/innobase/include/read0types.h
bool changes_visible(trx_id_t id, const table_name_t &name) constMY_ATTRIBUTE((warn_unused_result)) {ut_ad(id > 0);//如果ID小于Read View中最小的, 则这条记录是可以看到。说明这条记录是在select这个事务开始之前就结束的if (id < m_up_limit_id || id == m_creator_trx_id) {return (true);}check_trx_id_sanity(id, name);//如果比Read View中最大的还要大,则说明这条记录是在事务开始之后进行修改的,所以此条记录不应查看到if (id >= m_low_limit_id) {return (false);} else if (m_ids.empty()) {return (true);}const ids_t::value_type *p = m_ids.data();//判断是否在Read View中, 如果在说明在创建Read View时 此条记录还处于活跃状态则不应该查询到,//否则说明创建Read View是此条记录已经是不活跃状态则可以查询到return (!std::binary_search(p, p + m_ids.size(), id));}
Purge
InnoDB由于要支持多版本协议, 因此无论是更新、 删除, 都只是设置记录上的deleted bit标记位, 而不是真正的删除记录。
为了清理磁盘空间,后续这些记录的真正删除, 是通过Purge后台进程(根据参数srv_n_purge_threads配置, 由下面两个线程中的一个来执行purge: srv_purge_thread(); srv_master_thread())实现的。
Purge进程定期扫描InnoDB的undo, 按照先读老undo, 再读新undo的顺序, 读取每条undo record. 对于每一条undo record, 判断其对应的记录是否可以被purge(purge进程有自己的read view, 等同于进程开始时最老的活动事务之前的view, 保证purge的数据, 一定是不可见数据, 对任何人来说), 如果可以purge, 则构造完整记录(row_purge_parse_undo_rec). 然后按照先purge二级索引, 最后purge聚簇索引的顺序, purge一个操作生成的旧版本完整记录。
Purge流程执行细节