使用RESTClientFor(Config)可以创建指定Kubeconfig配置的Kubernetes Client-go REST客户端。
使用如下:
restClient, err := rest.RESTClientFor(config)
代码片段1:RESTClientFor()
代码路径k8s.io/client-go/rest/config.go
// RESTClientFor returns a RESTClient that satisfies the requested attributes on a client Config// object. Note that a RESTClient may require fields that are optional when initializing a Client.// A RESTClient created by this method is generic - it expects to operate on an API that follows// the Kubernetes conventions, but may not be the Kubernetes API.func RESTClientFor(config *Config) (*RESTClient, error) {// 需要在Config中指定GV和Codecif config.GroupVersion == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("GroupVersion is required when initializing a RESTClient")}if config.NegotiatedSerializer == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("NegotiatedSerializer is required when initializing a RESTClient")}// 从config中获取访问的K8s apiserver的baseURL和versionedAPIPath// 详细分析见后文代码片段1.1baseURL, versionedAPIPath, err := defaultServerUrlFor(config)if err != nil {return nil, err}transport, err := TransportFor(config)if err != nil {return nil, err}var httpClient *http.Clientif transport != http.DefaultTransport {httpClient = &http.Client{Transport: transport}if config.Timeout > 0 {httpClient.Timeout = config.Timeout}}rateLimiter := config.RateLimiterif rateLimiter == nil {qps := config.QPSif config.QPS == 0.0 {qps = DefaultQPS}burst := config.Burstif config.Burst == 0 {burst = DefaultBurst}if qps > 0 {rateLimiter = flowcontrol.NewTokenBucketRateLimiter(qps, burst)}}var gv schema.GroupVersionif config.GroupVersion != nil {gv = *config.GroupVersion}clientContent := ClientContentConfig{AcceptContentTypes: config.AcceptContentTypes,ContentType: config.ContentType,GroupVersion: gv,Negotiator: runtime.NewClientNegotiator(config.NegotiatedSerializer, gv),}restClient, err := NewRESTClient(baseURL, versionedAPIPath, clientContent, rateLimiter, httpClient)if err == nil && config.WarningHandler != nil {restClient.warningHandler = config.WarningHandler}return restClient, err}
代码片段1.1:defaultServerUrlFor(config)
defaultServerUrlFor(config)用来获取config配置中的Host信息。
代码路径:k8s.io/client-go/rest/url_utils
// defaultServerUrlFor is shared between IsConfigTransportTLS and RESTClientFor. It// requires Host and Version to be set prior to being called.func defaultServerUrlFor(config *Config) (*url.URL, string, error) {// TODO: move the default to secure when the apiserver supports TLS by default// config.Insecure is taken to mean "I want HTTPS but don't bother checking the certs against a CA."hasCA := len(config.CAFile) != 0 || len(config.CAData) != 0hasCert := len(config.CertFile) != 0 || len(config.CertData) != 0defaultTLS := hasCA || hasCert || config.Insecure // 判断是否开启TLS认证host := config.Hostif host == "" {host = "localhost" //如果host为空,则使用Localhost}// 调用DefaultServerURL获取baseURL, versionedAPIPathif config.GroupVersion != nil {return DefaultServerURL(host, config.APIPath, *config.GroupVersion, defaultTLS)}return DefaultServerURL(host, config.APIPath, schema.GroupVersion{}, defaultTLS)}
代码片段1.1.1:DefaultServerURL()
// DefaultServerURL converts a host, host:port, or URL string to the default base server API path// to use with a Client at a given API version following the standard conventions for a// Kubernetes API.func DefaultServerURL(host, apiPath string, groupVersion schema.GroupVersion, defaultTLS bool) (*url.URL, string, error) {if host == "" {return nil, "", fmt.Errorf("host must be a URL or a host:port pair")}base := host// 使用内置函数url.Parse()将config中的host字段解析为net/url.URL结构,hostURL内容如下图所示。hostURL, err := url.Parse(base)// 这里处理解析错误的情况、scheme解析为空、host解析为空的情况if err != nil || hostURL.Scheme == "" || hostURL.Host == "" {scheme := "http://"if defaultTLS {scheme = "https://"}hostURL, err = url.Parse(scheme + base) // 使用scheme+base再尝试一次,可能config.Host中未配置scheme.if err != nil {return nil, "", err}if hostURL.Path != "" && hostURL.Path != "/" {return nil, "", fmt.Errorf("host must be a URL or a host:port pair: %q", base)}}// hostURL.Path is optional; a non-empty Path is treated as a prefix that is to be applied to// all URIs used to access the host. this is useful when there's a proxy in front of the// apiserver that has relocated the apiserver endpoints, forwarding all requests from, for// example, /a/b/c to the apiserver. in this case the Path should be /a/b/c.//// if running without a frontend proxy (that changes the location of the apiserver), then// hostURL.Path should be blank.//// versionedAPIPath, a path relative to baseURL.Path, points to a versioned API base// DefaultVersionedAPIPath将apiPath和groupVersion的内容拼凑为versionedAPIPath,详细分析见代码片段1.1.2versionedAPIPath := DefaultVersionedAPIPath(apiPath, groupVersion)return hostURL, versionedAPIPath, nil}
如果config中配置的host为https://10.176.122.1:6443,则url.Parse()将config中的host字段解析为net/url.URL结构如下所示: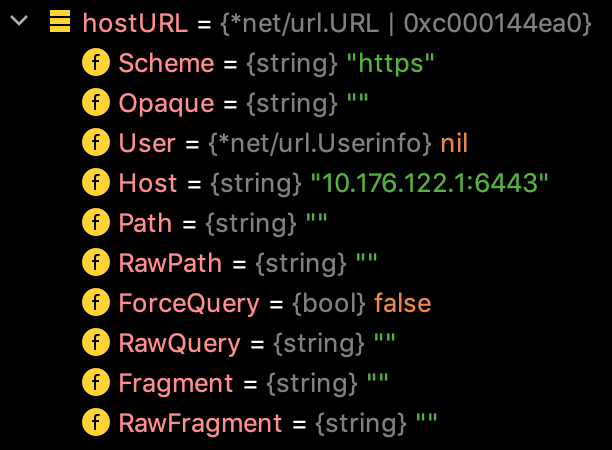
代码片段1.1.2:DefaultVersionedAPIPath
设置API访问的版本路径。
// DefaultVersionedAPIPathFor constructs the default path for the given group version, assuming the given// API path, following the standard conventions of the Kubernetes API.func DefaultVersionedAPIPath(apiPath string, groupVersion schema.GroupVersion) string {// 使用path包下的Join函数将apiPath添加到/末尾,通常versionedAPIPath为/api或者apis// /api主要用于Kubernetes内置的资源对象(即核心资源组,没有组名),例如/api/v1/pods// /apis主要用于非核心资源组,有组名,例如/apis/apps/v1/deploymentsversionedAPIPath := path.Join("/", apiPath)// Add the version to the end of the pathif len(groupVersion.Group) > 0 { // 如果有组名,则将versionedAPIPath+group+versionversionedAPIPath = path.Join(versionedAPIPath, groupVersion.Group, groupVersion.Version)} else { // 如果没有组名,则versionedAPIPath+versionversionedAPIPath = path.Join(versionedAPIPath, groupVersion.Version)}return versionedAPIPath}
代码片段1.2:TransportFor(Config)
// TransportFor returns an http.RoundTripper that will provide the authentication// or transport level security defined by the provided Config. Will return the// default http.DefaultTransport if no special case behavior is needed.// TransportForfan将返回一个http.RoundTripper对象,这个对象将提供Config配置的认证或者传输层的安全保证。// 如果没有特别的需要,将返回http.DefaultTransportfunc TransportFor(config *Config) (http.RoundTripper, error) {// 使用config.TransportConfig()方法,将client Config转化为 transport Configcfg, err := config.TransportConfig()if err != nil {return nil, err}return transport.New(cfg)}
代码片段1.2.1:TransportConfig()
将rest.Config转化为transport.Config,以便用于传输层的安全认证
// TransportConfig converts a client config to an appropriate transport config.func (c *Config) TransportConfig() (*transport.Config, error) {conf := &transport.Config{UserAgent: c.UserAgent,Transport: c.Transport,WrapTransport: c.WrapTransport,DisableCompression: c.DisableCompression,TLS: transport.TLSConfig{Insecure: c.Insecure,ServerName: c.ServerName,CAFile: c.CAFile,CAData: c.CAData,CertFile: c.CertFile,CertData: c.CertData,KeyFile: c.KeyFile,KeyData: c.KeyData,NextProtos: c.NextProtos,},Username: c.Username,Password: c.Password,BearerToken: c.BearerToken,BearerTokenFile: c.BearerTokenFile,Impersonate: transport.ImpersonationConfig{UserName: c.Impersonate.UserName,Groups: c.Impersonate.Groups,Extra: c.Impersonate.Extra,},Dial: c.Dial,Proxy: c.Proxy,}if c.ExecProvider != nil && c.AuthProvider != nil {return nil, errors.New("execProvider and authProvider cannot be used in combination")}if c.ExecProvider != nil {provider, err := exec.GetAuthenticator(c.ExecProvider)if err != nil {return nil, err}if err := provider.UpdateTransportConfig(conf); err != nil {return nil, err}}if c.AuthProvider != nil {provider, err := GetAuthProvider(c.Host, c.AuthProvider, c.AuthConfigPersister)if err != nil {return nil, err}conf.Wrap(provider.WrapTransport)}return conf, nil}
下图为rest.Config配置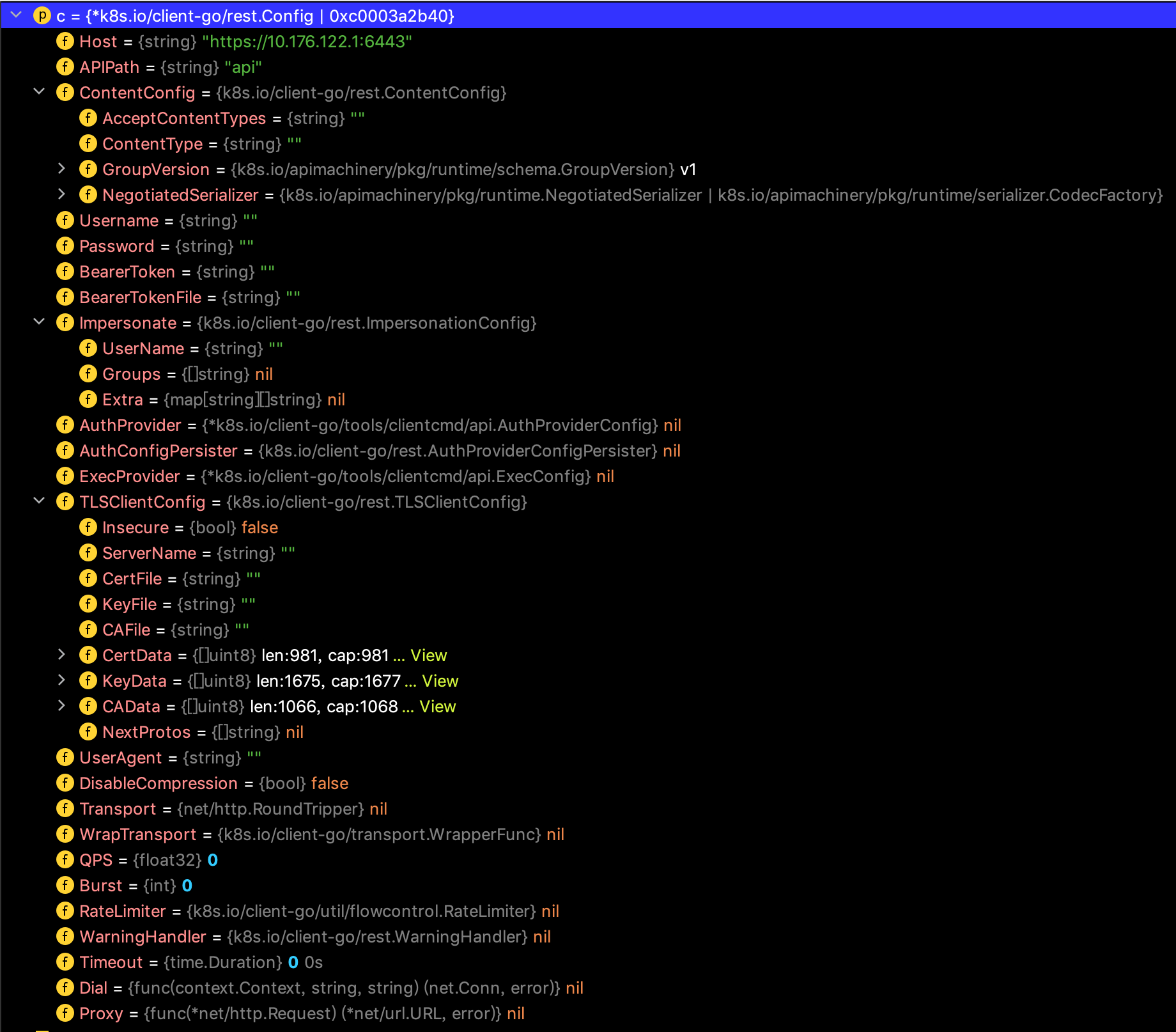
下图为transport.Config配置
代码片段1.2.2:
// New returns an http.RoundTripper that will provide the authentication// or transport level security defined by the provided Config.func New(config *Config) (http.RoundTripper, error) {// Set transport level securityif config.Transport != nil && (config.HasCA() || config.HasCertAuth() || config.HasCertCallback() || config.TLS.Insecure) {return nil, fmt.Errorf("using a custom transport with TLS certificate options or the insecure flag is not allowed")}var (rt http.RoundTrippererr error)if config.Transport != nil {rt = config.Transport} else {// client-go内部维护了一个transport的缓存,map[tlsCacheKey]*http.Transportrt, err = tlsCache.get(config)if err != nil {return nil, err}}return HTTPWrappersForConfig(config, rt)}
代码片段1.2.2.1
func (c *tlsTransportCache) get(config *Config) (http.RoundTripper, error) {// 为tls.Config生成为一个Key,详细分析见1.2.2.1.1key, canCache, err := tlsConfigKey(config)if err != nil {return nil, err}// 如果可以缓存,则为给定的tls生成单个transportif canCache {// Ensure we only create a single transport for the given TLS optionsc.mu.Lock()defer c.mu.Unlock()// See if we already have a custom transport for this configif t, ok := c.transports[key]; ok {return t, nil}}// Get the TLS options for this client configtlsConfig, err := TLSConfigFor(config)if err != nil {return nil, err}// The options didn't require a custom TLS configif tlsConfig == nil && config.Dial == nil && config.Proxy == nil {return http.DefaultTransport, nil}dial := config.Dialif dial == nil {dial = (&net.Dialer{Timeout: 30 * time.Second,KeepAlive: 30 * time.Second,}).DialContext}// If we use are reloading files, we need to handle certificate rotation properly// TODO(jackkleeman): We can also add rotation here when config.HasCertCallback() is trueif config.TLS.ReloadTLSFiles {dynamicCertDialer := certRotatingDialer(tlsConfig.GetClientCertificate, dial)tlsConfig.GetClientCertificate = dynamicCertDialer.GetClientCertificatedial = dynamicCertDialer.connDialer.DialContextgo dynamicCertDialer.Run(wait.NeverStop)}proxy := http.ProxyFromEnvironmentif config.Proxy != nil {proxy = config.Proxy}transport := utilnet.SetTransportDefaults(&http.Transport{Proxy: proxy,TLSHandshakeTimeout: 10 * time.Second,TLSClientConfig: tlsConfig,MaxIdleConnsPerHost: idleConnsPerHost,DialContext: dial,DisableCompression: config.DisableCompression,})if canCache {// Cache a single transport for these optionsc.transports[key] = transport}return transport, nil}// TlsTransportCache caches TLS http.RoundTrippers different configurations. The// same RoundTripper will be returned for configs with identical TLS options If// the config has no custom TLS options, http.DefaultTransport is returned.type tlsTransportCache struct {mu sync.Mutextransports map[tlsCacheKey]*http.Transport}
1.2.2.1.1
// tlsConfigKey returns a unique key for tls.Config objects returned from TLSConfigForfunc tlsConfigKey(c *Config) (tlsCacheKey, bool, error) {// Make sure ca/key/cert content is loadedif err := loadTLSFiles(c); err != nil {return tlsCacheKey{}, false, err}if c.TLS.GetCert != nil || c.Dial != nil || c.Proxy != nil {// cannot determine equality for functionsreturn tlsCacheKey{}, false, nil}k := tlsCacheKey{insecure: c.TLS.Insecure,caData: string(c.TLS.CAData),serverName: c.TLS.ServerName,nextProtos: strings.Join(c.TLS.NextProtos, ","),disableCompression: c.DisableCompression,}if c.TLS.ReloadTLSFiles {k.certFile = c.TLS.CertFilek.keyFile = c.TLS.KeyFile} else {k.certData = string(c.TLS.CertData)k.keyData = string(c.TLS.KeyData)}return k, true, nil}

