协程
生态框架
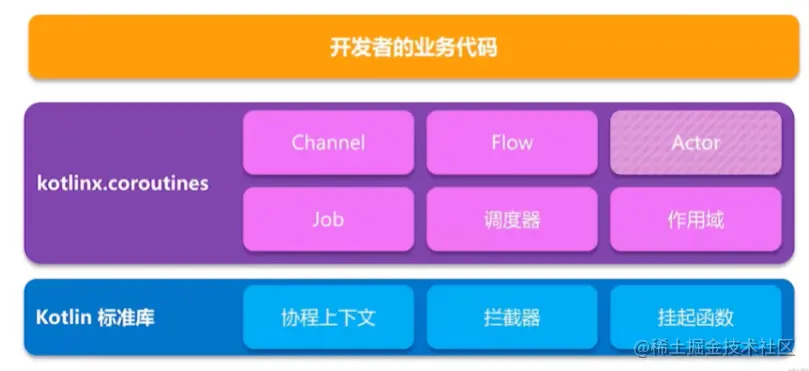
相关依赖库
dependencies {// Kotlinimplementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:1.4.32"// 协程核心库implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.4.3"// 协程Android支持库implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.4.3"// 协程Java8支持库implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-jdk8:1.4.3"// lifecycle对于协程的扩展封装implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.2.0"implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.2.0"implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-livedata-ktx:2.2.0"}
挂起函数
suspend
挂起函数中能调用任何函数。
非挂起函数只能调用非挂起函数。
换句话说,suspend函数只能在suspend函数中调用。
挂起函数:
//com.example.studycoroutine.chapter.CoroutineRun.kt
suspend fun suspendFun(): Int {
return 1;
}
java:
public static final Object suspendFun(Continuation completion) {
return Boxing.boxInt(1);
}
想要让suspend函数干活必须要先满足它,就是给它里面塞入completion。
然后他想调用其他的suspend函数,只需将completion继续塞到其它的suspend方法里面。
普通函数里没completion,所以压根没法调用suspend函数
常用关键字
launch、runBlocking、withContext、async/await
前两者启动协程,后两者调度线程
launch、runBlocking
launch是非阻塞的而runBlocking是阻塞的
launch:
private fun testCoroutine1() {
//这里只是协程作用域
// GlobalScope.launch {
// lifecycleScope.launch {
// viewModelScope.launch { 都可以
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main).launch {
delay(500)
YYLogUtils.w("协程1作用域内部执行")
}
YYLogUtils.w("协程1作用域外部执行")
}
结果为先执行外部,再执行内部
runBlocking:
private fun testCoroutine2() {
runBlocking {
delay(500)
YYLogUtils.w("协程2作用域内部执行")
}
YYLogUtils.w("协程2作用域外部执行")
}
结果相反,先执行内部,再执行外部,因为阻塞
所以在大多数情况下都是使用launch
withContext、async/await
withContext和 async/await一半都是用来进行切换线程,区别在于顺序执行还是并发执行
顺序执行:
例子,先等待1秒输入1234,然后调用接口获取Industry,请求完成之后再调用接口获取School,当前全部完成之后隐藏Loading
viewModelScope.launch {
//开始Loading
loadStartProgress()
val startTimeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis()
val res = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
//异步执行
delay(1000)
return@withContext "1234"
}
val endTimeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis()
YYLogUtils.w("res: $res time: ${endTimeStamp-startTimeStamp}")
//网络请求获取行业数据
val industrys = mRepository.getIndustry()
//返回的数据是封装过的,检查是否成功
industrys.checkResult({
//成功
_industryLD.postValue(it)
}, {
//失败
toastError(it)
})
//上面的请求执行完毕才会执行这个请求
val schools = mRepository.getSchool()
//返回的数据是封装过的,检查是否成功
schools.checkSuccess {
_schoollLD.postValue(it)
}
//完成Loading
loadHideProgress()
}
并发执行:
同时调用Industry和School接口,等待两者都完成之后再展示UI
viewModelScope.launch {
//开始Loading
loadStartProgress()
val industryResult = async {
mRepository.getIndustry()
}
val schoolResult = async {
mRepository.getSchool()
}
val localDBResult = async {
//loadDB()
YYLogUtils.w("thread:" + CommUtils.isRunOnUIThread())
delay(10000)
}
//一起处理数据
val industry = industryResult.await()
val school = schoolResult.await()
//如果都成功了才一起返回
if (industry is OkResult.Success && school is OkResult.Success) {
loadHideProgress()
_industryLD.postValue(industry.data!!)
_schoollLD.postValue(school.data!!)
}
YYLogUtils.e(localDBResult.await().toString() + "完成")
}
网络请求去重
- 取消上一次的
- 队列排队一个一个来
/**
* 网络请求去重
*/
private var controlledRunner = ControlledRunner<OkResult<List<Industry>>>() //取消之前的
private val singleRunner = SingleRunner() //任务队列,排队,单独的
fun netDuplicate() {
viewModelScope.launch {
//比较常用
//取消上一次的,执行这一次的
controlledRunner.cancelPreviousThenRun {
return@cancelPreviousThenRun mRepository.getIndustry()
}.checkSuccess {
YYLogUtils.e("请求成功:")
_industryLD.postValue(it)
}
//前一个执行完毕了,再执行下一个
// singleRunner.afterPrevious {
// mMainRepository.getIndustry()
// }.checkSuccess {
// YYLogUtils.e("测试重复的数据:" + it.toString())
// }
}
}
控制器:
class SingleRunner {
private val mutex = Mutex()
/**
* 加入到任务队列,前一个任务执行完毕再执行下一个任务
*/
suspend fun <T> afterPrevious(block: suspend () -> T): T {
mutex.withLock {
return block()
}
}
}
class ControlledRunner<T> {
private val activeTask = AtomicReference<Deferred<T>?>(null)
suspend fun cancelPreviousThenRun(block: suspend () -> T): T {
activeTask.get()?.cancelAndJoin()
return coroutineScope {
val newTask = async(start = LAZY) {
block()
}
newTask.invokeOnCompletion {
activeTask.compareAndSet(newTask, null)
}
val result: T
while (true) {
if (!activeTask.compareAndSet(null, newTask)) {
activeTask.get()?.cancelAndJoin()
yield()
} else {
result = newTask.await()
break
}
}
result
}
}
/**
* 不执行新任务,返回上一个任务的结果
*/
suspend fun joinPreviousOrRun(block: suspend () -> T): T {
activeTask.get()?.let {
return it.await()
}
return coroutineScope {
val newTask = async(start = LAZY) {
block()
}
newTask.invokeOnCompletion {
activeTask.compareAndSet(newTask, null)
}
val result: T
while (true) {
if (!activeTask.compareAndSet(null, newTask)) {
val currentTask = activeTask.get()
if (currentTask != null) {
newTask.cancel()
result = currentTask.await()
break
} else {
yield()
}
} else {
result = newTask.await()
break
}
}
result
}
}
}
网络请求封装(Retrofit+协程)
方式一:
处理BaseRepository:
open class BaseRepository {
//无异常处理 -> 一般不用这个,一旦报错会App崩溃
suspend inline fun <T : Any> handleApiCall(call: suspend () -> BaseBean<T>): BaseBean<T> {
return call.invoke()
}
/**
* 推荐使用拓展函数extRequestHttp
* 如果要使用Base里面的方法请求网络这么使用
* return handleErrorApiCall(call = {
handleApiErrorResponse()
})
* 都可以实现网络请求
*/
//处理Http错误-内部再处理Api错误
suspend fun <T : Any> handleErrorApiCall(call: suspend () -> OkResult<T>, errorMessage: String = ""): OkResult<T> {
return try {
call()
} catch (e: Exception) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(errorMessage)) {
OkResult.Error(IOException(errorMessage))
} else {
OkResult.Error(handleExceptionMessage(e))
}
}
}
//处理Api错误,例如403Token过期 把BaseBean的数据转换为自定义的Result数据
suspend fun <T : Any> handleApiErrorResponse(
response: BaseBean<T>,
successBlock: (suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit)? = null,
errorBlock: (suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit)? = null
): OkResult<T> {
return coroutineScope {
//执行挂起函数
if (response.code == 200) { //这里根据业务逻辑来 200 -1 等
successBlock?.let { it() }
OkResult.Success(response.data)
} else {
errorBlock?.let { it() }
OkResult.Error(IOException(response.message))
}
}
}
//处理自定义错误消息
fun handleExceptionMessage(e: Exception): IOException {
return when (e) {
is UnknownHostException -> IOException("Unable to access domain name, unknown domain name.")
is JsonParseException -> IOException("Data parsing exception.")
is HttpException -> IOException("The server is on business. Please try again later.")
is ConnectException -> IOException("Network connection exception, please check the network.")
is SocketException -> IOException("Network connection exception, please check the network.")
is SocketTimeoutException -> IOException("Network connection timeout.")
is RuntimeException -> IOException("Error running, please try again.")
else -> IOException("unknown error.")
}
}
}
使用:
suspend fun getServerTime(): OkResult<ServerTimeBean> {
return handleErrorApiCall({
handleApiErrorResponse(
MainRetrofit.apiService.getServerTime(
Constants.NETWORK_CONTENT_TYPE,
Constants.NETWORK_ACCEPT_V1
)
)
})
}
方式二:
使用扩展方法的直接一步到位处理:
suspend fun <T : Any> BaseRepository.extRequestHttp(call: suspend () -> BaseBean<T>): OkResult<T> {
//两种方式都可以,自用下面一种方式
// runCatching {
// call.invoke()
// }.onSuccess { response: BaseBean<T> ->
// if (response.code == 200) {
// OkResult.Success(response.data)
// } else {
// OkResult.Error(ApiException(response.code, response.message))
// }
// }.onFailure { e ->
// e.printStackTrace()
// OkResult.Error(handleExceptionMessage(Exception(e.message, e)))
// }
return try {
val response = call()
if (response.code == 200) {
OkResult.Success(response.data)
} else {
OkResult.Error(ApiException(response.code, response.message))
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
e.printStackTrace()
OkResult.Error(handleExceptionMessage(e))
}
}
使用:
suspend inline fun getIndustry(): OkResult<List<Industry>> {
return extRequestHttp {
DemoRetrofit.apiService.getIndustry(
Constants.NETWORK_CONTENT_TYPE,
Constants.NETWORK_ACCEPT_V1
)
}
}

