最近在做接口测试时用到了 requests 库做网络请求的client,使用过程中遇到了一些困惑,经过查阅文档和源码,特作如下总结,限于水平,难免有所纰漏,希望读者给予更正建议。
现象
在做微信请求时,报了如下错误:
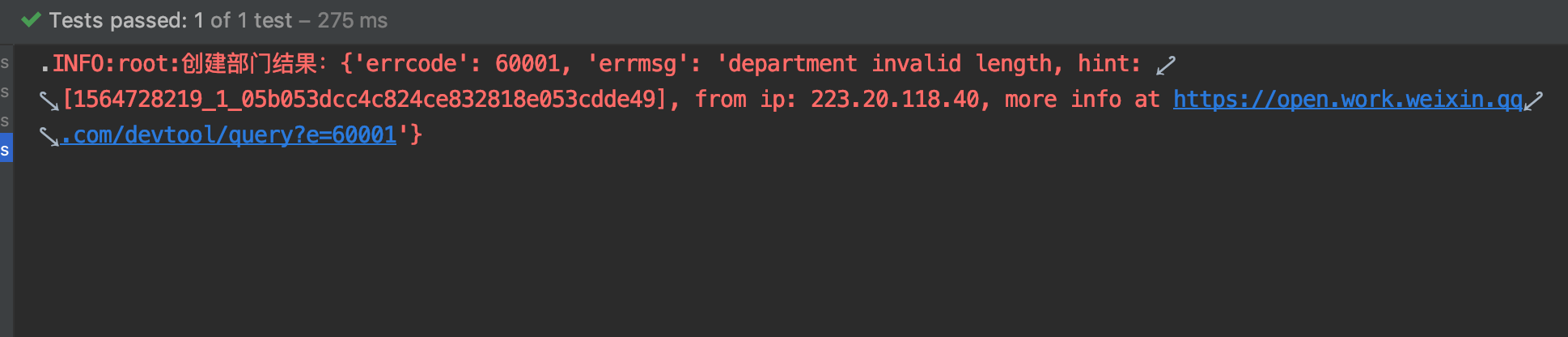
代码如下:
def create_department(self):url = 'https://qyapi.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/department/create'params = {"access_token": WeChat.get_token()}json_obj = {'name': "广州研发中心","parentid": 1,"order": 1}r = requests.post(url, params=params, data=json_obj).json()logging.info("创建部门结果:%s " %r)return r
根据如上现象,我推测时data出了问题。
排查问题
经过chares抓包
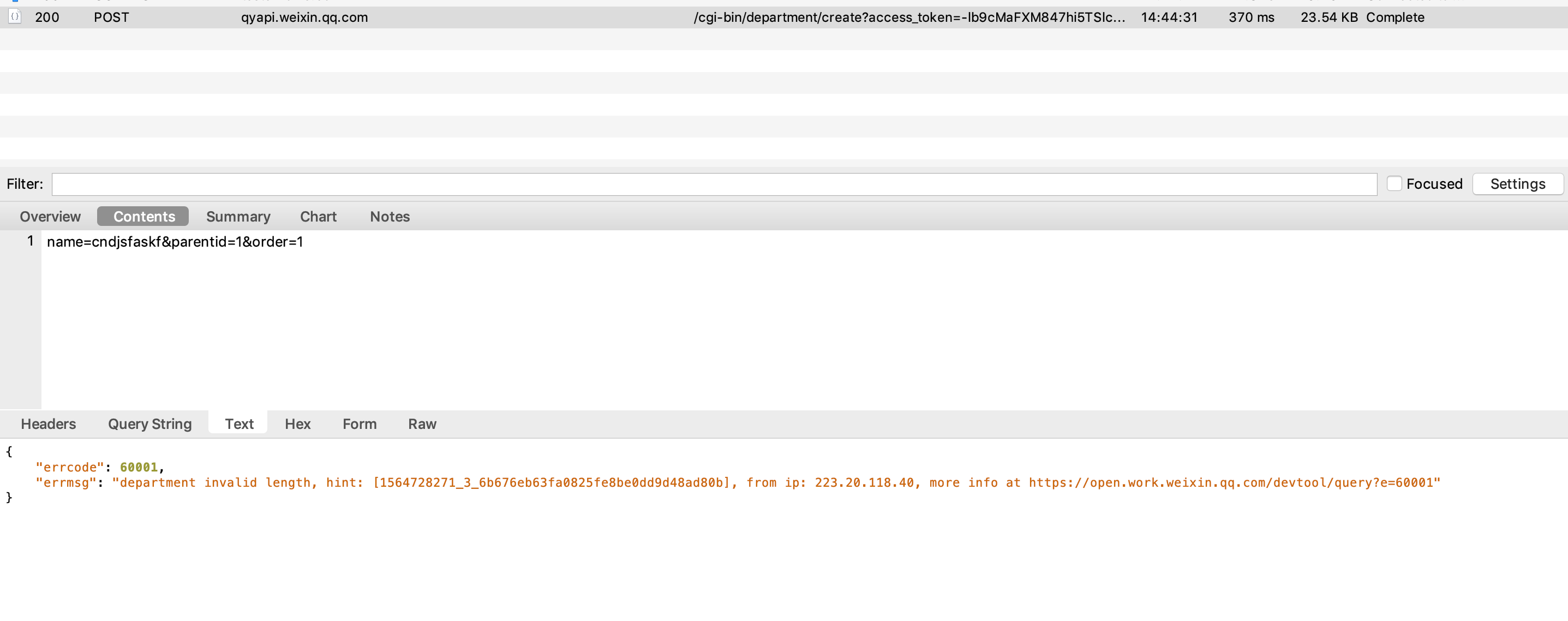

发现:
content-type:’application/x-www-form-urlencode’,
request body:’name=XXX&parentid=1&order=1’
该用json传可以解决上面的问题,应该是微信服务器,只处理json格式请求体。虽然问题解决了,但这激起了我的好奇心,为什么data是个字典,却被urlencode了呢?源码里做了什么处理?
HTTP的post方法
回忆下HTTP的 post 方法:其主要用于发送数据(request body )给服务器。 而数据的MIME类型和charset等,由 Content-Type 首部指定(理论上不能为空,因为服务端需要根据类型进行解析)。
常用的 content-type 有四种:
application/jsonapplication/``x-www-form-urlencoded: 数据被编码成以'&'分隔的键-值对, 同时以'='分隔键和值. 非字母或数字的字符会被 percent-encoding: 这也就是为什么这种类型不支持二进制数据的原因 (应使用multipart/form-data代替).multipart/form-datatext/plain
requests源码部分
一步一步找到相关源码:
def post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs):request('post', url, data=data, json=json, **kwargs)session.request(method=method, url=url, **kwargs)prep = self.prepare_request(req)def prepare(self,method=None, url=None, headers=None, files=None, data=None,params=None, auth=None, cookies=None, hooks=None, json=None):self.prepare_body(data, files, json)
def prepare_body(self, data, files, json=None):
"""Prepares the given HTTP body data."""
# Check if file, fo, generator, iterator.
# If not, run through normal process.
# Nottin' on you.
body = None
content_type = None
if not data and json is not None:
# urllib3 requires a bytes-like body. Python 2's json.dumps
# provides this natively, but Python 3 gives a Unicode string.
content_type = 'application/json'
body = complexjson.dumps(json)
if not isinstance(body, bytes):
body = body.encode('utf-8')
is_stream = all([
hasattr(data, '__iter__'),
not isinstance(data, (basestring, list, tuple, Mapping))
])
try:
length = super_len(data)
except (TypeError, AttributeError, UnsupportedOperation):
length = None
if is_stream:
body = data
if getattr(body, 'tell', None) is not None:
# Record the current file position before reading.
# This will allow us to rewind a file in the event
# of a redirect.
try:
self._body_position = body.tell()
except (IOError, OSError):
# This differentiates from None, allowing us to catch
# a failed `tell()` later when trying to rewind the body
self._body_position = object()
if files:
raise NotImplementedError('Streamed bodies and files are mutually exclusive.')
if length:
self.headers['Content-Length'] = builtin_str(length)
else:
self.headers['Transfer-Encoding'] = 'chunked'
else:
# Multi-part file uploads.
if files:
(body, content_type) = self._encode_files(files, data)
else:
if data:
body = self._encode_params(data)
if isinstance(data, basestring) or hasattr(data, 'read'):
content_type = None
else:
content_type = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
self.prepare_content_length(body)
# Add content-type if it wasn't explicitly provided.
if content_type and ('content-type' not in self.headers):
self.headers['Content-Type'] = content_type
self.body = body
找到了 prepare_body 方法,可以发现,json 、 data 和 files 是会被当成request body来处理的。在requests发送post请求前,会根据传入参数处理 content-type 。
过下代码:
- 默认对body和content-type都是None
- 如果传入了json而没有传data
- 值接将content-type设置为application/json,并将json转成字符串
- 如何不是字节类型就给body在做下utf-8编码
- 尝试获得data的长度
- is_stream判断,有迭代器属性,且不是list、basestring、tuple或Mapping,这就可能是个genarator,对应到文档是块编码请求
- 尝试获得块的位置
- 这时同时给post传入files的话,就会抛出错误了
- 不是块编码请求的话
- 判断是否传入files参数,files调用_encode_files方法处理,获取conetn-type和body
- 再判断是否传了data
- 这时data可能是字符串、list、tuple、或map等类型,先进行_encode_params,list、tuple和map转成urlencode(即”key1=value1&key2=value2”),字符串、字节码和其他情况不处理直接返回(代码如下)
- 再判断,如果是字符串的话,content-type设为None
- 其他情况设为content-type:’application/x-www-form-urlencoded’
- 这时data可能是字符串、list、tuple、或map等类型,先进行_encode_params,list、tuple和map转成urlencode(即”key1=value1&key2=value2”),字符串、字节码和其他情况不处理直接返回(代码如下)
def _encode_params(data):
"""Encode parameters in a piece of data.
Will successfully encode parameters when passed as a dict or a list of
2-tuples. Order is retained if data is a list of 2-tuples but arbitrary
if parameters are supplied as a dict.
"""
if isinstance(data, (str, bytes)):
return data
elif hasattr(data, 'read'):
return data
elif hasattr(data, '__iter__'):
result = []
for k, vs in to_key_val_list(data):
if isinstance(vs, basestring) or not hasattr(vs, '__iter__'):
vs = [vs]
for v in vs:
if v is not None:
result.append(
(k.encode('utf-8') if isinstance(k, str) else k,
v.encode('utf-8') if isinstance(v, str) else v))
return urlencode(result, doseq=True)
else:
return data

