- 1、简介
- 2、常用注解
- 3、最佳实践
3.1、maven依赖- 3.2、Mock静态方法
- 3.4、被Mock的类没有无参构造函数
- 3.5、对private方法进行单测
- 3.6、仅在指定条件下mock,其他条件执行原逻辑
- 3.7、直接在测试方法的参数列表里注入mock对象
- 3.8、@Mocked和@Injectable的区别
- 3.9、模拟返回值类型为void的方法
- 3.10、模拟抛出Exception
- 3.11、当在spring环境中Autowired一个List变量时,该如何mock
- 3.12、mock代码块和静态代码块
- 3.13、使用Verifications进行验证
- 3.14 使用Delegate委托来mock
- 3.15、使用any参数
- 3.16、使用with方法
1、简介
单元测试(unit testing)
是指对软件中的最小可测试单元进行检查和验证。对于单元测试中单元的含义,一般来说,要根据实际情况去判定其具体含义,Java里单元指一个类。单元就是人为规定的最小的被测功能模块。单元测试是在软件开发过程中要进行的最低级别的测试活动,软件的独立单元将在与程序的其他部分相隔离的情况下进行测试。
模拟测试(mock testing)
就是在测试过程中,对于某些不容易构造或者不容易获取的对象,用一个虚拟的对象来创建以便测试的测试方法。
JUnit
是一个Java语言的单元测试框架。Junit测试是程序员测试,即所谓白盒测试,因为程序员知道被测试的软件如何(How)完成功能和完成什么样(What)的功能。Junit是一套框架,继承TestCase类,就可以用Junit进行自动测试了。
JMockit
JMockit 是用以帮助开发人员编写测试程序的一组工具和API,该项目完全基于 Java 5 SE 的 java.lang.instrument 包开发,内部使用 ASM 库来修改Java的Bytecode。所以他能解决当测试的代码包含了一些静态方法,未实现方法,未实现接口的问题。
ASM 是一个 Java 字节码操控框架。它能被用来动态生成类或者增强既有类的功能。
Jmockit中文网:http://jmockit.cn/
Jmockit官网:http://jmockit.github.io/
2、常用注解
@Mocked
@Mocked不仅能修饰一个类,也能修饰接口。@Mocked修饰的普通类/接口/抽象类,是告诉JMockit,帮我生成一个Mocked对象,这个对象的方法(包含静态方法)都会返回return type的默认值,比如return type是int,则返回0,return type 是String,则返回null。
使用@Mocked时需要注意,如果是定义为测试类的成员变量,则被mock类的所有实例都是mock生成的,如下:
public class HelloJMockitTest {@TestedHelloJMockit helloJMockit;//mock成员变量,Something类的所有实例均由mock生成@MockedSomething something;@Testpublic void sayHelloTest(){String msg = helloJMockit.sayHello();}}
如果是mocked方法参数,则只在该测试内的实例是mock生成的,如下:
public class HelloJMockitTest {@TestedHelloJMockit helloJMockit;@Testpublic void sayHelloTest(@Mocked Something something){//作为方法参数,仅在该方法内是由mock生成实例something.doSomething();String msg = helloJMockit.sayHello();}}
@Tested & @Injectable
@Injectable 也是告诉 JMockit生成一个Mocked对象,但@Injectable只是针对其修饰的实例,而@Mocked是针对其修饰类的所有实例。此外,@Injectable对类的静态方法,构造函数没有影响。因为它只影响某一个实例。
@Tested修饰的类,表示是我们要测试对象,如果该对象没有赋值,JMockit会去实例化它。该注解不能实例化接口。
@Tested & @Injectable通常搭配使用。若@Tested的构造函数有参数,则JMockit通过在测试属性、测试参数中查找@Injectable修饰的Mocked对象注入@Tested对象的构造函数来实例化,不然,则用无参构造函数来实例化。
除了构造函数的注入,JMockit还会通过属性查找的方式,把@Injectable对象注入到@Tested对象中。注入的匹配规则:先类型,再名称(构造函数参数名,类的属性名)。若找到多个可以注入的@Injectable,则选择最优先定义的@Injectable对象。当然,我们的测试程序要尽量避免这种情况出现。因为给哪个测试属性/测试参数加@Injectable,是人为控制的。
@Capturing
@Capturing主要用于子类/实现类的Mock, 我们只知道父类或接口时,但我们需要控制它所有子类的行为时,子类可能有多个实现(可能有人工写的,也可能是AOP代理自动生成时)。就用@Capturing。
MockUp & @Mock
MockUp & @Mock比较适合于一个项目中,用于对一些通用类的Mock,以减少大量重复的new Exceptations{{}}代码。
在实际Mock场景中,我们需要灵活运用JMockit其它的Mock API。让我们的Mock程序简单,高效。
一个类有多个实例,但只对其中某1个实例进行mock的场景是MockUp & @Mock做不到的,这种时候就需要上述的@Capturing注解了。
Expectations
Expectations的作用主要是用于录制。即录制类/对象的调用,返回值是什么。主要有两种使用方式:
a.通过引用外部类的Mock对象(@Injectabe,@Mocked,@Capturing)来录制;
b.通过构建函数注入类/对象来录制.
Verifications
Verifications是用于做验证。验证Mock对象(即@Moked/@Injectable@Capturing修饰的或传入Expectation构造函数的对象)有没有调用过某方法,调用了多少次。
通常在实际测试程序中,我们更倾向于通过JUnit/TestNG/SpringTest的Assert类对测试结果的验证, 对类的某个方法有没调用,调用多少次的测试场景并不是太多。因此在验证阶段,我们完全可以用JUnit/TestNG/SpringTest的Assert类取代new Verifications() {{}}验证代码块。除非,你的测试程序关心类的某个方法有没有调用,调用多少次,你可以使用new Verifications() {{}}验证代码块。
3、最佳实践
3.1、maven依赖
<!-- 引入dependency --><dependency><groupId>org.jmockit</groupId><artifactId>jmockit</artifactId><version>1.49</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.13</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId></exclusion><exclusion><groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId><artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><!-- 同时引入plugin --><plugin><artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId><version>2.22.2</version><configuration><argLine>-javaagent:${settings.localRepository}/org/jmockit/jmockit/1.49/jmockit-1.49.jar=coverage</argLine><disableXmlReport>true</disableXmlReport></configuration></plugin>
3.2、Mock静态方法
//需要mock的静态方法public class StaticTarget {public static int m1() {return 1;}public static String m2(String s) {return 2;}}public class RunState {@Beforepublic void stepUp(){//打桩需要被mock的静态方法new MockUp<StaticTarget>() {//被mock的静态方法,可以自己定义返回结果@Mockpublic String m2(String s) {return "TEST";}@Mockpublic int m1() {return 100;}};}//单元测试中调用@Test //import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;public void test() {//调用静态方法int i = StaticTarget.m1();//判断返回值结果Assert.assertEquals(100, i));//调用静态方法String s = StaticTarget.m2();//判断返回值结果Assert.assertEquals("ATY", s);}}
3.3、Mock普通方法和私有方法
//需要mock的普通方法public class CommonTarget {public int m3() {return 1;}public void m4(String s) {int i = 1 + 1;}}
public class RunState {//打桩需要被mock的静态方法@Beforepublic void stepUp(){//打桩需要mock的方法所属的类new MockUp<CommonTarget>() {@Mockpublic String m3(String s) {return "TEST";}@Mockpublic int m4() {return 100;}};}//单元测试中调用@Testpublic void test() {CommonTarget commonTarget = new CommonTarget();Assert.assertEquals("ATY", commonTarget.m3());Assert.assertEquals(100, commonTarget.m4());}}
tips:private方法不能被mock。在Jmockit的早期版本里,提供了反射的工具类来mock私有方法,但是在1.36版本之后,就移除了该功能,并且作者没有提供替代的方案。
3.4、被Mock的类没有无参构造函数
若@Tested的构造函数有参数,则JMockit通过在测试属性、测试参数中查找@Injectable修饰的Mocked对象注入@Tested对象的构造函数来实例化,不然,则用无参构造函数来实例化。
/**● 待测试的类*/public class HelloJMockit {private static Locale locale;private int num=0;//不含有无参构造函数HelloJMockit(int num){this.num = num;}public String sayHello() {locale = Locale.getDefault();if (locale.equals(Locale.CHINA)) {// 在中国,就说中文return "你好,JMockit!";} else {// 在其它国家,就说英文return "Hello,JMockit!";}}}
public class HelloJMockitTest {@TestedHelloJMockit helloJMockit;@Testpublic void sayHelloTest(@Injectable("123")int num){String msg = helloJMockit.sayHello();}}
3.5、对private方法进行单测
使用JMockit时,private方法不能被mock,1.36之前的版本可以mock私有方法,但是在之后的版本里,作者移除了该功能,并且没有给出相应的替代方案。
当需要对某个类中的private方法进行单元测试时,无法直接通过普通方式进行调用,这里推荐使用反射进行调用测试。
public class PrivateMethodDemo {private String saySomething(String something){System.out.println(something);return something+" is said!";}}
import mockit.Injectable;import mockit.Tested;import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class PrivateMethodDemoTest {@TestedPrivateMethodDemo privateMethodDemo;@Testpublic void saySomethingTest(@Injectable("hello")String something) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {Method method = PrivateMethodDemo.class.getDeclaredMethod("saySomething",String.class);method.setAccessible(true);Assert.assertEquals(something+" is said!",method.invoke(privateMethodDemo,something));}}
3.6、仅在指定条件下mock,其他条件执行原逻辑
在某些场景下,我们需要仅在某种条件下执行mock逻辑,其他条件执行原逻辑,这里以平台常用的SPI工具类FactoriesLoader举例。
在待测试类中,通过spi机制来获取一个数据库连接管理工厂的实例,如果不对其进行mock,会抛出空指针异常;
待模拟方法如下:
public class FactoriesLoader{//...some code...public static <T> T getDefaultFactory(Class<T> factoryClass) {SPI spi = factoryClass.getAnnotation(SPI.class);if (spi == null)return null;String id = spi.defaultId();if (id != null) {Map<String, T> factoryInstances = getFactories(factoryClass);return factoryInstances.get(id);}return null;}//...some code...}
先创建一个工厂类,然后通过mock生成该类的实例对象。
//interface也可以被@Mockedpublic interface DBConnectionManagerFactory {public DBConnectionManager getDBConnectionManager();}
然后模拟SPI工具类的方法,由于该方法在执行过程中,还有其他地方也要调用,比如获取日志输出对象,所以在模拟的时候,要求只有当此处调用该方法时,才执行mock逻辑,否则应执行原逻辑。测试代码如下:
public class EdspTransactionManagerTest {//待测试类@TestedEdspTransactionManager edspTransactionManager;//模拟的工厂类@MockedDBConnectionManagerFactory dbConnectionManagerFactory;@Testpublic void getDBConnectionEnableTest() throws NoSuchMethodException,InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {//模拟SPI工具类new MockUp<FactoriesLoader>() {@Mockpublic <T> T getDefaultFactory(Invocation invocation, Class<T> factoryClass) {//factoryClass是原方法的参数,invocation是JMcokit的参数//只有满足条件,才执行模拟逻辑if (factoryClass == DBConnectionManagerFactory.class) {return (T) dbConnectionManagerFactory;}//否则执行原逻辑return invocation.proceed(factoryClass);}};}}
3.7、直接在测试方法的参数列表里注入mock对象
在测试方法的参数列表里加入参数,这在以往的印象中是不行的,但是Jmockit允许我们这样做,使用@Mocked和@Injectable注解即可实现。如下:
public class InjectableDemoTest {@TestedInjectableDemo injectableDemoTested;@Testpublic void doSomethingWhitParamTest(@Injectable User user, @Mocked JobEntity jobEntity){new Expectations(){{user.getUsername();result = "Davi";}{jobEntity.getId();result = 1;}};String msg = injectableDemoTested.doSomethingWhitParam(user);Assert.assertEquals("hello,Davi",msg);Assert.assertEquals(1,jobEntity.getId());}}
此处有个需要注意的点,使用@Injectable时,如果不存在@Tested,那么Injectable的对象不会被mock,会为null。
3.8、@Mocked和@Injectable的区别
使用@Mocked注解修饰一个变量实例,则该实例所属的类的所有实例都会被mock,包括类的静态方法、构造函数都会被mock;
使用@Injectable注解修饰一个变量实例,只有该变量实例会被mock,该变量实例所属类的其他实例不受影响,类的静态方法、构造函数也不受影响。
@Mocked注解可以mock接口、抽象类、普通类;而@Injectable注解只能mock普通类
如下:
@Testpublic void showDifferenceTest(@Injectable User user1, @Mocked JobEntity jobEntity1){new Expectations(){{user1.getUsername();result = "张三";}{jobEntity1.getId();result = 1;}};User user2 = new User();//重新new的一个对象user2.setUsername("李四");System.out.println("user1:"+user1.getUsername());System.out.println("user2:"+user2.getUsername());JobEntity jobEntity2 = new JobEntity();//重新new的一个对象jobEntity2.setId(2);System.out.println("jobEntity1:"+jobEntity1.getId());System.out.println("jobEntity2:"+jobEntity2.getId());}//控制台输出://user1:张三//user2:李四//jobEntity1:1//jobEntity2:1
3.9、模拟返回值类型为void的方法
返回值类型为void的方法,不能使用Expectation来模拟,可以通过MockUp来模拟如下:
public class VoidMethodDemo {//要被模拟的void类型方法public void doSomething(){System.out.println("do something with void return type");}}public class VoidMethodDemoTest {@TestedVoidMethodDemo voidMethodDemo;@Testpublic void doSomethingTest(){new MockUp<VoidMethodDemo>(){@Mockpublic void doSomething(){System.out.println("had been mocked!");}};voidMethodDemo.doSomething();}}
3.10、模拟抛出Exception
当需要测试一些异常场景时,需要模拟某个方法运行时抛出Exception。如下:
public class ExceptioneDemoTest {@TestedUser user;/*** 使用result返回一个exception实例*/@Testpublic void doSomethingTest2(){new Expectations(user){{user.getUsername();result = new RuntimeException();}};Assert.assertThrows(RuntimeException.class,()->{user.getUsername();});}/*** 使用MockUp&Mock直接mock原方法抛出异常*/@Testpublic void exceptionTest(){new MockUp<User>(){@Mockpublic int getId() {throw new RuntimeException();}};Assert.assertThrows(RuntimeException.class,()->{user.getId();});}}
3.11、当在spring环境中Autowired一个List变量时,该如何mock
在spring中,容器中的bean都是单例bean,而且并不会有List类型在容器中,但是当容器中有多个同类型的bean时,spring自动注入@Autowired就支持用list来接收。JMockit在这方面也对spring做了支持。代码如下:
public class ListFieldDemo {//如果没有@AutoWired注解,则mock不生效@Autowiredprivate List<User> userList;public List<User> getUserList(){return userList;}}
public class ListFieldDemoTest {@TestedListFieldDemo listFieldDemo;@InjectableUser user1;@InjectableUser user2;@Testpublic void getUserListTest(){List<User> userList = listFieldDemo.getUserList();Assert.assertNotNull(userList);System.out.println(userList.size());//size值是2,jmockit会像spring一样自动把user1和user2注入到userList中}}
3.12、mock代码块和静态代码块
public class StaticCodeBlockDemo {{System.out.println("代码块执行了");}static {System.out.println("静态代码块执行了");}public void sayHello(){System.out.println("hello");}}
public class StaticCodeBlockDemoTest {@TestedStaticCodeBlockDemo staticCodeBlockDemo;@BeforeEachpublic void mockStaticCodeBlock(){new MockUp<StaticCodeBlockDemo>(){//模拟代码块@Mockpublic void $init(){System.out.println("代码块被mock了");}//模拟静态代码块@Mockpublic void $clinit(){System.out.println("静态代码块被mock了");}};}@Testpublic void getUserTest(){staticCodeBlockDemo.sayHello();}}
3.13、使用Verifications进行验证
JMockit的Record-Replay-Verify中,使用Expectations进行模拟,使用Verifications进行验证。通过Verifications,可以验证模拟方法被调用的次数,通过VerificationInOrder可以验证模拟方法的调用顺序。代码如下:
public class VerificationsDemo {public String method1(){return "method1 ";}public String method2(){return "method2";}public String method3(){return "method3";}}
public class VerificationsDemoTest {@TestedVerificationsDemo verificationsDemo;/*** 验证调用次数*/@Testpublic void verficationDemo(){//Recordnew Expectations(verificationsDemo){{verificationsDemo.method1();result = "mocked";}};//ReplaySystem.out.println(verificationsDemo.method1());//System.out.println(verificationsDemo.method1());//System.out.println(verificationsDemo.method1());//Verifynew Verifications(){{verificationsDemo.method1();times = 3;}//{// verificationsDemo.method1();// maxTimes = 2;//}//{// verificationsDemo.method1();// minTimes = 2;//}};}/*** 验证调用顺序*/@Testpublic void verificationInOrderTest(){new Expectations(verificationsDemo){{verificationsDemo.method1();result = "method1 mocked";}{verificationsDemo.method2();result = "method2 mocked";}{verificationsDemo.method3();result = "method3 mocked";}};System.out.println(verificationsDemo.method1());System.out.println(verificationsDemo.method2());System.out.println(verificationsDemo.method3());new VerificationsInOrder(){//验证调用顺序{verificationsDemo.method1();verificationsDemo.method2();verificationsDemo.method3();}};}}
3.14 使用Delegate委托来mock
Delegate类可以起到一个委托的效果,将原方法的逻辑委托给一个自定义方法,从而达到mock的效果。
定义一个DelegateService类:
public class DelegateService {//被委托mock的方法public int intReturningMethod(String arg1, int arg2){return 1;}}
定义一个测试类,在其中调用上面的委托方法:
public class DelegateDemo {public int testService(){DelegateService delegateService = new DelegateService();return delegateService.intReturningMethod("hello",2);}}
测试代码如下:
public class DelegateDemoTest {@TestedDelegateDemo delegateDemo;//使用@Mocked修饰的类的所有实例都会走mock逻辑@MockedDelegateService delegateService;@Testpublic void testServiceTest(){new Expectations() {{delegateService.intReturningMethod(anyString,anyInt );result = new Delegate() {int aDelegateMethod(String s,int i ) {System.out.println( "代理方法执行了,原入参:arg1:"+s+" arg2:"+i );return 100;}};}};System.out.println( delegateDemo.testService() );}}
测试结果: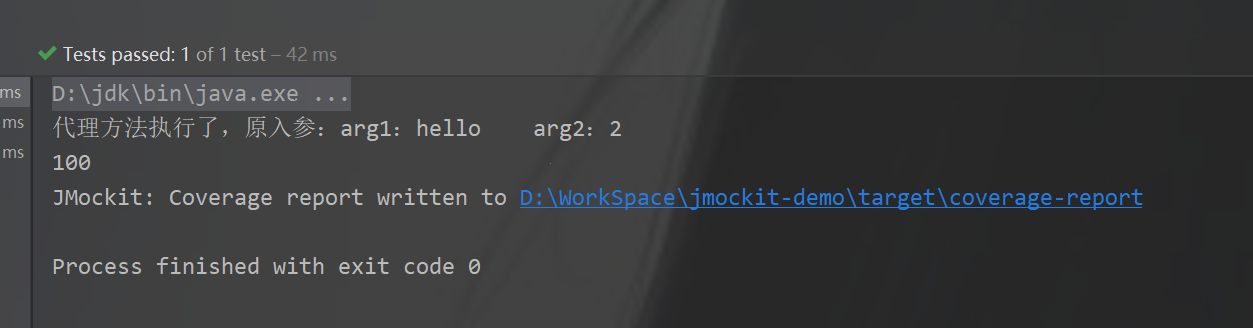
3.15、使用any参数
anyString、anyInt、anyLong等。。。。
“any”可以匹配Object类型的参数,也可以强转它,比如:”(User)any”可以得到一个User对象示例
3.16、使用with方法
@Test
void someTestMethod(@Mocked DependencyAbc abc) {
DataItem item = new DataItem(...);
new Expectations() {{
// 只要第二个参数不为null就可以匹配上
abc.voidMethod("str", (List<?>) withNotNull());
result = 1000;
// 第一个参数要和item是同一个对象实例
// 第二个参数要包含"xyz"字符串
// 同时满足以上两个条件才能匹配上
abc.stringReturningMethod(withSameInstance(item), withSubstring("xyz"));
result = 100;
}};
cut.doSomething(item);
new Verifications() {{
// withAny(T) :只要参数类型为T就会匹配上
abc.anotherVoidMethod(withAny(1L));
}};
}

