You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST) and an integer val.
Find the node in the BST that the node’s value equals val and return the subtree rooted with that node. If such a node does not exist, return null.
Example 1: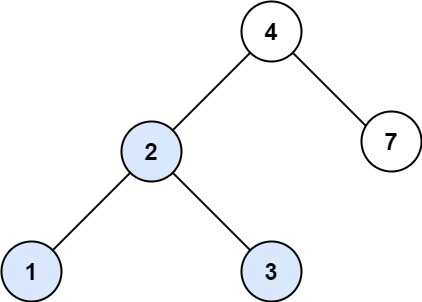
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2 Output: [2,1,3]
Example 2: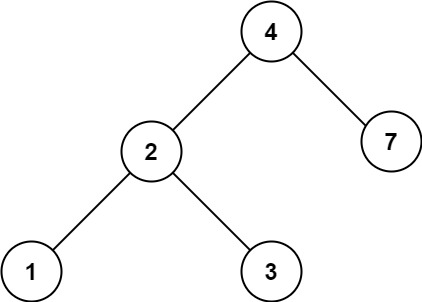
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 5000].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 107
- root is a binary search tree.
- 1 <= val <= 107
Runtime: 92 ms, faster than 84.88% of JavaScript online submissions for Search in a Binary Search Tree.
Memory Usage: 45.2 MB, less than 33.90% of JavaScript online submissions for Search in a Binary Search Tree.
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*//*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} val* @return {TreeNode}*/var searchBST = function(root, val) {if (!root) {return null;}if (root.val === val) {return root;}if (root.val > val) {return searchBST(root.left, val);}return searchBST(root.right, val);};
Runtime: 88 ms, faster than 92.84% of JavaScript online submissions for Search in a Binary Search Tree.
Memory Usage: 45.6 MB, less than 8.59% of JavaScript online submissions for Search in a Binary Search Tree.
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*//*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} val* @return {TreeNode}*/var searchBST = function(root, val) {if (!root) {return null;}let node = root;while(node) {if (node.val === val) {return node;}if (node.val > val) {node = node.left;} else {node = node.right;}}return null;};

