1.Redis命令
1.1 入门案例操作
@Testpublic void testHash() throws InterruptedException {Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129",6379);jedis.hset("person", "id", "18");jedis.hset("person", "name", "hash测试");jedis.hset("person", "age", "2");Map<String,String> map = jedis.hgetAll("person");Set<String> set = jedis.hkeys("person"); //获取所有的keyList<String> list = jedis.hvals("person");}@Testpublic void testList() throws InterruptedException {Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129",6379);jedis.lpush("list", "1","2","3","4");System.out.println(jedis.rpop("list"));}@Testpublic void testTx(){Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.126.129",6379);//1.开启事务Transaction transaction = jedis.multi();try {transaction.set("a", "a");transaction.set("b", "b");transaction.set("c", "c");transaction.exec(); //提交事务}catch (Exception e){transaction.discard();}}
2 SpringBoot整合Redis
2.1 编辑pro配置文件
由于redis的IP地址和端口都是动态变化的,所以通过配置文件标识数据. 由于redis是公共部分,所以写到common中.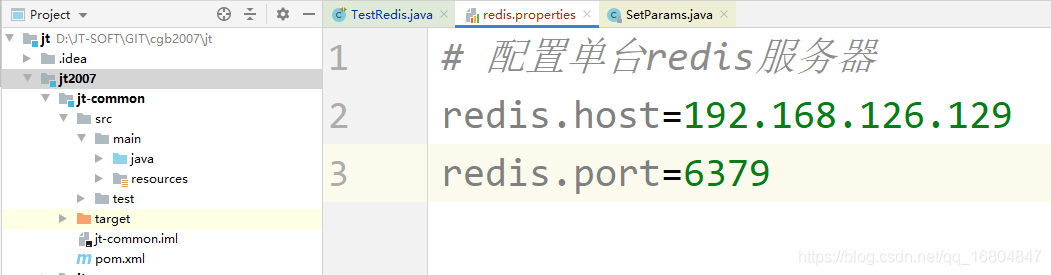
2.2 编辑配置类
package com.jt.config;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;@Configuration //标识我是配置类@PropertySource("classpath:/properties/redis.properties")public class RedisConfig {@Value("${redis.host}")private String host;@Value("${redis.port}")private Integer port;@Beanpublic Jedis jedis(){return new Jedis(host, port);}}
3 对象与JSON串转化
3.1 对象转化JSON入门案例
package com.jt;import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.jt.pojo.ItemDesc;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.Date;public class TestObjectMapper {private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();/*** 1.对象如何转化为JSON串的???* 步骤:* 1.获取对象的所有的getXXXX()方法.* 2.将获取的getXXX方法的前缀get去掉 形成了json的key=xxx* 3.通过getXXX方法的调用获取属性的值,形成了json的value的值.* 4.将获取到的数据 利用json格式进行拼接 {key : value,key2:value2....}* 2.JSON如何转化为对象???* {lyj:xxx}* 步骤:* 1. 根据class参数类型,利用java的反射机制,实例化对象.* 2. 解析json格式,区分 key:value* 3. 进行方法的拼接 setLyj()名称.* 4.调用对象的setXXX(value) 将数据进行传递,* 5.最终将所有的json串中的key转化为对象的属性.*** @throws JsonProcessingException*/@Testpublic void testTOJSON() throws JsonProcessingException {ItemDesc itemDesc = new ItemDesc();itemDesc.setItemId(100L).setItemDesc("测试数据转化").setCreated(new Date()).setUpdated(new Date());//1.将对象转化为JSONString json = MAPPER.writeValueAsString(itemDesc);System.out.println(json);//2.将json转化为对象 src:需要转化的JSON串, valueType:需要转化为什么对象ItemDesc itemDesc2 = MAPPER.readValue(json, ItemDesc.class);/*** 字符串转化对象的原理:*/System.out.println(itemDesc2.toString());}}
3.2 编辑ObjectMapper工具API
package com.jt.util;import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;public class ObjectMapperUtil {private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();//将对象转化为JSONpublic static String toJSON(Object target){try {return MAPPER.writeValueAsString(target);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {e.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException(e);}}//将JSON转化为对象//需求: 如果用户传递什么类型,则返回什么对象public static <T> T toObject(String json,Class<T> targetClass){try {return MAPPER.readValue(json, targetClass);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {e.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
4 实现商品分类缓存实现
4.1 编辑ItemCatController
说明: 切换业务调用方法,执行缓存调用
/*** 业务: 实现商品分类的查询* url地址: /item/cat/list* 参数: id: 默认应该0 否则就是用户的ID* 返回值结果: List<EasyUITree>*/@RequestMapping("/list")public List<EasyUITree> findItemCatList(Long id){Long parentId = (id==null)?0:id;//return itemCatService.findItemCatList(parentId);return itemCatService.findItemCatCache(parentId);}
4.2 编辑ItemCatService
package com.jt.service;import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;import com.jt.mapper.ItemCatMapper;import com.jt.pojo.ItemCat;import com.jt.util.ObjectMapperUtil;import com.jt.vo.EasyUITree;import org.omg.PortableInterceptor.SYSTEM_EXCEPTION;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;@Servicepublic class ItemCatServiceImpl implements ItemCatService{@Autowiredprivate ItemCatMapper itemCatMapper;@Autowired(required = false) //程序启动是,如果没有改对象 暂时不加载private Jedis jedis;@Overridepublic String findItemCatName(Long itemCatId) {return itemCatMapper.selectById(itemCatId).getName();}@Overridepublic List<EasyUITree> findItemCatList(Long parentId) {//1.准备返回值数据List<EasyUITree> treeList = new ArrayList<>();//思路.返回值的数据从哪来? VO 转化 POJO数据//2.实现数据库查询QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper();queryWrapper.eq("parent_id",parentId);List<ItemCat> catList = itemCatMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);//3.实现数据的转化 catList转化为 treeListfor (ItemCat itemCat : catList){long id = itemCat.getId(); //获取ID值String text = itemCat.getName(); //获取商品分类名称//判断:如果是父级 应该closed 如果不是父级 则openString state = itemCat.getIsParent()?"closed":"open";EasyUITree easyUITree = new EasyUITree(id,text,state);treeList.add(easyUITree);}return treeList;}/*** Redis:* 2大要素: key: 业务标识+::+变化的参数 ITEMCAT::0* value: String 数据的JSON串* 实现步骤:* 1.应该查询Redis缓存* 有: 获取缓存数据之后转化为对象返回* 没有: 应该查询数据库,并且将查询的结果转化为JSON之后保存到redis 方便下次使用* @param parentId* @return*/@Overridepublic List<EasyUITree> findItemCatCache(Long parentId) {Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();List<EasyUITree> treeList = new ArrayList<>();String key = "ITEMCAT_PARENT::"+parentId;if(jedis.exists(key)){//redis中有数据String json = jedis.get(key);treeList = ObjectMapperUtil.toObject(json,treeList.getClass());Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("查询redis缓存的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");}else{//redis中没有数据.应该查询数据库.treeList = findItemCatList(parentId);//需要把数据,转化为JSONString json = ObjectMapperUtil.toJSON(treeList);jedis.set(key, json);Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("查询数据库的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");}return treeList;}}
5. AOP实现Redis缓存
5.1 现有代码存在的问题
1.如果直接将缓存业务,写到业务层中,如果将来的缓存代码发生变化,则代码耦合高,必然重写编辑代码.
2.如果其他的业务也需要缓存,则代码的重复率高,开发效率低.
解决方案: 采用AOP方式实现缓存.
5.2 AOP
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
5.3 AOP实现步骤
公式: AOP(切面) = 通知方法(5种) + 切入点表达式(4种)
5.3.1 通知复习
1.before通知 在执行目标方法之前执行
2.afterReturning通知 在目标方法执行之后执行
3.afterThrowing通知 在目标方法执行之后报错时执行
4.after通知 无论什么时候程序执行完成都要执行的通知
上述的4大通知类型,不能控制目标方法是否执行.一般用来记录程序的执行的状态.
一般应用与监控的操作.
5.around通知(功能最为强大的) 在目标方法执行前后执行.
因为环绕通知可以控制目标方法是否执行.控制程序的执行的轨迹.
5.3.2 切入点表达式
1.bean(“bean的ID”) 粒度: 粗粒度 按bean匹配 当前bean中的方法都会执行通知.
2.within(“包名.类名”) 粒度: 粗粒度 可以匹配多个类
3.execution(“返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表)”) 粒度: 细粒度 方法参数级别
4.@annotation(“包名.类名”) 粒度:细粒度 按照注解匹配
5.3.3 AOP入门案例
package com.jt.aop;import lombok.extern.apachecommons.CommonsLog;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.Arrays;@Aspect //标识我是一个切面@Component //交给Spring容器管理public class CacheAOP {//切面 = 切入点表达式 + 通知方法//@Pointcut("bean(itemCatServiceImpl)")//@Pointcut("within(com.jt.service.ItemCatServiceImpl)")//@Pointcut("within(com.jt.service.*)") // .* 一级包路径 ..* 所有子孙后代包//@Pointcut("execution(返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表))")@Pointcut("execution(* com.jt.service..*.*(..))")//注释: 返回值类型任意类型 在com.jt.service下的所有子孙类 以add开头的方法,任意参数类型public void pointCut(){}/*** 需求:* 1.获取目标方法的路径* 2.获取目标方法的参数.* 3.获取目标方法的名称*/@Before("pointCut()")public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){String classNamePath = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName();String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("方法路径:"+classNamePath);System.out.println("方法参数:"+ Arrays.toString(args));System.out.println("方法名称:"+methodName);}@Around("pointCut()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){try {System.out.println("环绕通知开始");Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();//如果有下一个通知,就执行下一个通知,如果没有就执行目标方法(业务方法)System.out.println("环绕通知结束");return null;} catch (Throwable throwable) {throwable.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException(throwable);}}}
5.4 AOP实现Redis缓存
5.4.1 业务实现策略
1).需要自定义注解CacheFind
2).设定注解的参数 key的前缀,数据的超时时间.
3).在方法中标识注解.
4).利用AOP 拦截指定的注解.
5).应该使用Around通知实现缓存业务.
5.4.2 编辑自定义注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //注解对方法有效@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //运行期有效public @interface CacheFind {public String preKey(); //定义key的前缀public int seconds() default 0; //定义数据的超时时间.}
5.4.3 方法中标识注解
5.4.4 编辑CacheAOP
package com.jt.aop;import com.jt.anno.CacheFind;import com.jt.util.ObjectMapperUtil;import lombok.extern.apachecommons.CommonsLog;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.util.Arrays;@Aspect //标识我是一个切面@Component //交给Spring容器管理public class CacheAOP {@Autowiredprivate Jedis jedis;/*** 注意事项: 当有多个参数时,joinPoint必须位于第一位.* 需求:* 1.准备key= 注解的前缀 + 用户的参数* 2.从redis中获取数据* 有: 从缓存中获取数据之后,直接返回值* 没有: 查询数据库之后再次保存到缓存中即可.** 方法:* 动态获取注解的类型,看上去是注解的名称,但是实质是注解的类型. 只要切入点表达式满足条件* 则会传递注解对象类型.* @param joinPoint* @return* @throws Throwable*/@Around("@annotation(cacheFind)")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,CacheFind cacheFind) throws Throwable {Object result = null; //定义返回值对象String preKey = cacheFind.preKey();String key = preKey + "::" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());//1.校验redis中是否有数据if(jedis.exists(key)){//如果数据存在,需要从redis中获取json数据,之后直接返回String json = jedis.get(key);//1.获取方法对象, 2.获取方法的返回值类型MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();//2.获取返回值类型Class returnType = methodSignature.getReturnType();result = ObjectMapperUtil.toObject(json,returnType);System.out.println("AOP查询redis缓存!!!");}else{//代表没有数据,需要查询数据库result = joinPoint.proceed();//将数据转化为JSONString json = ObjectMapperUtil.toJSON(result);if(cacheFind.seconds() > 0){jedis.setex(key, cacheFind.seconds(), json);}else{jedis.set(key,json);}System.out.println("AOP查询数据库!!!");}return result;}/* @Around("@annotation(com.jt.anno.CacheFind)")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {//1.获取目标对象的Class类型Class targetClass = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass();//2.获取目标方法名称String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();//3.获取参数类型Object[] argsObj = joinPoint.getArgs();Class[] argsClass = null;//4.对象转化为class类型if(argsObj.length>0){argsClass = new Class[argsObj.length];for(int i=0;i<argsObj.length;i++){argsClass[i] = argsObj[i].getClass();}}//3.获取方法对象Method targetMethod = targetClass.getMethod(methodName,argsClass);//4.获取方法上的注解if(targetMethod.isAnnotationPresent(CacheFind.class)){CacheFind cacheFind = targetMethod.getAnnotation(CacheFind.class);String key = cacheFind.preKey() + "::"+Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());System.out.println(key);}Object object = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("环绕开始后");return object;}*//* //切面 = 切入点表达式 + 通知方法//@Pointcut("bean(itemCatServiceImpl)")//@Pointcut("within(com.jt.service.ItemCatServiceImpl)")//@Pointcut("within(com.jt.service.*)") // .* 一级包路径 ..* 所有子孙后代包//@Pointcut("execution(返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表))")@Pointcut("execution(* com.jt.service..*.*(..))")//注释: 返回值类型任意类型 在com.jt.service下的所有子孙类 以add开头的方法,任意参数类型public void pointCut(){}*//*** 需求:* 1.获取目标方法的路径* 2.获取目标方法的参数.* 3.获取目标方法的名称*//* @Before("pointCut()")public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){String classNamePath = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName();String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("方法路径:"+classNamePath);System.out.println("方法参数:"+ Arrays.toString(args));System.out.println("方法名称:"+methodName);}@Around("pointCut()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){try {System.out.println("环绕通知开始");Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();//如果有下一个通知,就执行下一个通知,如果没有就执行目标方法(业务方法)System.out.println("环绕通知结束");return null;} catch (Throwable throwable) {throwable.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException(throwable);}}*/}
6.总结
本节主要是进一步了解Redis的使用,对象和Json之间相互转换的过程,以及后续AOP实现redis缓存的基本流程步骤。


