1.类加载器
1.1 类加载器【理解】
- 作用
负责将.class文件(存储的物理文件)加载在到内存中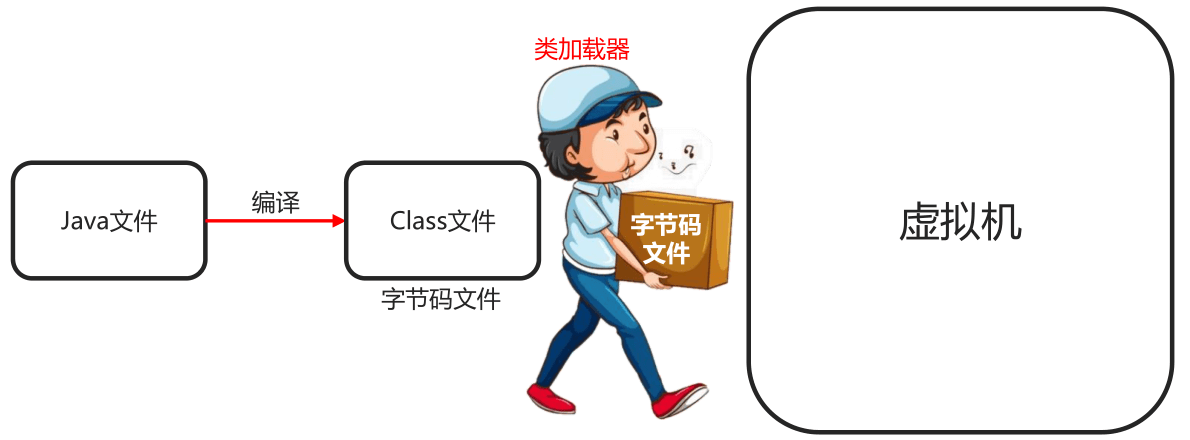
- 类加载器和VM
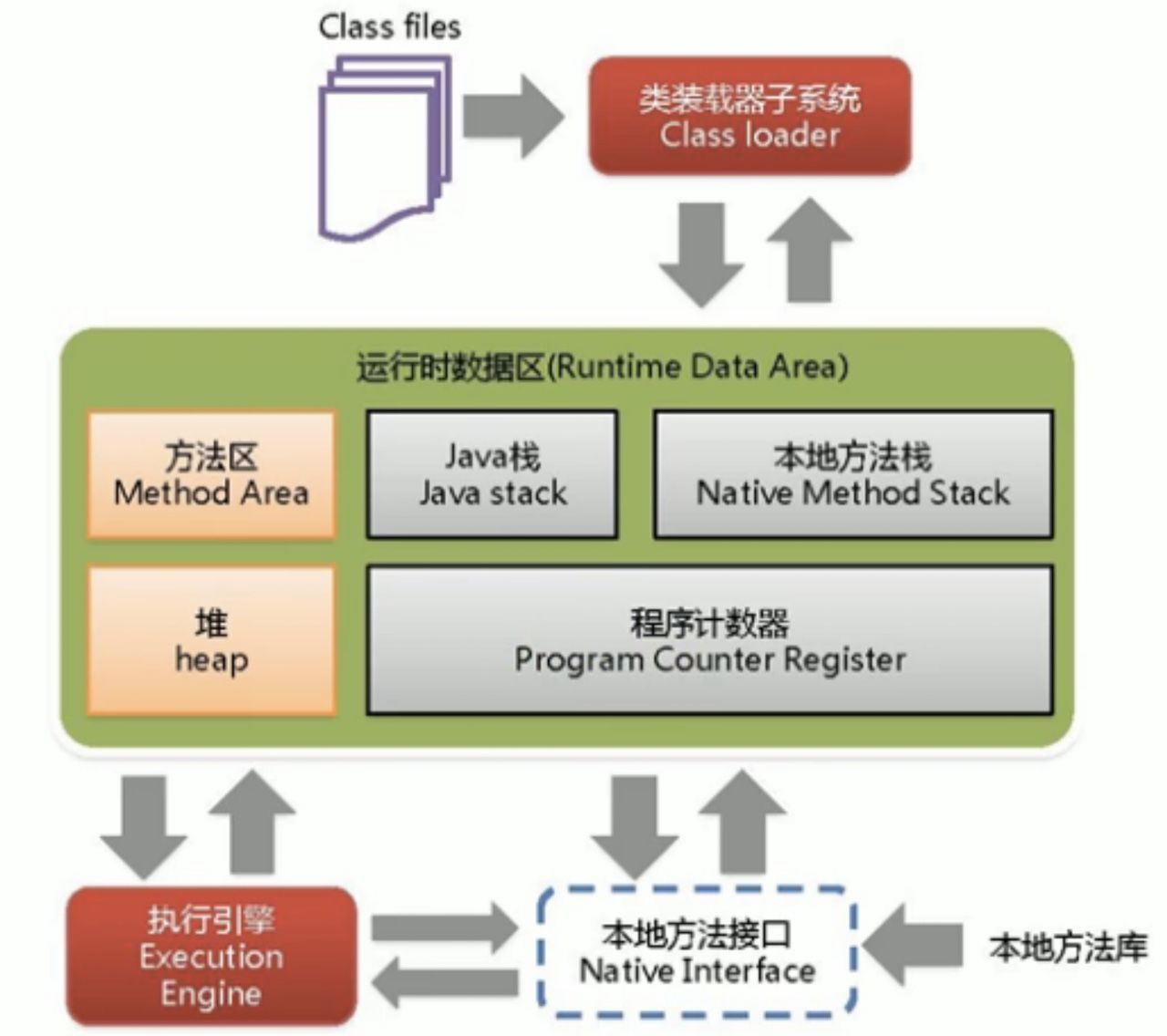
1.2 加载的时机【理解】
- 类加载时机
- 创建类的实例(对象)
- 调用类的类方法
- 访问类或者接口的类变量,或者为该类变量赋值
- 使用反射方式来强制创建某个类或接口对应的java.lang.Class对象
- 初始化某个类的子类
- 直接使用java.exe命令来运行某个主类
- 类加载时机总结:
- 用到就加载
1.3 类加载过程
- 加载
- 通过包名 + 类名,获取这个类,准备用流进行传输
- 在这个类加载到内存中
- 加载完毕创建一个Class对象
- 在内存中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区这个类的各种数据的访问入口
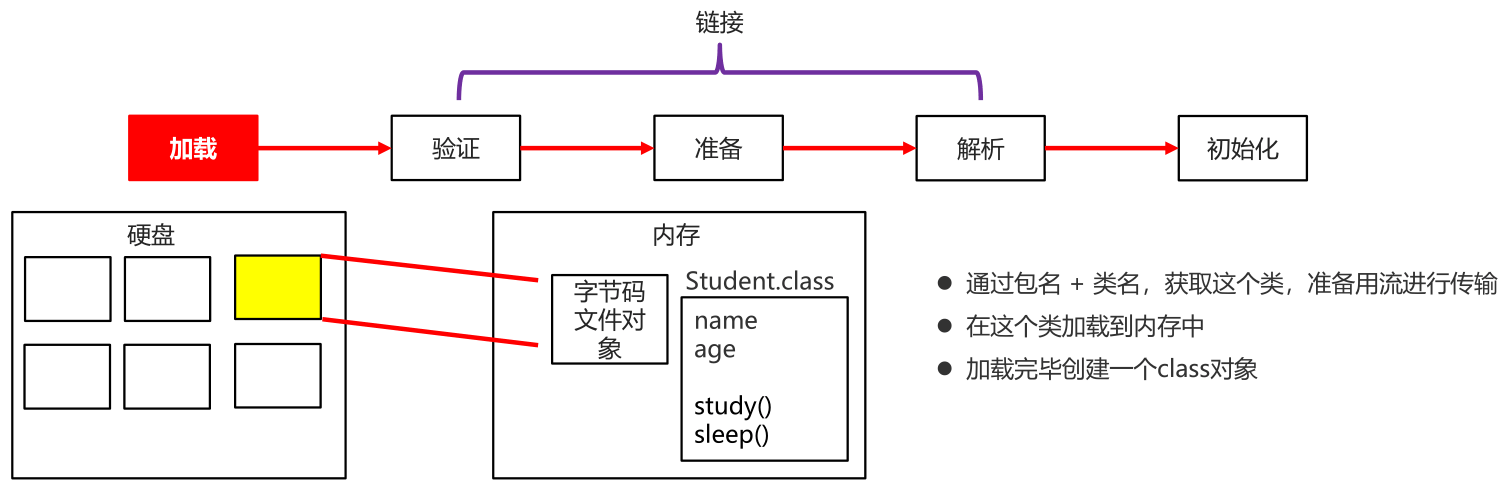
- 链接
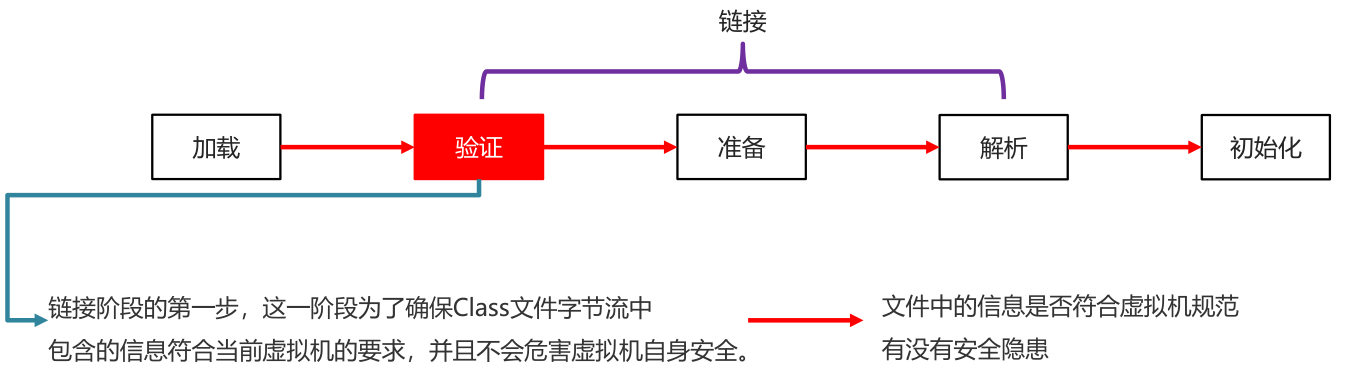
- 验证
确保Class文件字节流中包含的信息符合当前虚拟机的要求,并且不会危害虚拟机自身安全
(文件中的信息是否符合虚拟机规范有没有安全隐患)
- 验证
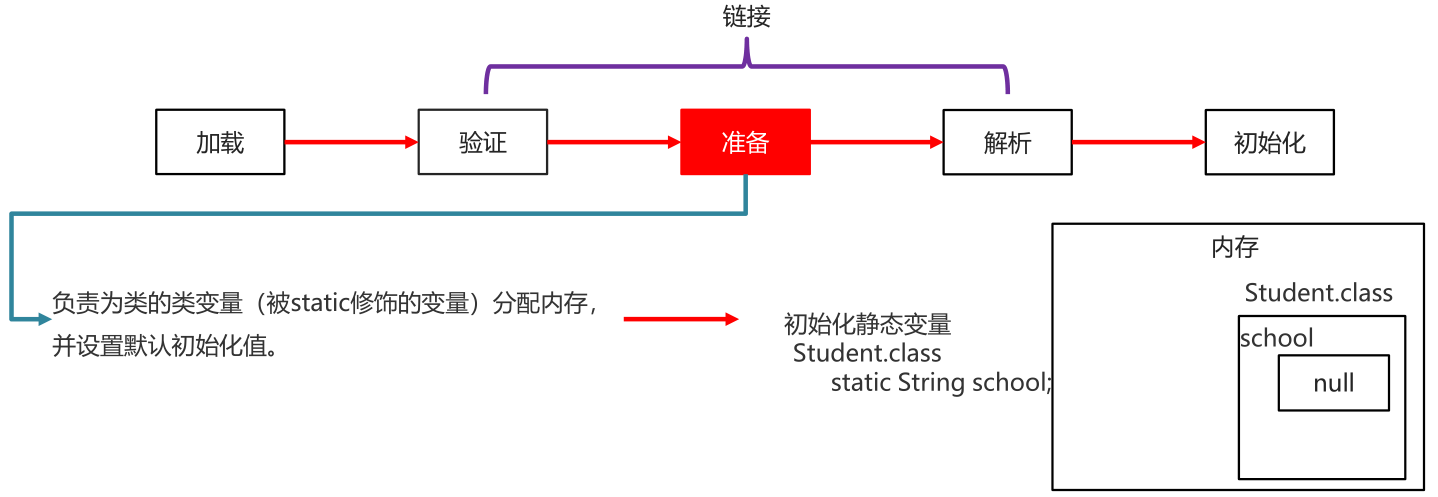
准备
负责为类的类变量(被static修饰的变量)分配内存,并设置默认初始化值。public class Test01 {public static int nn = 200; //准备阶段 nn=0 初始化阶段nn=20public final int NUM = 200;public int age = 200;public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(nn);}}
扩展内容
这里不包含final修饰的static,因为final在编译的时候就会分配了,准备阶段会显示初始化
这里不会为实例变量分配初始化,类变量会分配在方法区中,而实例变量是会随着对象一起分配到Java堆中。
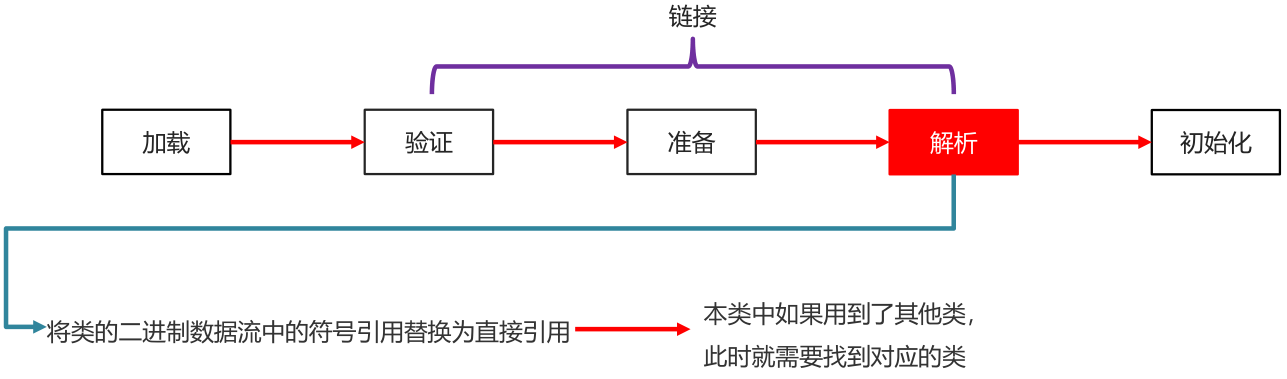
- 解析
将类的二进制数据流中的符号引用替换为直接引用
(本类中如果用到了其他类,此时就需要找到对应的类)
- 初始化
根据程序员通过程序制定的主观计划去初始化类变量和其他资源
(静态变量赋值以及初始化其他资源)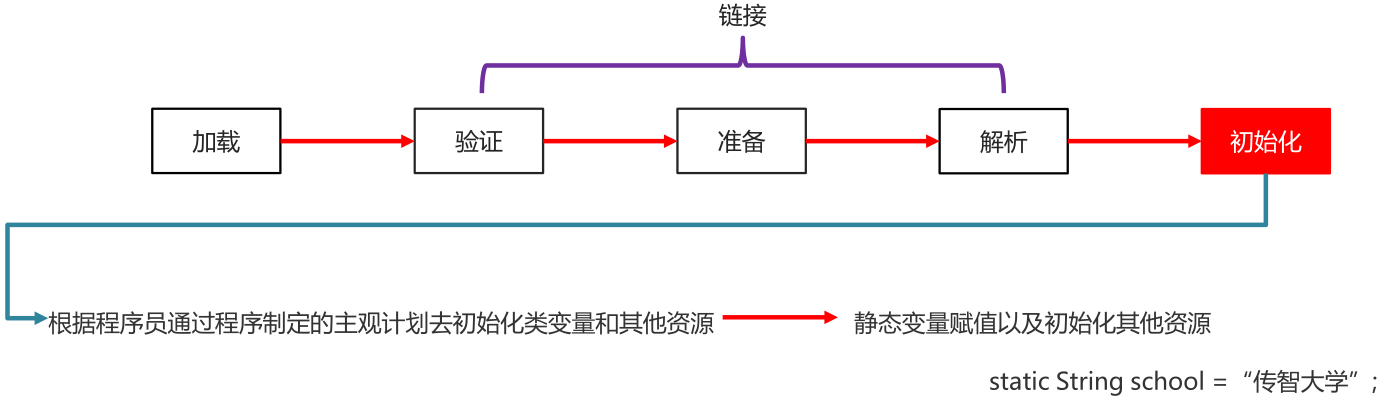
public class Test01 {public static int nn = 200; //准备阶段 nn=0 初始化阶段nn=20public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(nn);}}
- 小结
- 当一个类被使用的时候,才会加载到内存
- 类加载的过程:
- 加载、验证、准备、解析、初始化
1.4 类加载的分类【理解】
- 分类
- Bootstrap class loader:虚拟机的内置类加载器,通常表示为null ,因为用C语言实现的,并且没有父
- Platform class loader:平台类加载器,负责加载JDK中一些特殊的模块
- System class loader:系统类加载器,负责加载用户类路径上所指定的类库
- 作用
- 启动类加载器 bootstrap class loader :
- 用来加载JAVA的核心库
- 出于安全考虑,只加载包名为java、javax、sun等开头的类
- 平台类加载器 platform class loader :加载jre/lib/ext/*.jar
- 如果用户创建的JAR放在此目录,也会自动使用扩展类加载器加载
- 系统类加载器 system class loader:加载classpath上指定的类库
- 启动类加载器 bootstrap class loader :
- 类加载器的继承关系
- System的父加载器为Platform
- Platform的父加载器为Bootstrap
代码演示
public class ClassLoaderDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//获取系统类加载器ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();//获取系统类加载器的父加载器 --- 平台类加载器ClassLoader classLoader1 = systemClassLoader.getParent();//获取平台类加载器的父加载器 --- 启动类加载器ClassLoader classLoader2 = classLoader1.getParent();System.out.println("系统类加载器" + systemClassLoader);System.out.println("平台类加载器" + classLoader1);System.out.println("启动类加载器" + classLoader2);}}
1.5 双亲委派模型【理解】
- 介绍
- 如果一个类加载器收到了类加载请求,它并不会自己先去加载,而是把这个请求委托给父类的加载器去执行。
- 如果父类加载器还存在其父类加载器,则进一步向上委托,依次递归,请求最终将到达顶层的启动类加载器。
- 如果父类加载器可以完成类加载任务,就成功返回,倘若父类加载器无法完成此加载任务,子加载器才会尝试自己去加载,这就是双亲委派模式。
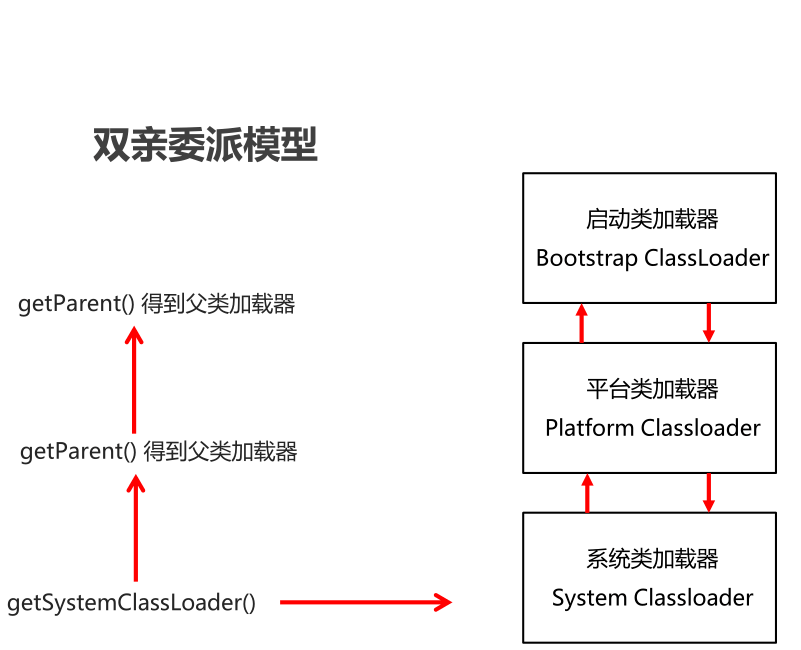
- 当Application ClassLoader 收到一个类加载请求时,他首先不会自己去尝试加载这个类,而是将这个请求委派给父类加载器Extension ClassLoader去完成。
- 当Extension ClassLoader收到一个类加载请求时,他首先也不会自己去尝试加载这个类,而是将请求委派给父类加载器Bootstrap ClassLoader去完成。
- 如果Bootstrap ClassLoader加载失败(在
\lib中未找到所需类),就会让Extension ClassLoader尝试加载。 - 如果Extension ClassLoader也加载失败,就会使用Application ClassLoader加载。
- 如果Application ClassLoader也加载失败,就会使用自定义加载器去尝试加载。
- 如果均加载失败,就会抛出ClassNotFoundException异常。
例子:
当一个Hello.class这样的文件要被加载时。不考虑我们自定义类加载器,首先会在AppClassLoader中检查是否加载过,如果有那就无需再加载了。如果没有,那么会拿到父加载器,然后调用父加载器的loadClass方法。父类中同理会先检查自己是否已经加载过,如果没有再往上。注意这个过程,直到到达Bootstrap classLoader之前,都是没有哪个加载器自己选择加载的。如果父加载器无法加载,会下沉到子加载器去加载,一直到最底层,如果没有任何加载器能加载,就会抛出ClassNotFoundException
1.6 ClassLoader 中的两个方法【应用】
方法介绍 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader() | 获取系统类加载器 | | public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) | 加载某一个资源文件 |
示例代码
public class ClassLoaderDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader() 获取系统类加载器//InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) 加载某一个资源文件//获取系统类加载器ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();//利用加载器去加载一个指定的文件//参数:文件的路径(放在src的根目录下,默认去那里加载)//返回值:字节流。InputStream is = systemClassLoader.getResourceAsStream("prop.properties");Properties prop = new Properties();prop.load(is);System.out.println(prop);is.close();}}
2.反射
2.1 反射的概述【理解】
- 反射机制
是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;
对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意属性和方法;
这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为Java语言的反射机制。 - 理解
- 利用反射可以无视修饰符获取类里面所有的属性和方法。
- 先获取配置文件中的信息,动态获取信息并创建对象和调用方法。
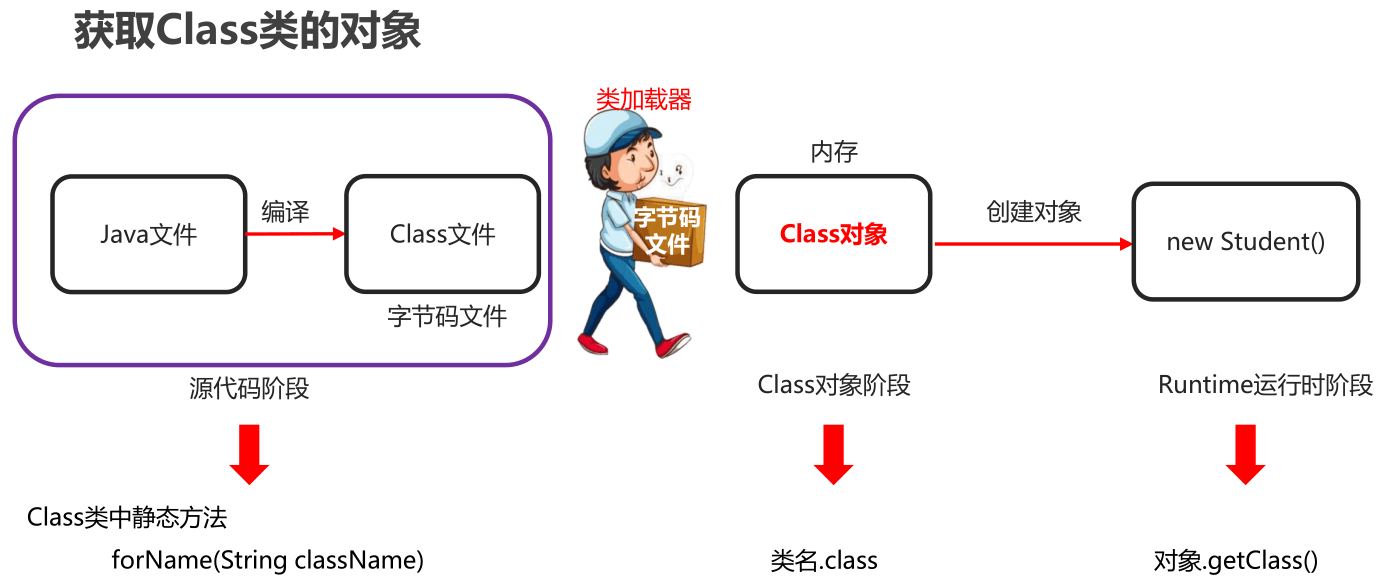
2.2 获取Class类对象的三种方式【应用】
- 三种方式分类
- 类名.class属性
- 对象名.getClass()方法
- Class.forName(全类名)方法
示例代码 ```java public class Student { private String name; private int age;
public Student() { }
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("学生在学习");
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';
} }
public class ReflectDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { //1.Class类中的静态方法forName(“全类名”) //全类名:包名 + 类名 Class clazz = Class.forName(“com.itheima.myreflect2.Student”); System.out.println(clazz);
//2.通过class属性来获取Class clazz2 = Student.class;System.out.println(clazz2);//3.利用对象的getClass方法来获取class对象//getClass方法是定义在Object类中.Student s = new Student();Class clazz3 = s.getClass();System.out.println(clazz3);System.out.println(clazz == clazz2);System.out.println(clazz2 == clazz3);}
}
<a name="21d6441b"></a>### 2.3 反射获取构造方法并使用【应用】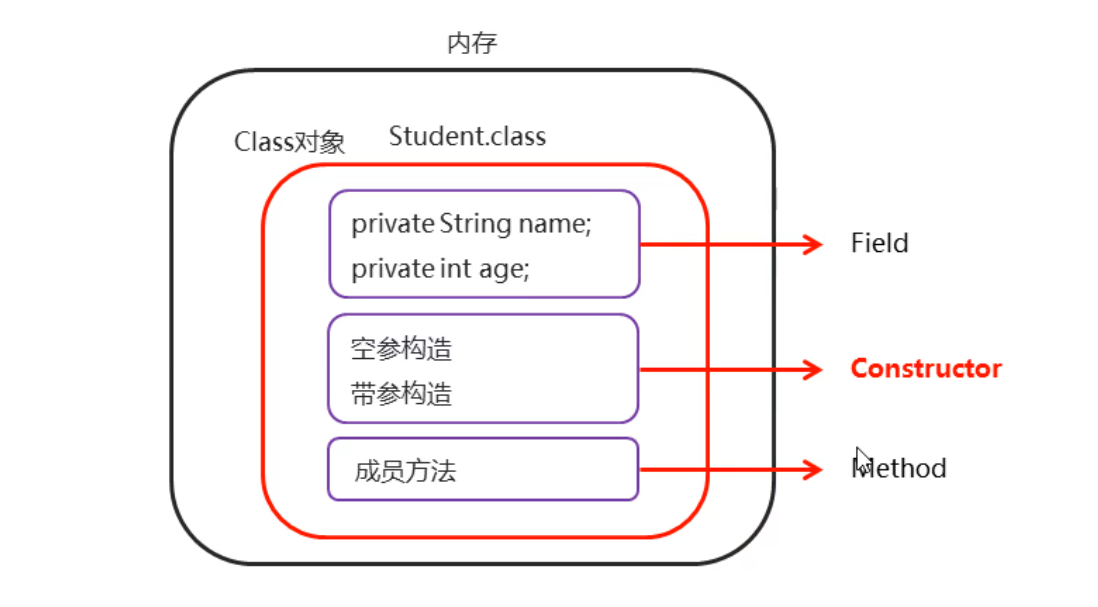<a name="d9ab33f3"></a>#### 2.3.1 Class类获取构造方法对象的方法- 方法介绍| 方法名 | 说明 || --- | --- || Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() | 返回所有公共构造方法对象的数组 || Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() | 返回所有构造方法对象的数组 || Constructor getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) | 返回单个公共构造方法对象 || Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) | 返回单个构造方法对象 |- 示例代码```javapublic class Student {private String name;private int age;//私有的有参构造方法private Student(String name) {System.out.println("name的值为:" + name);System.out.println("private...Student...有参构造方法");}//公共的无参构造方法public Student() {System.out.println("public...Student...无参构造方法");}//公共的有参构造方法public Student(String name, int age) {System.out.println("name的值为:" + name + "age的值为:" + age);System.out.println("public...Student...有参构造方法");}}public class ReflectDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {//method1();//method2();//method3();//method4();}private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {// Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes):// 返回单个构造方法对象//1.获取Class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);System.out.println(constructor);}private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {// Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes):// 返回单个公共构造方法对象//1.获取Class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");//小括号中,一定要跟构造方法的形参保持一致.Constructor constructor1 = clazz.getConstructor();System.out.println(constructor1);Constructor constructor2 = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);System.out.println(constructor2);//因为Student类中,没有只有一个int的构造,所以这里会报错.Constructor constructor3 = clazz.getConstructor(int.class);System.out.println(constructor3);}private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {// Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors():// 返回所有构造方法对象的数组//1.获取Class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {System.out.println(constructor);}}private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {// Constructor<?>[] getConstructors():// 返回所有公共构造方法对象的数组//1.获取Class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {System.out.println(constructor);}}}
2.3.2 Constructor类用于创建对象的方法
方法介绍 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | T newInstance(Object…initargs) | 根据指定的构造方法创建对象 | | setAccessible(boolean flag) | 设置为true,表示取消访问检查 |
示例代码
// Student类同上一个示例,这里就不在重复提供了public class ReflectDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {//T newInstance(Object... initargs):根据指定的构造方法创建对象//method1();//method2();//method3();//method4();}private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {//获取一个私有的构造方法并创建对象//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");//2.获取一个私有化的构造方法.Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);//被private修饰的成员,不能直接使用的//如果用反射强行获取并使用,需要临时取消访问检查constructor.setAccessible(true);//3.直接创建对象Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance("zhangsan");System.out.println(student);}private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {//简写格式//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");//2.在Class类中,有一个newInstance方法,可以利用空参直接创建一个对象Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();//这个方法现在已经过时了,了解一下System.out.println(student);}private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");//2.获取构造方法对象Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();//3.利用空参来创建Student的对象Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance();System.out.println(student);}private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect3.Student");//2.获取构造方法对象Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);//3.利用newInstance创建Student的对象Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance("zhangsan", 23);System.out.println(student);}}
2.3.3 小结
- 获取class对象
三种方式:
Class.forName(“全类名”),
类名.class,
对象名.getClass() - 获取里面的构造方法对象
getConstructor (Class<?>… parameterTypes)
getDeclaredConstructor (Class<?>… parameterTypes) - 如果是public的,直接创建对象
newInstance(Object… initargs) - 如果是非public的,需要临时取消检查,然后再创建对象
setAccessible(boolean) 暴力反射
2.4 反射获取成员变量并使用【应用】
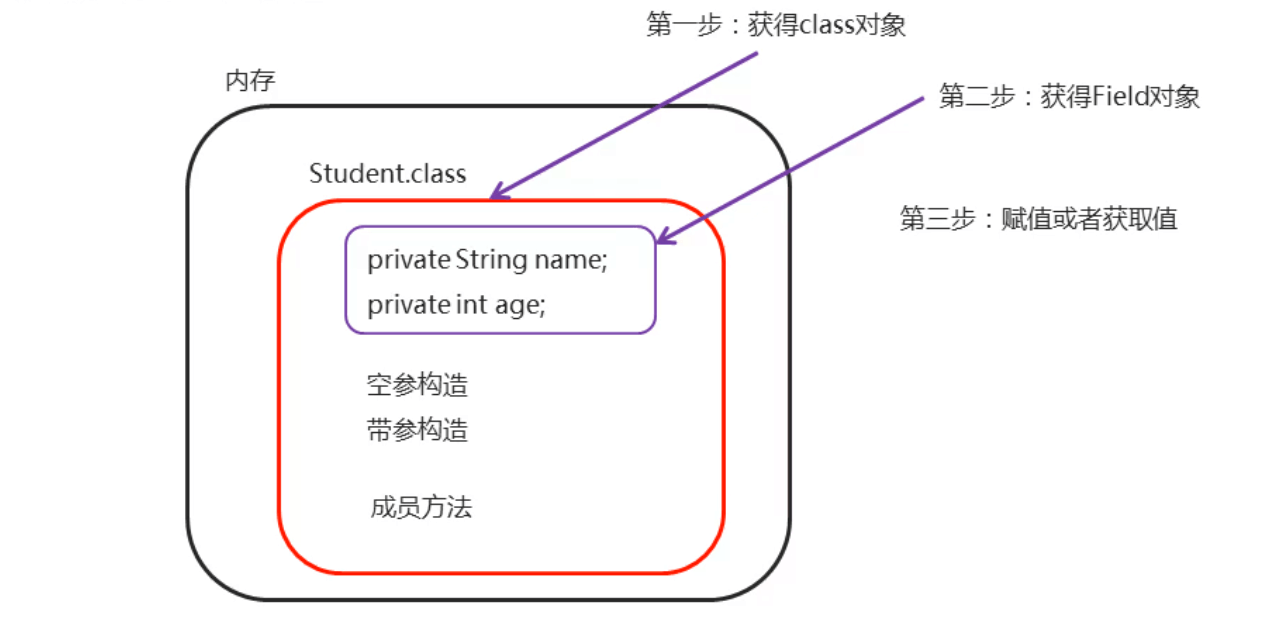
2.4.1 Class类获取成员变量对象的方法
方法分类 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | Field[] getFields() | 返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组 | | Field[] getDeclaredFields() | 返回所有成员变量对象的数组 | | Field getField(String name) | 返回单个公共成员变量对象 | | Field getDeclaredField(String name) | 返回单个成员变量对象 |
示例代码
public class Student {public String name;public int age;public String gender;private int money = 300;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", gender='" + gender + '\'' +", money=" + money +'}';}}public class ReflectDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {//method1();//method2();//method3();//method4();}private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {// Field getDeclaredField(String name):返回单个成员变量对象//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");//2.获取money成员变量Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("money");//3.打印一下System.out.println(field);}private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {// Field getField(String name):返回单个公共成员变量对象//想要获取的成员变量必须是真实存在的//且必须是public修饰的.//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");//2.获取name这个成员变量//Field field = clazz.getField("name");//Field field = clazz.getField("name1");Field field = clazz.getField("money");//3.打印一下System.out.println(field);}private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {// Field[] getDeclaredFields():返回所有成员变量对象的数组//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");//2.获取所有的Field对象Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();//3.遍历for (Field field : fields) {System.out.println(field);}}private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {// Field[] getFields():返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");//2.获取Field对象.Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();//3.遍历for (Field field : fields) {System.out.println(field);}}}
2.4.2 Field类用于给成员变量赋值的方法
方法介绍 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | void set(Object obj, Object value) | 赋值 | | Object get(Object obj) | 获取值 |
示例代码
public class ReflectDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {//method1();//method2();}private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");//2.获取成员变量Field的对象Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("money");//3.取消一下访问检查field.setAccessible(true);//4.调用get方法来获取值//4.1创建一个对象Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();//4.2获取指定对象的money的值Object o = field.get(student);//5.打印一下System.out.println(o);}private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect4.Student");//2.获取name这个Field对象Field field = clazz.getField("name");//3.利用set方法进行赋值.//3.1先创建一个Student对象Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();//3.2有了对象才可以给指定对象进行赋值field.set(student,"zhangsan");System.out.println(student);}}
2.5 反射获取成员方法并使用【应用】
2.5.1 Class类获取成员方法对象的方法
方法分类 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | Method[] getMethods() | 返回所有公共成员方法对象的数组,包括继承的 | | Method[] getDeclaredMethods() | 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,不包括继承的 | | Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>… parameterTypes) | 返回单个公共成员方法对象 | | Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>… parameterTypes) | 返回单个成员方法对象 |
示例代码
public class Student {//私有的,无参无返回值private void show() {System.out.println("私有的show方法,无参无返回值");}//公共的,无参无返回值public void function1() {System.out.println("function1方法,无参无返回值");}//公共的,有参无返回值public void function2(String name) {System.out.println("function2方法,有参无返回值,参数为" + name);}//公共的,无参有返回值public String function3() {System.out.println("function3方法,无参有返回值");return "aaa";}//公共的,有参有返回值public String function4(String name) {System.out.println("function4方法,有参有返回值,参数为" + name);return "aaa";}}public class ReflectDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {//method1();//method2();//method3();//method4();//method5();}private static void method5() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {// Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes):// 返回单个成员方法对象//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");//2.获取一个成员方法showMethod method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");//3.打印一下System.out.println(method);}private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");//2.获取一个有形参的方法function2Method method = clazz.getMethod("function2", String.class);//3.打印一下System.out.println(method);}private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {// Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) :// 返回单个公共成员方法对象//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");//2.获取成员方法function1Method method1 = clazz.getMethod("function1");//3.打印一下System.out.println(method1);}private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {// Method[] getDeclaredMethods():// 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,不包括继承的//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");//2.获取Method对象Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();//3.遍历一下数组for (Method method : methods) {System.out.println(method);}}private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {// Method[] getMethods():返回所有公共成员方法对象的数组,包括继承的//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");//2.获取成员方法对象Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();//3.遍历for (Method method : methods) {System.out.println(method);}}}
2.5.2 Method类用于执行方法的方法
方法介绍 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | Object invoke(Object obj, Object… args) | 运行方法 |
参数一: 用obj对象调用该方法
参数二: 调用方法的传递的参数(如果没有就不写)
返回值: 方法的返回值(如果没有就不写)示例代码
public class ReflectDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {// Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args):运行方法// 参数一:用obj对象调用该方法// 参数二:调用方法的传递的参数(如果没有就不写)// 返回值:方法的返回值(如果没有就不写)//1.获取class对象Class clazz = Class.forName("com.itheima.myreflect5.Student");//2.获取里面的Method对象 function4Method method = clazz.getMethod("function4", String.class);//3.运行function4方法就可以了//3.1创建一个Student对象,当做方法的调用者Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();//3.2运行方法Object result = method.invoke(student, "zhangsan");//4.打印一下返回值System.out.println(result);}}

